DDT full Form || What was DDT used for? || Is DDT harmful to humans?
Dichloro diphenyl trichloro ethane (DDT) :-
DDT is a synthetic insecticide that was widely used in the mid-20th century to control insect-borne diseases such as malaria, yellow fever and typhus. However, it was discovered to be persistent in the environment and toxic to wildlife leading to its ban in many countries, including the U.S. in 1972. Despite this DDT is still used in some countries for disease control due to limited alternatives.

What is ddt ? :-
DDT (Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) is a synthetic insecticide that was widely used in the mid-20th century to control insect-borne diseases. However, it was discovered to have toxic effects on the environment and wildlife, leading to its ban in many countries.
How is DDT prepared ?
DDT is synthesized through a reaction between chloral and chlorobenzene in the presence of an alkaline catalyst. The reaction produces a mixture of DDT and several other chlorinated compounds, which are then separated and purified to obtain pure DDT. The specific method used can vary, but the general principles are the same.
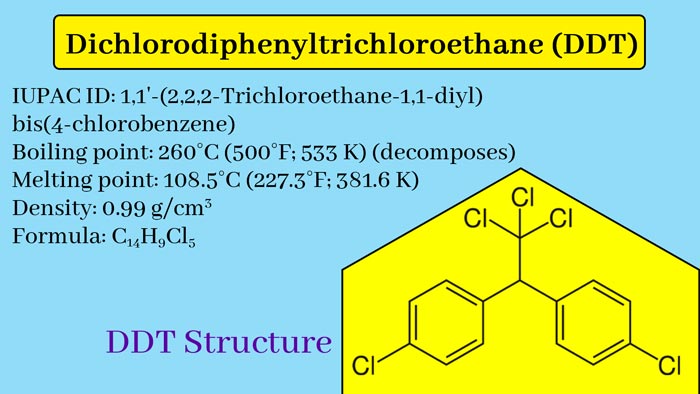
Properties of DDT
· DDT is a chlorinated hydrocarbon insecticide with the following properties:
· Chemical formula: C14H9Cl5
· Colorless crystalline solid, with a characteristic odor
· Low solubility in water, but soluble in most organic solvents
· Stable and persistent in the environment, with a half-life of several years
· Highly toxic to insects and other arthropods, with a low toxicity to mammals
· Persistent in the environment, bioaccumulating in the food chain and causing harm to wildlife
· Banned or restricted in many countries due to its negative impact on the environment and wildlife.
DDT is also called DDT223, and its chemical name is Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT full Form dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane), with the chemical formula (ClC₆H₄)₂CH(CCl₃).
It is a white crystal, insoluble in water, soluble in kerosene, and can be made into an emulsion. It is an effective pesticide. In the first half of the 20th century, it played a significant role in preventing agricultural diseases and insect pests and reducing the hazards of mosquito and fly-borne diseases such as malaria typhoid.
Read more Topics:
- Ammonia Formula || why ammonia is toxic || Ammonia Poisoning
- Why Ozone Layer is Important || Ozone Layer Depletion
- What is the Concentration of solution || How Concentration Affects Reaction
- Why Carbon Cycle is Important || How it Works
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes NCERT Solutions || Haloalkane Structure
- Carbon Dioxide Cycle and Formula || How Carbon Dioxide is Produced
However, due to its serious environmental pollution, many countries and regions have banned its use. The World Health Organization announced in 2002 that DDT was re-enabled for controlling mosquito breeding and preventing malaria, dengue fever, yellow fever, and other worldwide resurgences.
Physical and chemical constants
- English name: 2,2-bis (4-Chlorophenyl) -1,1,1-trichloroethane
- Major isomers and homologs: o, p’-DDT; p, p’-DDE; p, p’-DDD
- Molecular formula: C 1₄H₉Cl₅
- Appearance and properties: All isomers of DDT compounds are white crystalline solid or light yellow powder, odorless and almost odorless
- Molecular weight: 354.5
- Vapor pressure: 2.53 × 10-8 kPa / 20℃
- Flashpoint: 72 ~ 77 ℃
- Melting point: 108 ~ 109 ℃
- Boiling point: 260 °C
- Solubility: DDT is extremely difficult to dissolve in water. The solubility in organic solvents is as follows (g / 100mL): benzene is 106, Cyclohexanone is 100, chloroform is 96, petroleum solvents are 4-10, and ethanol is 1.5
- Density: 1.55 (25 ℃)
- Stability: DDT is chemically stable and does not decompose at room temperature. It is stable to acid, strong alkali and iron-containing solutions are easy to promote its decomposition. When the temperature is higher than the melting point, especially in the presence of catalyst or light, p, p’-DDT can form DDE by dehydrochlorination.
- Danger sign: 14 (with drugs)
- Main use: as an agricultural pesticide
Symptoms of Poisoning
Mild poisoning may cause headaches, dizziness, weakness, sweating, insomnia, nausea, vomiting, and occasionally tremor of hand and finger muscles.
Severe poisoning is often accompanied by high fever, sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, nervous system excitement, tonic convulsions in upper, lower limbs, and facial muscles, and epilepsy-like convulsions, seizures, respiratory problems, dyspnea, cyanosis, and sometimes lungs Edema, even respiratory failure, damage to liver and kidney organs, liver enlargement, liver function changes; oliguria, anuria, protein in the urine, red blood cells, etc. redness, swelling, itching, and itching on skin irritation Dermatitis occurs, and if it splashes into the eye, it can cause temporary blindness.

The general toxicity of DDT is the same as that of 666. It is a nerve and parenchymal organ poison, and it has moderate-level acute toxicity to humans and most other organisms. It can be absorbed through the skin and is a typical representative of contact poisoning. Because it has a certain amount of evaporation even under 12℃ at normal pressure, inhalation of DDT vapor can cause poisoning.
Toxicity
Chronic toxicity
Symptoms of chronic poisoning in the population include loss of appetite, pain in the upper abdomen and right ribs, and headache, dizziness, muscle weakness, fatigue, insomnia, visual and speech impairment, tremor, anemia, and deep extremity deep reflection. There are liver and kidney damage, skin lesions, cardiac arrhythmia, weak heart sounds, sinus bradycardia, bundle branch block, and myocardial damage.
Cause Disease
Carcinogenic
11 ~ 20mg / kg.d, oral
administration of mice, 2 years, liver
tumor risk increased 4.4 times 0.16 ~ 0.31mg / kg.d, oral administration
of mice, 2 passages, male liver tumor
risk increased 2 times, female Unchanged.
Liver tumors were induced in mice (and possibly in rats) using DDT, DDE, and DDD, but there are still different opinions about the significance of these tumors. According to the data, there is no evidence to confirm that DDT is carcinogenic to humans.
Read more Topics:
- Halogenation Reaction|| What is the Mechanism of Halogenation?
- Chemical Properties of Alkanes || What are Examples of Alkanes?
- Atomic Structure Chemistry || How do you find the Atomic Structure?
- Periodic Table Elements|| How many Elements are in the Periodic Table?
- Exciting and Entertaining Chemical Tricks || List of Nobel Prize in Chemistry
- Importance of Biomolecules in Life || What are the 4 main biomolecules?
Laws et al. (1967) investigated a large number of 35 workers exposed to DDT at a DDT production plant and found no cancer or blood disease. In the 19 years since the factory opened, the number of staff has increased from 111 to 135, and no cancer patient has been seen. The United States began to use DDT in large numbers from 1942. According to the results of total mortality of liver and hepatobiliary cancer, there was a significant downward trend, from 8.8 in 1930 to 8.4 in 1944, to 5.6 in 1972 (both according to 100,000) Artificial base count). It shows that there is no evidence that liver cancer has increased in the decades of using DDT.
Teratogenic
In experimental studies of DDT effects, studies in mice, rats and dogs have not shown any teratogenic effects.
Mutagenic
There is sufficient evidence to prove that DDT has no mutagenic effect in bacterial systems with and without metabolic activation, and the evidence obtained from mammalian experimental systems (in vivo and in vitro) has not yet reached a conclusive conclusion. The significance of DDT on human mutagenicity is not clear.