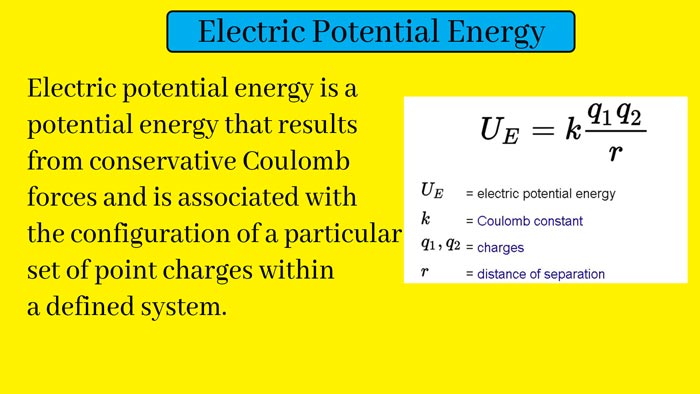
Electric Potential Energy: Definition, Formula and Example | Electrode and Electrode Potential
Electrode Potential : The electric potential of an object is equal to the amount of work that has to be done to bring the unit positive charge from the infinite distance to that object.
Hence the voltage of positively charged objects is positive, the voltage of negatively charged items is negative and the voltage of electric neutral objects is zero.
The current flows from the side of the object with more potential to the object with less potential. The direction of current of the electric is exactly opposite to the direction of flow of the electrons.
Electrode and Electrode Potential
When a metal rod is immersed in a solution of one of its salts, the metal rod is charged with positive or negative charge and the solution has an equal charge of opposite charge.
In that way positive or negative electrical potential is generated on the metal rod and its opposite electric potential is generated on the solution.
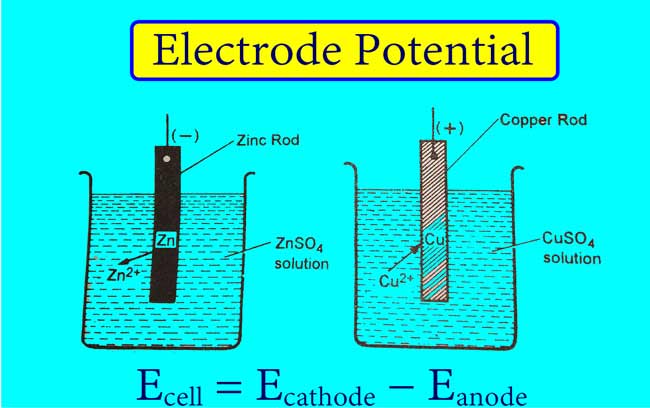
Example 01: The following semi-reaction takes place when the zinc rod is immersed in the zinc ions solution.
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e
Some atoms of Zn present on the zinc rod form Zn2+. Zn2+ moves into the solution and electrons remain on the rod. Hence a negative charge comes on the rod of Zn and a positive charge comes on the solution of Zn2+.
In this way, the negative electrical potential on the rod of Zn and on the solution of Zn2+ the positive electrical potential is generated.
- Fertilizers Chemistry : Types of Fertilizers used in agriculture
- Electric Potential Energy: Definition, Formula and Example | Electrode and Electrode Potential
- Phosphine Gas: Preparation, formula, and Uses
- Nitrous Acid: Preparation, Formula, uses, Solubility | Is nitrous acid dangerous?
- Ammonia Gas: Preparation, Properties, uses
Example 02: The following semi-reaction occurs when the copper rod is immersed in the copper ion solution.
Cu2+ + 2e → Cu
Some Cu2+ solutions in Cu2+ receive electrons from Cu rod to form Cu. Cu atoms accumulate on copper rods. Therefore, there is positive charge on Cu rod and negative charge on Cu2+ solution.
Thus the positive electric potential is generated on the Cu rod and the negative electric potential is generated on the Cu2+ solution.
The rod of that metal immersed in a salt of a metal is called electrode, this device is called half-cell. And the potential generated on a metal rod is called electrode potential of that electrode or semi-reaction occurring on it.
When an element is placed in contact with a solution of one of its ions, and the conductor of an electrical device is in contact with both of them, then this conductor of the power or this device is called this electrode.
1) Hydrogen gas in a hydrogen electrode is in contact with a solution of cation of hydrogen and a foil solution of platinum and is in contact with the gas.
2) The device that is formed when platinum wire or rod is added to the solution of Fe2+ and Fe3+ is called the electrode of this redox system.
Electrode potential Definition
According to Nernst, when a metal rod is immersed in a solution of one of its salts, there are two types of force or pressure acting between the metal rod and the solution.
· Electrolytic solution pressure of the metal
· Osmotic pressure of the solution
Due to the legitimate solution pressure of the metal, metal cations from metal rods tend to move into the solution. If M is the atom of metal and Mn+ is the cation of metal-
M → Mn+ + ne–
Metal atoms make electron cations by giving electrons which run in the solution and electrons remain on the metal rod. In this way, the metal rod has negative charge and negative electric potential and the metal solution has positive charge and positive electric potential.
In the ion electron equation above, M is oxidized to Mn+, that is, in this case the oxidation occurs on the electrode.
Due to the osmotic pressure of the solution, the metal cation tends to accumulate on the metal rod from the solution. If M is the atom of metal and Mn+ is the cation of metal.
- Sodium Chloride Properties || Why Sodium Chloride is Soluble in Water
- Is methane gas harmful to humans?|| Why Methane is a good fuel
- Introduction of Inductive-Effect || How does Inductive Effect Work?
- Glucose Structure: Physical and chemical properties, Glucose Chemical Reaction
- Importance of Biomolecules in Life || What are the 4 main biomolecules?
Mn+ + ne– → M
Metal cations take electrons from metal rods and make metal atoms which are deposited on metal rods. In this way, the metal rod has positive charge and positive electric potential and metal solution brings negative charge and negative electric potential.
In the above ion electron equation, Mn+ is reduced to M, that is, in this case the action of reduction on the electrode.
Both these pressures are employed in each half cell. The half-cell in which the legitimate solution pressure of the metal is greater than the osmolality pressure of the solution has negative charge and negative electric potential at the electrode of the half cell.
In this case, oxidation occurs on the electrode. The half-cell in which the osmolality pressure is greater than the legitimate solution pressure of the metal has positive charge and positive electric potential at the electrode of the half-cell.
In this case, the action of reduction on the electrode occurs.
Cell
A cell is a device that:
Electrical energy is converted into chemical energy.
Eg electrolytic cell
Chemical energy is converted into legislative energy.
The functioning of each cell is based on a redox
reaction. In other words, oxidation of one substance and reduction of another
must occur in every cell.