General Properties of Alkene : Physical and Chemical
Physical Properties
The first three members of this series are ethene, propene and butene gases. After this the members up to C16H32 are liquid and the members higher than this are solid.
They are insoluble in water but soluble in carbonic solvents such as alcohol, benzene and ether.
Their relative density, melting point and boiling point increase with increase in molecular weight.
All alkenes burn with a light-containing flame in air.
Anesthetic properties are found in the lower members of this category.
Chemical Properties
Due to the presence of double bonds, these compounds are highly reactive and often exhibit such reactions in which the pi bond of the double bond is broken. Following are their major chemical reactions –
Addition reactions :- Due to presence of double bond in alkenes, these compounds show addition reactions. In these reactions, the pi bond of the double bond is broken, the reagent splits into two parts, one part of the reagent gets attached to a carbon atom forming the double bond and the other part to another atom.
Following are some important examples of addition reactions of alkenes:

Addition of hydrogen : Alkene combines with hydrogen at 250-300°C temperature to form alkane in the presence of nickel powder.
CH2 = CH2 + H2 → CH3 – CH3
CH3 – CH = CH2 + H2 → CH3 – CH2 – CH3
The addition reaction of alkenes and hydrogen in the presence of nickel is called Sebastian and Senderens Reaction. This reaction takes place at high temperature. In the presence of palladium or paletium catalyst, alkene and hydrogen react at ordinary temperature to form alkene.
Addition of halogens:- Alkene combines with halogens to form dihalogen compound. The order of reactivity of halogens in this reaction is Cl2 > Br2 > I2. This reaction is carried out in a non-polar solvent such as CCl4 and in the presence of sunlight or in a polar solvent such as water.
Example :
CH2 = CH2 + Cl2 → CH2Cl – CH2Cl
CH3 – CH = CH2 + Br2 → CH3 – CHBr – CH2Br
Addition of Hydrogen Halides: One molecule of any alkene combines with one molecule of any hydrogen halide to form an additive compound.
Example :-
CH2 = CH2 + H – Cl → CH3 – CH2 – Cl
The order of reactivity of hydrogen halides in the above reaction is as follows –
H – I > H – Br > H – Cl > H – F
If hydrogen halide combines with an unsymmetrical alkene, then two types of additive products can be formed –
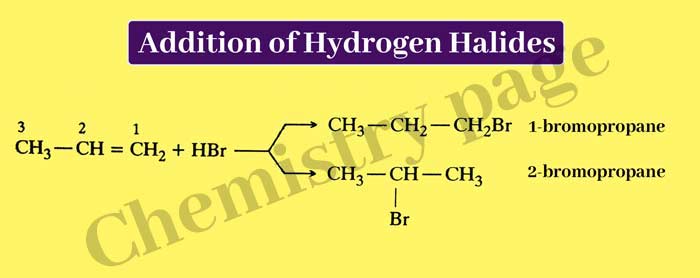
The main product in the above reaction is 2-bromo propane. In this regard, Markownikoff presented the following rule on the basis of many experiments, which is called Markownikoff law. according to this rule-
When an alkene alkene combines with a dissimilar molecule, the positive side of the joining molecule joins the carbon atom forming double bonds, on which more hydrogen atoms are present.
Thus, in the above reaction, the positive part of HBr i.e. H+ is combined with carbon atom No 1 because more hydrogen atom is present on carbon atom No 1 than carbon atom No 2.
Khrash and his colleagues found by experiments in 1933 that the addition of HBr to propene and other dissimilar alkenes in the presence of light (hv) and a peroxide such as benzoyl peroxide is contrary to the Markownikoff law.
Example :-
CH3 – CH = CH2 + HBr → CH3 – CH2 – CH2Br
This abnormal behavior of alkenes in the presence of light and peroxide is called the peroxide effect.
Addition of Hypochlorous acid :- Like hydrogen halides, hypochlorous acid also reacts with alkenes to form compounds.
example :
CH2 = CH2 + HOCl → CH2Cl–CH2OH
In hypochlorous acid (HOCl) there is a partial negative charge on the hydraxyl group and a partial positive charge on the chlorin atom. Hence, the chlorine atom is the positive part of hypochlorous acid.
According to Markownikoff’s law, the hypochlorous acid chlorin atom is double bonded to the carbon atom which has more number of hydrogen atoms.
example :
CH3 – CH = CH2 + HOCl → CH3 – CH(OH) – CH2Cl
Addition of sulfuric acid : Concentrated sulfuric acid absorbs alkenes to form alkyl hydrogen sulfate.
example :
CH2 = CH2 + H2SO4 → CH
CH3 – CH = CH2 + H2SO4 → CH3 – CH(HSO4) – CH3
The addition of sulfuric acid with dissimilar alkenes occurs according to Markonikoff’s law. The positive part of sulfuric acid is H+ and the negative part is HSO4–. Therefore, in propene, the hydrogen atom is attached to the carbon atom no 1 and the hydrogen sulfate group with the carbon atom no 2.
On heating alkyl hydrogen sulfates to 160 – 170°C, they liberate alkenes and on heating with water form alcohol.
example :
C2H5.HSO4 → C2H4 + H2SO4
C2H5.HSO4 + H2O → C2H5OH + H2SO4
These reactions are used to separate alkenes from a gaseous mixture and to form alcohols.
Addition of water or Hydration: Alcohol is obtained as a result of the addition reaction of alkenes and water in the presence of a dilute acid. The addition of water takes place according to Markonikoff’s law and the H + ion of the acid acts as a catalyst.
example :
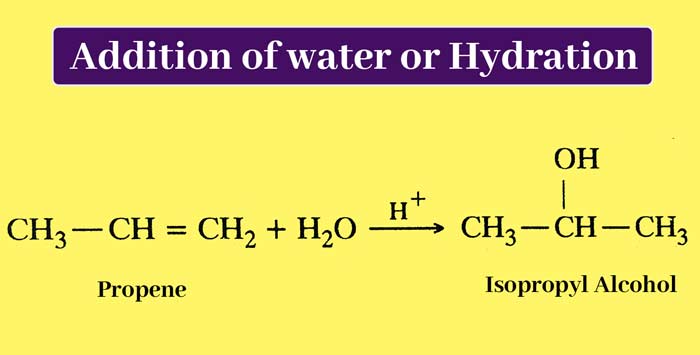
The above reaction is equivalent to the addition of concentrated acids on alkenes and hydrolysis of the product. In both the cases the same product is obtained.
Addition of oxygen: The primary members of alkene series react with oxygen to form additive compounds called epoxides. In this reaction, silver (Ag) is used as a catalyst and the temperature is about 200 – 400°C..
example :
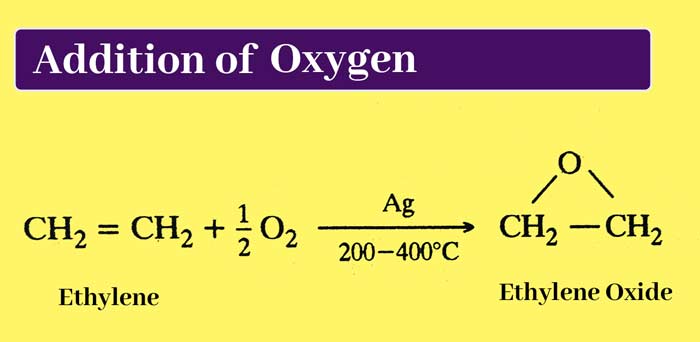
Addition of ozone: On passing ozone through ether solution of alkenes, additive compounds are formed which are called ozonides. When ozonides are boiled with water, they decompose. The process of hydrolysis is done in the presence of Zn powder.
It decomposes hydrogen peroxide obtained by hydrolysis so that it cannot react with other products. Hydrolysis of ozoonide results in the breaking of the chain of carbon atoms from the place where the double bond is present. In this way aldehyde or ketone compounds are obtained.
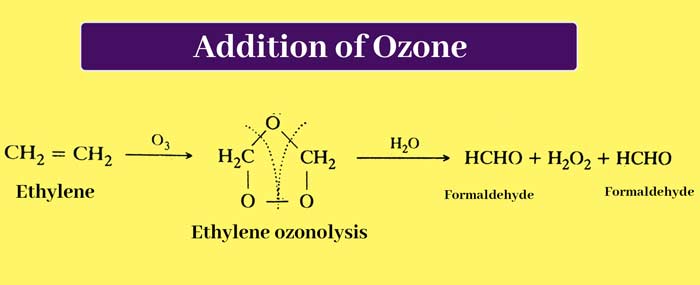
Based on the identification of the product obtained from this reaction, the position of the double bond in the carbon chain and the structure of the alkene used can be determined. The addition reaction of alkenes and ozone and the reaction of hydrolysis of ozonides, this whole process is called ozonolysis.
example:
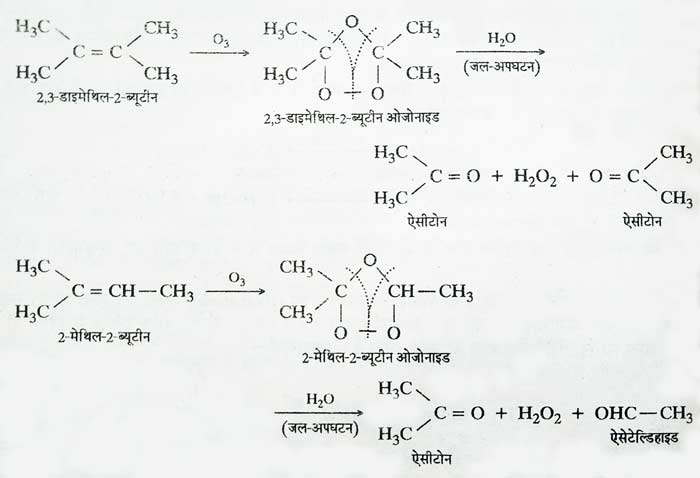
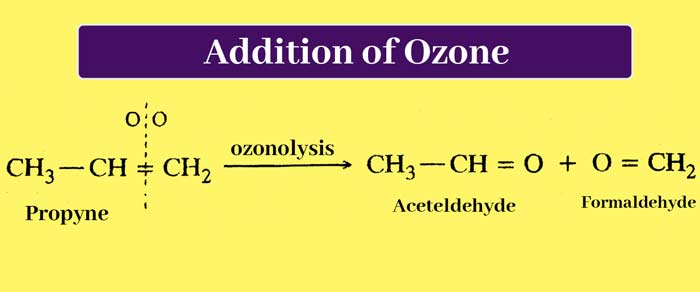
It is clear that in the whole reaction the double bond is broken and the carbon atoms to which the double bond was attached get attached to the oxygen atom. Taking the example of propene ozonisation, the whole reaction can be briefly represented as –
Formation of nitrosyl chloride : alkene combines with nitrosyl chloride to form nitroso chloride
Example:-
CH2 = CH2 + NO+Cl– → CH2Cl – CH2NO (Chloroacetamide)
Addition of acetyl chloride : Alkene combines with acetyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous aluminum chloride to form chloro-ketone.
Example:-
CH2 = CH2 + Cl – COCH3 → CH2Cl – CH2 – CO – CH3
Addition of Isoparaffin : Some alkenes in the presence of concentrated H2SO4, anhydrous BF3 or anhydrous HF or anhydrous AlCl3, combine with isoperafines to form branched paraffin. This reaction is called Alkylation.
Example:
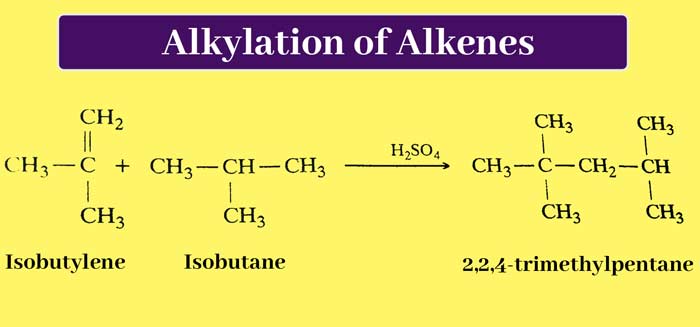
Substitution Reaction: Being unsaturated, alkene mainly undergoes addition reactions and does not show substitution reactions, but it also gives substitution products by combining with halogens at high temperature.
Example:
CH3 – CH = CH2 + Cl2 → CH2 = CH – CH2Cl + HCl
CH3–CH=CH–CH3 + Cl2 → CH2Cl–CH=CH–CH2–CH3 + CH3–CH=CH=CH–CHCl–CH3
Oxidation: Alkenes are easily oxidised. The product obtained from oxidation depends on the nature of the oxidizer.
Combustion: In air or oxygen, alkene burns with a radiant flame and carbon dioxide and water are formed.
CxHy + (x + y/4) O2 → xCO2 + y/2 H2O + Heat
C2H4 + 3O2 → CO2 + 2H2O + Heat
From Alkaline Potassium Permanganate Solution: Oxidized to 1% alkaline KMnO4 solution, alkene forms dihydroxy compounds called Diol or Glycol.
In this reaction the pink color of KMnO4 disappears and green color is obtained due to the formation of K2MnO4.
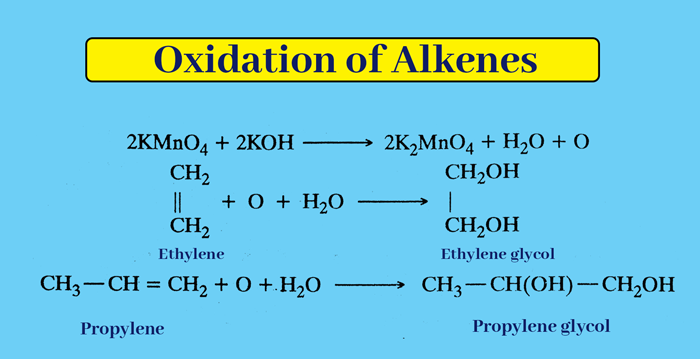
With the help of this reaction, the presence of carbon-carbond double bond or tri bond i.e. unsaturated can be checked in the given carbonic compound. This test of 1% alkaline KMnO4 with Baeyers reagent and unsaturated is called Baeyer’s test.
From acidic Potassium Parmagnate Solution – Acidic potassium parmagnate solution acts as a strong oxidising agent. Under the influence of this oxidizer, the alkene molecule disintegrates from the place where the double bond occurs and aldehyde or ketone is obtained.
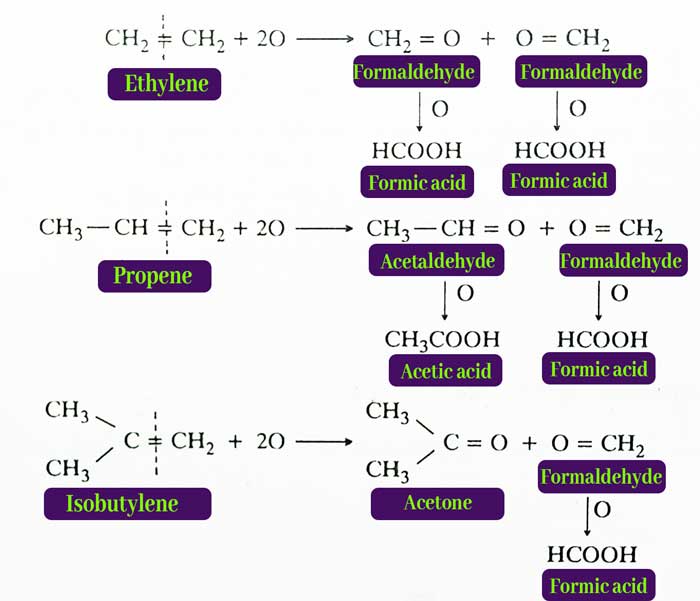
The aldehydes are easily oxidised. UnBder the conditions of the reaction, their oxidation results in carboxylic acid. Hence oxidation of alkenes by acidic potassium permagnate solution results in keton, carboxylic acid or both types of compounds.
example :
2KMnO4 + 3H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 3H2O + 5O
The pharmic acid obtained from the above reactions gets oxidised to carbon dioxide and water under the reaction conditions.
HCOOH + O → CO2 + H2O
In this reaction also the pink color of KMnO4 disappears but K2MnO4 is not formed, the immeasurable green color is not obtained. In addition, acidic KMnO4 is a strong oxidising agent and it loses its pink color in its reaction with many other substances. Hence, this reaction cannot be used to test for unsaturated.
Acidic K2Cr2O7 is also a strong oxidising agent like acidic KMnO4. Its reaction with alkenes is similar to the above reaction.
Perbenzoic acid or hydrogen peroxide – As a result of the reaction of Perbenzoic acid(C6H5COOOH) or Hydrogen Peroxide(H2O2), alkene is oxidised to form epoxides, which on dehydration give hydroxy compounds.
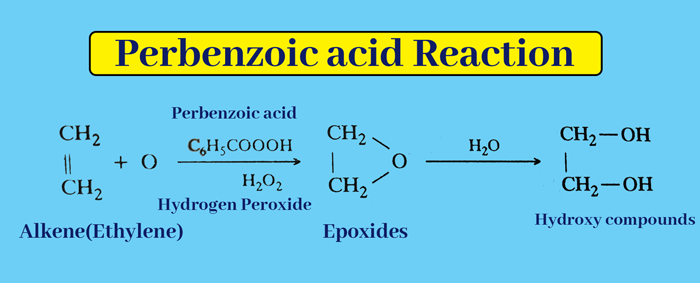
Isomerisation:- Some alkenes undergo isomerisation on heating in the presence of AlCl3 or any other luis acid.
Example :-
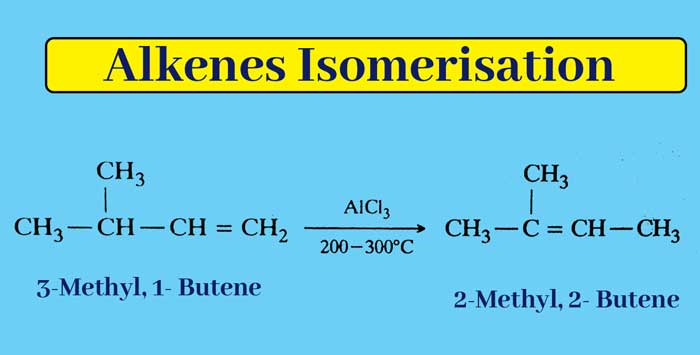
Polymerisation: Under suitable conditions, different molecules of the same alkene combine with each other. A molecule of a compound of higher molecular weight is formed by the addition of several molecules.
Example : Polytethene is obtained by heating ethylene gas in the presence of oxygen or peroxide to 250-300°C at about 500 atmospheric pressure.
n CH2 = CH2 → (– CH2 – CH2 – )n
In the above reaction, the value of n is about 1000. This is an example of reaction polymerization.
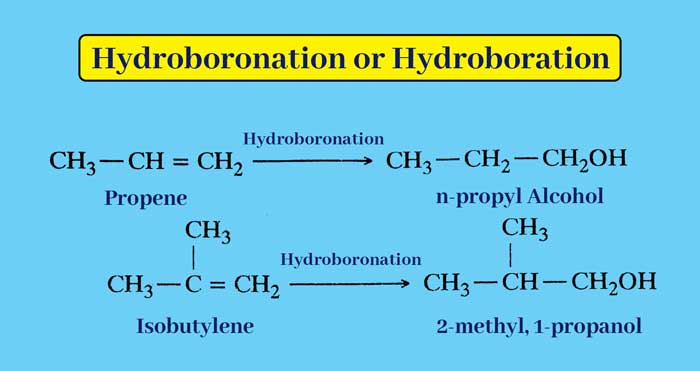
Hydroboronation or Hydroboration:- Alkene reacts with di-borane (B2H6) to form an additive product which on reaction with alkaline hydrogen peroxide gives an alcohol.
6R – CH = CH2 + B2H6 → 2(R – CH2 – CH2 –)3 B → 6R – CH2 – CH2 – OH + 2H3BO3
This whole reaction is called hydroboration or hydroboration. The net result of this whole reaction is that the addition of water to the alkene molecule is contrary to the Markovnikov rule.
example :
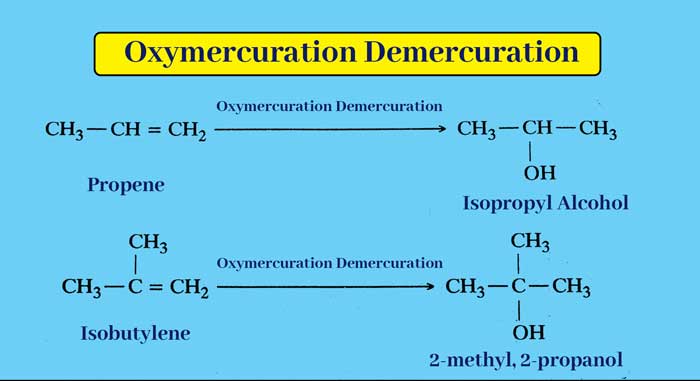
Oxymercuration Demercuration : Replacing a solution of alkenes in tetrahydrofuran with mercuric acetate gives an additive product. Whose reduction in alkaline medium by sodium borohydride gives an alcohol.
The net result of the above whole reaction is that the addition of water to the alkene molecule follows Markovnikov’s rule.
example :
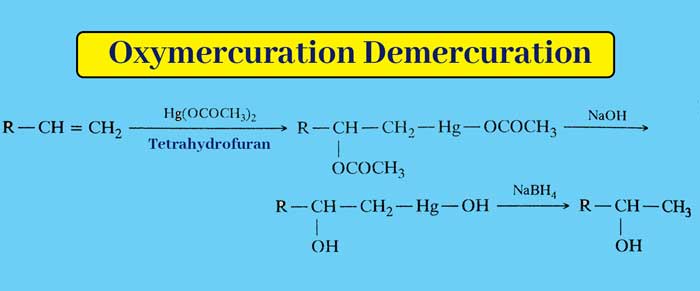
According to Markovnikov’s rule on alkenes, addition of water can also be done by the presence of dilute acids, but in this reaction carbonium ion is formed, due to rearrangement of which many side products are also obtained. Oxymercuration The advantage of demercuration is that carbonium ion is not formed in this reaction and side products are not obtained.