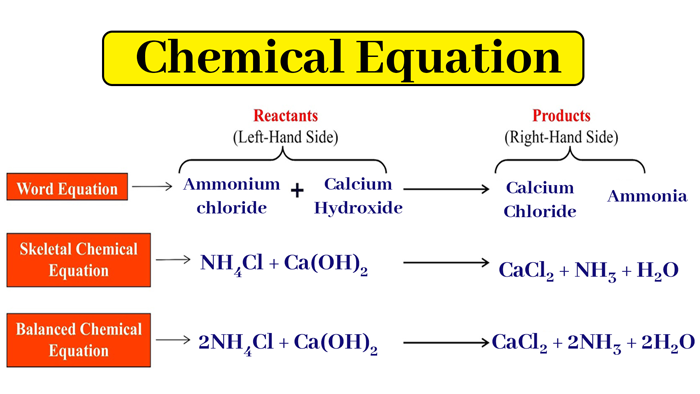
How is a chemical equation written in chemistry?
Just as a symbol represents an atom of an element and a formula for a molecule of a substance, so chemical equations represent an actual chemical reaction.
Different molecules participate in a chemical reaction and new types of molecules are formed after the exchange of atoms or countries present in them. All these molecules can be represented by formulas.
example :
The reaction of sodium chloride and silver nitrate can be represented as follows with the help of formulas.
AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO3
Here AgNO3 and NaCl are the reactants and AgCl and NaNO3 are the resultant or product. Representing a chemical reaction in this way is called a chemical equation.
Thus
Representing the reactants participating in a chemical reaction and the products or resultant substances resulting from the reaction by symbols and formulas is called chemical equation.
The reaction of hydrochloric acid on calcium carbonate forms calcium chloride and water and carbon dioxide is released.
CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
What is the Method of writing Chemical Equation
While writing the chemical equation of a reaction, the following points should be kept in mind –
1) The names and chemical formulas of the reactants and products of the reaction should be known.
2) Substances are always written in the form of molecules in an equation. For example, hydrogen, nigtogen, oxygen and chlorine etc. are written as H2, N2, O2 and Cl2 respectively, because all these gases are diatomic. Elements of a mono atomic are written by their symbols. Like sodium, magnesium and copper are written as Na, Mg and Cu respectively.
3) The reactants participating in a chemical reaction are written on the left side by symbols or formulas and a plus (+) sign is put between the different reactants. For example, magnesium metal (Mg) burns in oxygen (O2). For this the left side will be Mg + O2.
4) The products obtained after chemical reaction are written by symbols or formulas on the right side and plus (+) sign is put between different products.
For example, the product in the appropriate reaction is magnesium oxide. Hence MgO will be written on the right side.
5) Then an equal (=) or an arrow (→) sign is placed between the reactants and the products.
Mg + O2 → MgO
This equation is called the skelton equation. Finally this skelton equation is balanced.
Balancing the Equation
The number of atoms of each element on the left and the right side of the chemical equation should be equal, because according to the law of conservation of mass, neither an atom is lost nor a new atom is created in every chemical change.
So we should equalize the number of atoms of the element in both the sides of the above equation in the following way –
i) First of all we see that one molecule of oxygen has two atoms of oxygen which will form two molecules of magnesium oxide.
Therefore
Mg + O2 → 2MgO
We call the above equation as the chemical equation because the number of atoms of each element is equal on both its sides.
Balanced Chemical Equation
A chemical equation in which the number of atoms of each element is equal on both sides is called a balanced chemical equation.
example –
2KClO3 → 2KCl + 3O2
NH3 + HCl → NH4Cl
Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
Methods of Balancing Chemical Equation
Following are the four methods of balancing the Chemical Equation :-
Trial and error method
Partial equation method
Valency method
Ionic Equation method
Trial and Error method
First the reactants are written on the left side of the arrow and the products are written in the form of their formulas on the right, then the atom which has come in the least number is first balanced. After this balance the number of atoms in increasing order.
Example: The reaction of concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) on copper (Cu) gives copper sulfate (CuSO4), sulfer dioxide (SO2) and water (H2O).
Cu + H2SO4 → CuSO4 + SO2 + H2O
This equation is balanced by trial and error method in the following way –
(i) The number of copper (Cu) atoms is the least in the above equation. Therefore, first of all balance the number of atoms of copper. In this equation, the number of Cu atoms in the left side and the right side is equal.
(ii) In this equation, there is one atom of sulfur (S) on the left, while there are two atoms on the right. Therefore, by writing two molecules of sulfuric acid on the left, we make the number of sulfur (S) equal on both sides.
Cu + 2H2SO4 → CuSO4 + SO2 + H2O
In the equation, there are four hydrogen atoms on the left side, while there are two hydrogen atoms on the right side. Therefore, by writing two molecules of water (H2O) on the right side, we also balance the number of hydrogen atoms.
Cu + 2H2SO4 → CuSO4 + SO2 + 2H2O
In this equation, there are 8 atoms of oxygen on the left side and 8 atoms of oxygen on the right side. So it is a balanced equation.
Some other equations to be balanced by this method are as follows –
a:- KClO3 → KCl + O
2KClO3 → 2KCl + 3O2
b:- NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2 → CaCl2 + NH3 + H2O
2NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2 → CaCl2 + 2NH3 + 2H2O
c:- HCl + O2 → H2O + Cl2
4HCl + O2 → 2H2O + 2Cl2
Partial equation method
This method is used only to balance complex equations. Its various terms are as follows –
i) Complex chemical reactions take place in two or more steps. Write them separately. The chemical reactions of different terms are called partial equations.
ii) Different partial reactions are balanced by estimation method.
iii) Finally the total partial equations are summed up. While adding, keep in mind that the products in the middle which are on either side of the final sum equation are omitted.
Example
Magniz oxide and hydrochloric acid react with each other to form magniz chloride (MnCl2), chlorine (Cl2) and water (H2O). It can be written as follows –
MnO2 + HCl → MnCl2 + Cl2 + H2O
First step :-
In the first step, magniz dioxide reacts with hydrochloric acid to form magniz chloride, water and nascent oxygen.
MnO2 + HCl → MnCl2 + H2O + O
It is balanced by trial and error method. In this equation, there are two atoms of chlorine on the right side. Therefore, to equalize the number of chlorine atoms on the left, we write two molecules of hydrochloric acid, which makes the following equation –
MnO2 + 2HCl → MnCl2 + H2O + O
This is the first partial equation
Second step :
In this equation, hydrochloric acid reacts with nascent oxygen to form water and chlorine.
HCl + O → H2O + Cl2
In this equation there is one atom of chlorine on the left and two atoms of chlorine on the right. Therefore, by writing two molecules of hydrochloric acid on the left side, we equalize the number of atoms of chlorine on both sides, due to which the equation becomes in the following form –
2HCl + O → H2O + Cl2
This is second partial equation
Now by adding the partial equation (first and second), we get the balance equation of the above chemical reactions.
(1) MnO2 + 2HCl → MnCl2 + H2O + O
2HCl + O → H2O + Cl2
-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=
MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + Cl2 + 2H2O
-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=
Same :-
(2) H2SO4 → H2O + SO2 + O
H2S + O → H2O + S
-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=
H2SO4 + H2S → 2H2O + SO2 + S
-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=
Valency Method
In this method, the equations of the reaction occurring by the combination of atoms of two elements are balanced. Following steps are followed in this method –
(i) By writing the reactants on the left side of the equation, they show their valency and write the product on the right side.
(ii) Now write down the number of atoms required to complete the valency of each element.
Example :
Magnesium and nitrogen react to form magnesium nitride. This reaction is balanced by the following steps –
a. The valence element magnesium has a valency of two (positive) and nitrogen has a valency of three (negative).
Therefore
Mg++ + N— → Mg3N2
b. If 3 atoms of magnesium are taken and two atoms of nitrogen i.e. one molecule are taken, then the valencies of both the elements will be fulfilled. So the equation will have the following form –
3Mg++ + 2N— → Mg3N2
3Mg + N2 → Mg3N2
Other Examples:
Ca++ + H– → CaH2
Ca++ + 2H– → CaH2
Ca + H2 → CaH2
Ionic Equation Method
There are some compounds which, when dissolved in water, split into their ions. Such compounds are called electrolytes. The process of splitting into ions is called decomposition and the equation expressing this reaction is called ionic eqaution.
To balance the equations with this method, first of all, the ionic equations are written separately and balance them. Then add them and write the complete chemical equation.
A white precipitate of silver chloride is obtained when an aqueous solution of silver nitrate is added to an aqueous solution of sodium chloride (NaCl).
To balance the chemical equation of this reaction with the ionic equation method, first we write the following type of ionic equation for the dissociation of NaCl and AgNO3 –
NaCl ⇌ Na+ + Cl–
AgNO3 ⇌ Ag+ + NO3–
Now in these ionci equations, by adding (i) to (ii) anion and (i) to (ii) anion, we write the complete chemical equation.
NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
Some more Examples
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and hydrochloric acid react to form sodium chloride and water.
NaOH ⇌ Na+ + OH–
HCl ⇌ H+ + Cl–
-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=
K2SO4 ⇌ 2K+ + SO4—
K2SO4 ⇌ 2K+ + SO4—
-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=
Reaction of potassium sulfate and berium chloride gives the precipitate of berium sulfate –