P-Block Elements Short Notes: Download PDF, DPP and Online Test
P-Block Elements (General Properties)
- Inert pair effect:
- Nature of oxide:
- Diagonal relationship
- Covalency
- Types of bonding
p-block elements(13 Groups) Practice Set with Solution
Try it for free. No registration needed. But don’t forget to follow us our Social Pages
p-block elements(14 Groups) Practice Set with Solution
Try it for free. No registration needed. But don’t forget to follow us our Social Pages
NEET Exams 2021 p-block elements short notes
download p-block elements short notes
Chemistry Handwritten Notes (Sample)
Download PDF file of Chemistry Handwritten Notes. These are most valuable note for NEET/JEE exams.
Chemistry Handwritten Notes
Inert pair effect
The occurrence of oxidation states two unit less than the group oxidation states
Thus Tl+ is more stable in solution than Tl3+.
Thus Pb2+ is more stable in solution than Pb4+.
- General Properties of Alkene : Physical and Chemical
- Alkenes : Aliphatic Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
- How is a chemical equation written in chemistry?
- 14 Most Important Reactions in Chemistry
- The Gas Laws: Charle’s Law, Boyle’s Law and Gay-Lussac's law
Acidic oxide: React with base
Basic oxide: React with acid
Amphoteric oxide: React with both acid and base
Neutral oxide: Neither reacts with acid nor with base
Diagonal relationship
Basis of Diagonal relationship:
Ionic size, charge to mass ratio and polarization power
Covalency
It is the number of covalent bonds it forms with other atoms.
It is due to the absence of d orbitals that the maximum covalence of B,C,N,O is 4.
tetrahedral [M(OH)4]– and octahedral [M(H2O)6]3+,
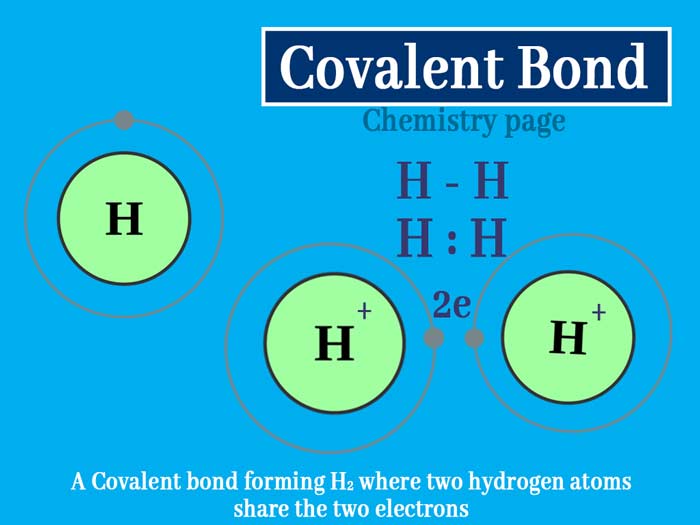
Types of Bonding
1. C=C, C≡C, C=O, N≡N, C=N, C≡N, N=O).
2. The heavier elements do form π bonds but this involves d orbitals (dπ–pπ or dπ –dπ).
3. d orbitals are of higher energy than the p orbitals, they contribute less to the overall stability of molecules than does p π – p π bonding.
Group-13 (Boron Family)
Gallium, melting point (303K), could exist in liquid state during summer. Boron high boiling point (2676K)
Atomic radius Atomic radius of Ga is less than that of Al
Ionization enthalpy B > Tl > Ga > Al > In
Electronegativity B > Al < Ga < In < Tl
+1 oxidation state B < Al < Ga < In < Tl
Boric acid (Orthoboric acid) (H₃BO₃)
Boric acid is a weak monobasic acid.
It is not a protonic acid but acts as a Lewis acid by accepting electrons from a hydroxyl ion
B(OH)3 + 2H2O → [B(OH)4]– + H3O+
Orthoboric acid is used as a mild antiseptic.
H3BO3 → HBO2 → B2O3
Group 14 Elements: Carbon Family
The dioxides
CO2, SiO2 and GeO2 are acidic,
SnO2 and PbO2 are amphoteric in nature.
Monoxides
CO is neutral,
GeO is distinctly acidic whereas
SnO and PbO are amphoteric
+2 oxidation state increases in the sequence Ge < Sn < Pb
GeX4 is more stable than GeX2, whereas PbX2 is more than PbX4.
Except CCl4, not hydrolysed by water because absence of d orbital.
- Importance of Biomolecules in Life || What are the 4 main biomolecules?
- Valency of Elements || How to Find Valency || What is the Valency of the atom?
- Resonance effect or mesomeric effect || What is resonance effect with example?
- Glucose Structure: Physical and chemical properties, Glucose Chemical Reaction
- Introduction of Inductive-Effect || How does Inductive Effect Work?
- IUPAC Name : How to find the IUPAC name of compounds.
- What is Urea || How to make Urea Fertilizer, || Urea uses
- Sodium Chloride Properties || Why Sodium Chloride is Soluble in Water
Catenation: Carbon atoms have the tendency to link with one another through covalent bonds to form chains and rings.
C > > Si > Ge ≈ Sn
Lead (Pb) does not show catenation.
Allotropes of Carbon
Allotropy or allotropism is the property of some chemical elements to exist in two or more different forms, in the same physical state
1. Two types crystalline as well as amorphous
2. Diamond and graphite are two well-known crystalline forms of carbon.
3. Amorphous: Coke, charcoal, carbon black
4. Third form of carbon known as fullerenes
5. Graphite is thermodynamically most stable allotrope of carbon and, therefore, Δf H(-) of graphite is taken as zero.
Diamond
1. Crystalline three dimensional lattice
2. Each carbon atom undergoes sp3 hybridization (tetrahedral)
3. The C–C bond length is 154 pm
4. Hardest substance on the earth
5. Bad conductor of electricity
6. Highest thermal conductivity
7. High refractive index
Graphite
1. Layered structure, black, metallic luster
2. Layers are held by van der Waals forces and distance between two layers is 340 pm.
3. Each layer is composed of planar hexagonal rings of carbon atoms. C—C bond length within the layer is 141.5 pm.
4. Each carbon atom sp2 hybridization (three sigma bonds)
5. Fourth electron forms a π bond. The electrons are delocalized over the whole sheet.
6. Good conductor of electricity (free mobile electrons)
7. It is very soft and slippery
Fullerene (buckminsterfullerene)
1. It’s a polygon, contains twenty six- membered rings and twelve five membered rings.
2. A six membered ring is fused with six or five membered rings
3. Five membered ring can only fuse with six membered rings.
4. All the carbon atoms are sp2 hybridisation.
5. Electron at each carbon is delocalised gives, aromatic character to molecule.
6. Each carbon atom forms three sigma bonds with other three carbon atoms.
7. Single and double bonds with C–C distances of 143.5 pm and 138.3 pm respectively.