Phosphine Gas: Preparation, formula, and Uses
Chemical Formula
Copper pyrites – CuFeS2
Meta Phosphoric Acid – HPO3
Lead Sulphide – PbS
Hematite – Fe2O3
Silicon Dioxide – SiO2
Magnesium Carbonate – MaCO3
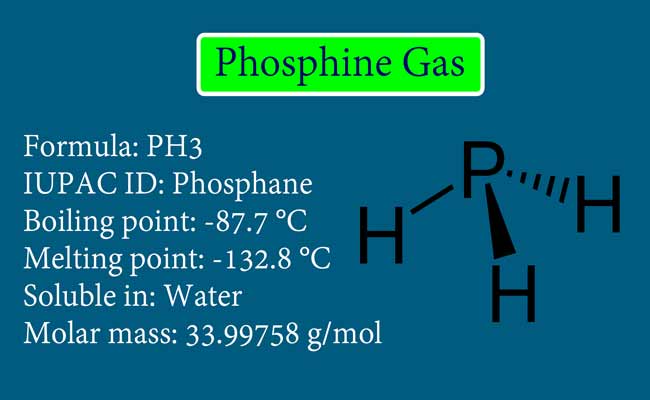
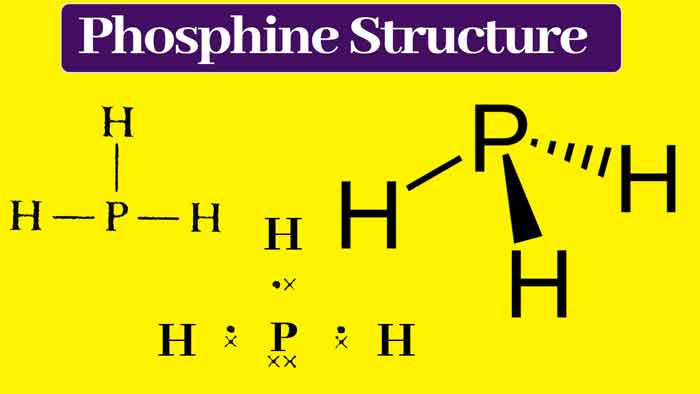
Phosphine gas was discovered by Philippe Gengembre in 1783. Gengembre made it by the action of caustic soda on phosphorus. It is chemical formula PH3.
Phosphine Gas Preparation
Phosphine gas is also obtained by the action of dilute sulfuric acid from aluminium phosphide.

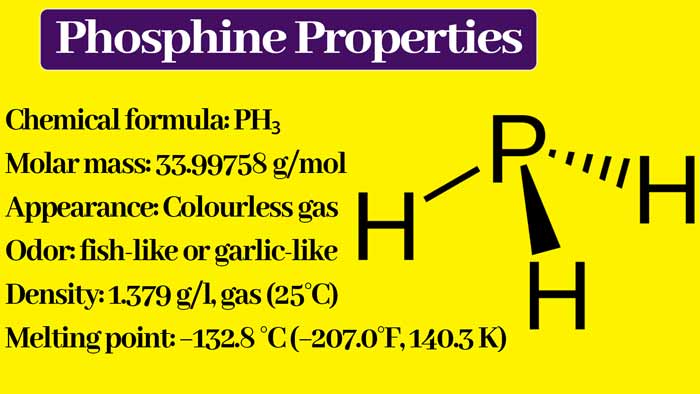
Chemical Properties