Preparation of Sulfuric Acid by Lead Chamber Process
History of Sulfuric Acid
Gaber first made it from the distillation of alum. Valentine made it in 1600 by distillation of green vitriol, FeSO4, 7H2O.
[FeSO4.7H2O → FeSO4 + 7H2O] x 2
2FeSO4 → Fe2O3 + SO2 + SO3
H2O + SO3 → H2SO4
2FeSO4.7H2O → Fe2O3 + SO2 + 13H2O + H2SO4
Due to its oily nature, it was named oil of vitriol. Since the middle of the eighteenth century, it is produced by the oxidation of sulphur. For this reason it is also called acid of sulfur.
Presence of Sulfuric Acid
Sulfuric acid in free state is found in a river called Rio Tinto. In the combined state, this sulfate is found in the form of SO42- minerals, such as gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O) etc.
Preparation of Sulfuric Acid
1. Sulfuric acid is formed when sulfur trioxide is dissolved in water.
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
2. Sulfuric acid is also formed when an aqueous solution of sulfur dioxide is oxygenated with oxygen, chlorine, bromine, nitrous acid or hydrogen peroxide.
2SO2 + 2H2O + O2 → 2H2SO4
SO2 + 2H2O + Cl2 → H2SO4 + 2HCl
SO2 + 2H2O + Br2 → H2SO4 + 2HBr
SO2 + 2HNO2 → H2SO4 + 2NO
SO2 + H2O2 → H2SO4
Industrial Manufacturing Methods
Since sulfur is found in abundance in nature, it is the starting material for the industrial manufacture of sulfuric acid.
To make sulfuric acid from sulfur, it is first burnt in the presence of oxygen, which gives sulfur di oxide gas. Sulfur di-oxide is oxidised to give sulfur tri-oxide gas, which when dissolved in water gives sulfuric acid.
S + O2 → SO2 → SO3 → H2SO4
The following two methods are used for the industrial manufacture of sulfuric acid.
- Lead Chamber Process
- Contact Proces
In this method sulfur dioxide is oxidized by oxygen in the air in the presence of oxides of nitrogen. Nitrogen oxides act as catalysts.
2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3
There are different opinions about the mechanism of this reaction.
According to Berzelius – Oxidation is by nitrogen peroxide (NO2).
SO2 + NO2 → SO3 + NO
2NO + O2 → 2NO2
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
According to Lunge – oxidation of SO2 by N2O3 forms nitroso-sulfuric acid which reacts with water to form sulfuric acid.
NO + NO2 → N2O3
2SO2 + H2O + N2O3 + O2 → 2HSO4.NO (Nitrosylsulfuric acid)
2HSO5N + H2O → H2SO4 + N2O3
According to Lunge – oxidation of SO2 by N2O3 forms nitroso-sulfuric acid which reacts with water to form sulfuric acid.
Preparation Method
The plant used in this method is shown. Following is the description of the main parts of this plant and the activities in them.
1 – Pyrite burner :- This is a type of furnace in which iron pyrite (FeS2) or sulfur (S) is burnt in the presence of air. In this way sulfur dioxide gas is obtained.
4FeS2 + 11O2 → 2Fe2O3 + 8SO2
S + O2 → SO2
2 – Dust chamber :- The gaseous mixture obtained from Pyrite burner is passed through such a chamber. Where the dust particles present in these gases are removed. This chamber is called Dust chamber.
3 – Nitre pot :- The gases received from the dust chamber are passed through the Nitre pot. A mixture of sodium nitrate and concentrated H2SO4 is heated in a nitre pot, or ammonia in modern plants is oxidized by air in the presence of platinum. Oxides of nitrogen (NO or NO2) are formed in these reactions.
NaNO3 + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + HNO3
4HNO3 → 4NO2 + 2H2O + O2
4HN3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O
2NO + O2→ 2NO2
In this way, in the nitre pot, sulfur dioxide and air get mixed with the oxides of nitrogen. This mixture is sent to the Glover’s tower.
4 – Glover ‘s tower :- It is a cylindrical column of 20 to 60 feet height and 3 to 6 feet in diameter. Its inner surface is made of acid proof bircks. It is filled with flint stone or bricks. In this, a mixture of oxides of sulfur dioxide, air and nitrogen (from the Nitre pot) is sent from below.
In this, nitroso-sulfuric acid (from the Gelusak column) and sulfuric acid (from the Lead Chamber) of about 65% concentration are sent from above. This column does the following:
(a) – Cools the gaseous mixture obtained from the Nitre pot to 50-80°C.
(b) – The sulfur di oxide obtained from the Nitre pot converts some amount into sulfuric acid.
SO2 + H2O + NO2 → H2SO4 + NO
(c) – Concentrates a dilute solution of sulfuric acid coming from the lead chamber.
(d) – Converts nitroso-sulfuric acid (HSO4.NO) coming from the Gay-Lussac column into sulfuric acid.
2 HSO4.NO + H2O → 2H2SO4 + NO + NO2
Concentrated sulfuric acid continues to be received from the bottom of the Glover column, which is kept on collecting. A mixture of sulfur dioxide, air and nitrogen oxides continues to be received at 50-80° C from the top of the Glover column. This mixture is sent to the Lead chamber.
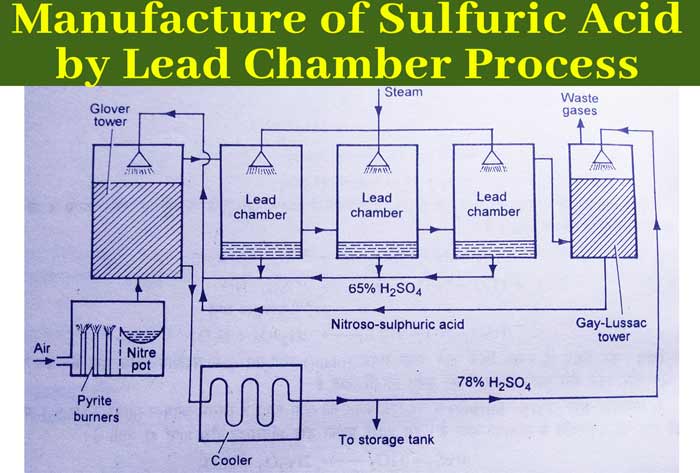
5 – Lead chamber :- These chambers are made of lead and their volume ranges from 40,000 to 60000 cubic feet. Many such cells are connected in series. In these chambers, water vents are released from the top or water vapor is passed through.
In the Glover column, a mixture of sulfur dioxide, air and nitrogen oxides received from the top, is sent to these chambers in sequence. In these chambers SO2 gets oxidised to SO3 and SO2 gas dissolves in water to form sulfuric acid.
2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
Thus sulfuric acid formed keeps accumulating on the floors of these chambers. The concentration of this acid is about 65% and it is called room acid. The room acid is sent to the Glover column for concentration. The remaining gaseous mixture is sent to the Gay-Lussac column.
6 – Gay-Lussac Tower :- This pillar is made of sheets of lead and is filled with coke (C). In this column, showers of cold and concentrated sulfuric acid are poured from the top. In this column, the gaseous mixture received from the Sis chamber is sent from the bottom. This gaseous mixture mainly consists of oxides of nitrogen. The following reaction takes place in this column.
2H2SO4 + NO + NO2 → 2HSO4.NO + H2O
Thus nitroso-sulfuric acid formed is sent to the Glover column with the help of a pump where it is converted into sulfuric acid.
2HSO4.NO + NO + H2O → 2H2SO4 + N2O3
Concentration of room acid- The concentration of room acid is only 60-70%. For its concentration, it is first sent to the Glover column. The concentration of sulfuric acid obtained from the Glover column is also not high. The following methods are used to make it more concentrated.
Cascade’s Method :- In this method, the silica bowls are placed on the stairs made of bricks in such a way that the acid from the upper cups continues to fall into the lower ones. These cups are heated with the help of hot gases.

A dilute acid is dropped from the top of the cup which comes down to the bottom passing through each other in sequence. These cups are heated by hot gases and water escapes in the form of vapor and sulfuric acid becomes concentrated. The concentration of the acid obtained by this method is about 90%.
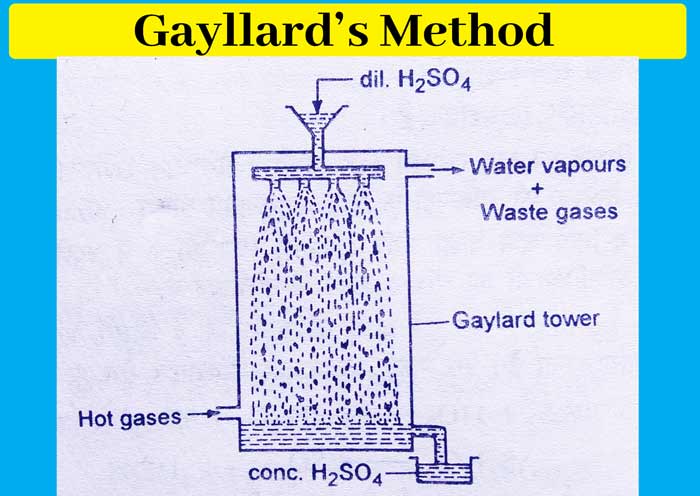
Gayllard’s Method :- In this method, the Gaylard pillar, which is made of acid proof stone, is showered with dilute acid from above and hot gas, which is obtained from the coal furnace, is passed from below. On coming in contact with these hot gases, the water of the acid dissociates as a vapor and on its release the acid becomes concentrated and its concentration becomes about 95%.
Removal of impurities of room acid : The acid obtained by Sis chamber method contains impurities of PbSO4, As2O3 and oxides of nitrogen which are removed in the following way :
Acid is slowly added to the water. Lead sulfate settles down as a white precipitate. It is filtered and separated. H2S is precipitated in the form of As and As2S3 on passing through the filtered solution.
The precipitate is filtered and separated and after distillation by adding ammonium sulphate to the filtered liquid, the oxides of nitrogen are reduced to give nitrogen which is separated in the form of gas.
As2O3 + 3H2S → 3H2O + As2S3
(NH4)2SO4 + NO + NO2 → 3H2O + 2N2 + H2SO4
Uses Of Sulfuric Acid
Sulfuric acid is a crucial chemical in various industries
due to its diverse range of applications. Here's a list of some common uses:
Manufacturing of Fertilizers: Sulfuric acid is a key
component in the production of phosphate and ammonium sulfate fertilizers. It
reacts with phosphate rock to produce phosphoric acid, which is then used to
make phosphate fertilizers.
Petroleum Refining: Sulfuric acid is used in the
refining of petroleum products. It helps in the alkylation process, where it
catalyzes the reaction between olefins and isobutane to produce high-octane
gasoline components.
Chemical Synthesis: It is widely employed in the synthesis
of various chemicals, including synthetic detergents, synthetic resins,
pharmaceuticals, and explosives such as nitroglycerin.
Metal Processing: Sulfuric acid is used for pickling
and cleaning metals to remove rust, scale, and oxides from their surfaces
before further processing or plating.
pH Control: In wastewater treatment plants and other
industrial processes, sulfuric acid is used to adjust the pH of solutions,
making it acidic. This is essential for various chemical reactions and water
treatment processes.
Battery Production: Sulfuric acid is a vital
component in the production of lead-acid batteries, commonly used in
automobiles, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and other applications where
a rechargeable battery is needed.
Textile Industry: It is used in the production of
synthetic fibers like nylon and rayon. Sulfuric acid helps in the production
process of these fibers by dissolving and modifying certain polymers.
Paper Manufacturing: Sulfuric acid is used in the
production of paper and pulp. It is used to hydrolyze cellulose and
hemicellulose in wood chips, which breaks them down into pulp for papermaking.
Cleaning and Etching: Sulfuric acid is employed for
cleaning and etching various materials, including glass, ceramics, and metals.
It can remove contaminants and create microstructures on surfaces for specific
applications.
Food Processing: In food processing, sulfuric acid is
used for various purposes, such as pH adjustment, water treatment, and as a
catalyst in certain reactions. However, its use in direct food processing is
strictly regulated due to its corrosive nature and potential health hazards.
These are just some of the many uses of sulfuric acid across
different industries, highlighting its importance in modern manufacturing and
chemical processes.
