Semiconductors : How Semiconductor works and Types
Conductors, Insulators and Semiconductors
Most solids can be placed in one of two classes, conductors and insulators. Conductors are those in which electric charges can flow easily, while insulators are those in which it is difficult for electric charges to flow.
This difference between conductors and insulators can be explained by the number of free electrons in them. There are a large number of free electrons in conductors, which act as charge carriers in the flow of current. In contrast, insulators have a negligible number of free electrons.
The resistance temperature coefficient of conductors is positive, that is, their electrical resistance increases or the electrical conductivity decreases with increase in temperature.
There are also some solid materials whose electrical conductivity lies between that of conductors and insulators. They are called Semiconductors. Carbon, silicon and germanium are examples of semiconductors.
In semiconductors, the most valence electrons are neither so strongly bound to an atom as in an indulator, nor as loosely bound as in a conductor.
The resistance temperature coefficient of semiconductors is negative, that is, their electrical resistance decreases or the electrical conductor increases with increase in temperature.
Conversely, the electrical resistance of semiconductors increases or the electrical conductivity decreases with decrease in temperature. At absolute zero temperature, a semiconductor behaves as an ideal insulator.
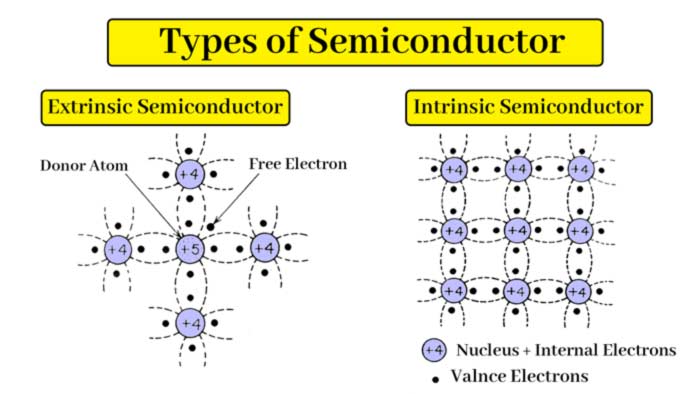
Intrinsic and Extrinsic Semiconductors
There are two types of semiconductor. intrinsic Semiconductor and electric Semiconductor
Intrinsic Semiconductor:
A pure semiconductor, in which no impurities are added, is called an intrinsic semiconductor. Thus, pure germenium and silicon in their natural state are intrinsic semiconductors.
![]()
Electric conduction in intrinsic semiconductors: Two well known pure semiconductors are germanium and silicon. Each of them has a valency of 4. We can assume that each atom of Ge or Si has 4 valence electrons around an inner core.
And the core has + 4e charge. In germenium crystal, these atoms are arranged in an ordered array such that each atom lies at some corner of the regular tetrahedron.
Atoms form covalent bonds by sharing one of the four valency electrons, one of the four closest electrons. These bonds provide binding force between neighboring atoms.
At temperatures near absolute zero, the atoms of pure germanium or silicon are strongly binding with all valence electron cores. Hence free electrons are not available for conduction.
But at normal temperatures, some covalent bonds are broken due to thermal agitation, so that some valent electrons are freed.
When an electric field is applied to the crystal, these free electrons move in the opposite direction of the field and the electric current starts to conduct in the crystal. On heating the crystal, more and more electrons are liberated due to which the conductivity of the crystal increases.
At room temperature, only one covalent bond is broken in germanium 109 atoms. Therefore, the conductivity of intrinsic semiconductors is very low, so that they cannot be of any practical use.
![]() Extrinsic Semiconductors :
Extrinsic Semiconductors :
Intrinsic semiconductors have very low electrical conductivity. But if a very small amount of such a substance, whose valency is 5 or 3, is mixed in pure germanium or silicon crystal as impurity, then the conductivity of the crystal increases significantly.
![]()
This action is called doping. Example the conductivity of germanium increases up to 16 times when 1 impurity atom is mixed in 108 germanium atoms. Such impure semiconductors are called extrinsic or impurity or doped semiconductors. By controlling the amount of impurity to be mixed in these semiconductors, desired conductivity can be achieved.
There are two types of extrinsic semiconductors.
n-type semiconductors
p-type semiconductors
![]()
n-type semiconductors: –
When pentavalent impurity (like: arsenic, antimony, phosphorus) is added to a germenium or silicon crystal, it replaces one atom of germanium by removing it.
Out of the 5 valence electrons of the impurity atom, 4 electrons form covelent bonds with one valence electron of the four germanium atoms located around them and the 5th valence electron is freed to move in the crystal. This electron acts as a charge carrier.
Thus, adding impurity to pure germanium increases the number of free electrons. That is, the conductivity of the crystal increases. This type of impurity germanium crystal is called n-type semiconductor. Because free electrons are negative in it. The impurity atoms are called donor atoms because they provide conducting electrons to the crystal.
p-type semiconductors: –
If a trivalent valence atom (like aluminum, boron, gallium and indium) is added to germanium or silicon crystal, then it also takes the place of a germanium atom.
Its three valence electrons form covalent bonds with one valence electron of the three nearest germanium atoms. And a valence electron bond of germanium is not able to form.
Therefore, a blank space remains on one side of the impurity atom in the crystal, which is called a hole. On applying a valid field, a binding electron comes from the neighboring germanium atom in this hole, due to which a space in the neighboring atom becomes vacant.
In this way, the hole starts moving in the direction of the field from one place to another within the crystal. It is unclear that a hole is equivalent to a positively charged particle that moves in the opposite direction with respect to the electron.
The germanium crystal found in this type of impurities is called p-type semiconductor because the charge carriers (Hole) are positive in it. The impurity atoms are called acceptor atoms. Because these atoms accept electrons from pure semiconductor in the process of making positive holes.
It is clear from the above explanation that n-type semiconductor crystal has a movable (negative) electron. And only their number has stable positive donor ions. Ions are positive because one electron has been separated from each atoms. The crystal remains neutral.
Similarly p-type semiconductor crystal has movable (positive) holes and same number of stable negative acceptor ions. But the mobility of holes in p-type semiconductors is less as compared to the mobility of electrons in n-type semiconductors.
Minority Carriers and Minority Carriers
Electrons in n-type semiconductor and holes in p-type semiconductor, which are obtained by mixing five-valent and tri-valent dissociative atoms respectively in the semiconductor, act as charge-carriers in their own semiconductor. They are called majority carriers.
In addition to the majority carriers (electron in n-type semiconductor and holes in p-type semiconductor) obtained due to impurity mixing, both p-type and n-type semiconductors have some electrons and holes resulting from thermal disturbance.
They arise from the breaking of some covalent bonds at normal temperature. The few electrons present in p-type crystal and the small number of holes present in n-type crystal are called minority carriers.