Surface Chemistry Notes: CBSE Notes Class 12 Download Short Note PDF
Surface Chemistry Definitions
Surface chemistry: It deals with phenomena that occur at the surfaces or interfaces.
Adsorption: It is the process of accumulation of molecular species at the surface rather than in the bulk of a solid or liquid.
Adsorbate: The molecular species or substance, which concentrates or accumulates at the surface.
Surface chemistry: It deals with phenomena that occur at the surfaces or interfaces.
Adsorption: It is the process of accumulation of molecular species at the surface rather than in the bulk of a solid or liquid.
Adsorbate: The molecular species or substance, which concentrates or accumulates at the surface.
NEET Exams 2021 Chemistry Notes Surface Chemistry
Try it for free. No registration needed. But don’t forget to follow us our Social Pages
Distinction between Adsorption and Absorption
Adsorption
It is a surface phenomenon, i.e., it occurs only at the surface of the adsorbent.
In this phenomenon, the concentration on the surface of adsorbent is different from that in the bulk.
Its rate is high in the beginning and then decreases till equilibrium is attained.
Absorption
It is a bulk phenomenon, i.e., occurs throughout the body of the material.
In this phenomenon, the concentration is same throughout the material.
Its rate remains same throughout the process.
Types of adsorption
Physical adsorption (Physisorption)
The particles are held to the surface by the physical forces like Van der waals forces.
Chemical adsorption (Chemisorption)
The particles are held to the surface by the chemical forces or by chemical bonds

Factors affecting adsorption of gases on solids
Nature of adsorbent: Greater are the strained forces on the surface, more is the ease with which adsorption takes place on the surface. Activated adsorbents have high adsorbing power.
Surface area of adsorbent: Greater the surface area, more is the adsorption.
Nature of gas being adsorbed: Easily liquefiable gases like NH3, HCl, Cl2, SO2,CO2, etc. (whose critical temperature is high) are adsorbed to greater extent.
Pressure: Adsorption increases with increase in pressure. The effect of pressure is large at low temperature.
Temperature: Since adsorption is an exothermic process so according to Le-Chatelier’s principle adsorption decreases with increase in temperature
Freundlich adsorption isotherm
The plot of x/m vs pressure at constant temperature is called Freundlich adsorption isotherm
where, m = mass of the adsorbent x = mass of the adsorbate

Catalysts and Catalysis
Substances, which accelerate the rate of a chemical reaction and themselves remain chemically and quantitatively unchanged after the reaction.
Promoters
Promoters are substances that enhance the activity of a catalyst
Poisons
Poisons decrease the activity of a catalyst.
Contact process: small amount of As2O3 act as poison for Pt
Haber’s process: H2S gas act as poison for Fe
Homogeneous catalysis
The reactants and the catalyst are in the same phase
Heterogeneous catalysis
The reactants and the catalyst are in different.
Zeolites: Shape-selective Catalysis
The catalytic reaction that depends upon the pore structure of the catalyst and the size of the reactant and product molecules. e.g., Zeolites (have honey–comb like structures).
Zeolites are being very widely used as catalysts in petrochemical industries for cracking of hydrocarbons and isomerisation.
An important zeolite catalyst used in the petroleum industry is ZSM-5.
It converts alcohols directly into gasoline (petrol) by dehydrating them to give a mixture of hydrocarbons.
Enzyme Catalysis
They are complex nitrogeneous organic compounds made up of proteins also called biochemical catalysts
The following characteristics are exhibited by enzyme catalysts:
- Most highly efficient
- Highly specific nature
- Highly active under optimum temperature
- Highly active under optimum pH
- Increasing activity in presence of activators and co-enzymes
- Influence of inhibitors and poisons
A colloid is a heterogeneous system in which one substance (dispersed phase) is in another substance called dispersion medium.
The range of diameters of colloidal particles is between 1 and 1000.
Associated colloids (Micelles)
The aggregated particles thus formed are called micelles. These are also known as associated colloids.
Micelles may contain as many as 100 molecules or more.
The formation of micelles takes place only above a particular temperature called Kraft temperature (Tk)
Above a particular concentration called critical micelle concentration (CMC).
Preparation of Colloids
- Chemical methods
- Electrical disintegration or Bredig’s Arc method
- Peptization
Chemical methods
This can be done by double decomposition, oxidation, reduction or hydrolysis. These molecules then aggregate leading to formation of sols.
Electrical disintegration or Bredig’s Arc method
This process involves dispersion as well as condensation.
Colloidal sols of metals such as gold, silver, platinum, etc., can be prepared
Peptization
The process of converting a precipitate into colloidal sol by shaking it with dispersion medium in the presence of a small amount of electrolyte.
The electrolyte used for this purpose is called peptizing agent.
During peptization, the precipitate adsorbs one of the ions of the electrolyte on its surface.
This causes the development of positive or negative charge on precipitates, which ultimately break up into smaller particles of the size of a colloid.
Purification of Colloidal Solutions
The process used for reducing the amount of impurities to a requisite minimum is known as purification of colloidal solution.
(i) Dialysis
(ii) Electro dialysis
(iii) Ultrafiltration
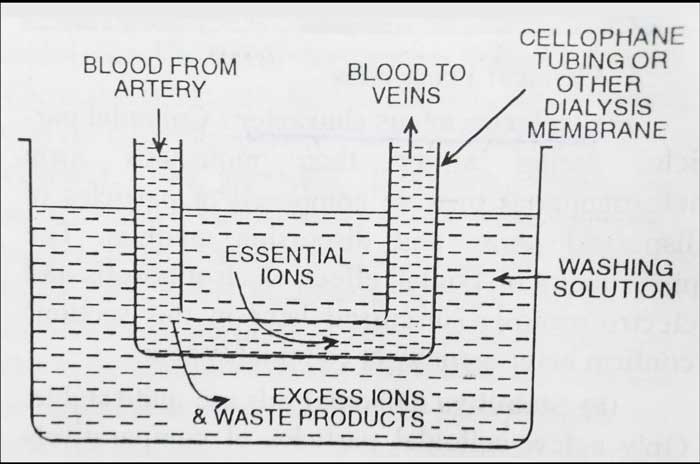
Dialysis & Electro dialysis
It is a process of removing a dissolved substance from a colloidal solution by means of diffusion through a suitable membrane (animal membrane (bladder) or parchment paper or cellophane sheet).
Properties of Colloidal Solutions
- Colligative properties
- Tyndall effect
- Colour
- Brownian movement
- Electrical Properties
Colligative properties
These are the properties which depend only on the number of solute (dispersed phase) particles but not on its nature.
The colligative properties are
1. Relative lowering of vapour pressure
2. Elevation in boiling point
3. Depression in freezing point
4. Osmotic pressure
Tyndall effect
Tyndall effect is observed only when the following two conditions are satisfied
- The diameter of the dispersed particles is not much smaller than the wavelength of the light used
- The refractive indices of the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium differ greatly in magnitude.
- The number of colloidal particles can be counted.
- To find average mass of particles

- The colour of colloidal solution depends on the wavelength of light scattered by the dispersed particles. The wavelength of light further depends on the size and nature of the particles.
- The colour of colloidal solution also changes with the manner in which the observer receives the light.
- For example, a mixture of milk and water appears blue when viewed by the reflected light and red when viewed by the transmitted light.
- Finest gold sol is red in colour as the size of particles increases, it appears purple, then blue and finally golden.
- The state of continuous zig-zag motion of particles.
- Depends on the size of the particles and viscosity of the solution.
- Smaller the size and lesser the viscosity, faster is the motion.
- The brownian movement has a stirring effect which does not permit the particles to settle and thus, is responsible for the stability of sols.
-
Stability of Colloids and Charge on colloidal particles
- Charge on colloidal particles: Due to preferential adsorption of ions from solution
- Charge on colloidal particles: Due to preferential adsorption of ions from solution
Zeta potential
This potential difference between the fixed layer and the diffused layer of opposite charges is called the electrokinetic potential or zeta potential.
Electrophoresis
The movement of colloidal particles under an applied electric potential is called electrophoresis.
Positively charged particles move towards the cathode while negatively charged particles move towards the anode.
Electroosmosis
Movement of particles of the dispersion medium begins to move in an electric field.
Coagulation or Flocculation or Precipitation
The process of settling of colloidal particles is called coagulation or precipitation of the sol
The ion responsible for neutralization of charge on the particles is called the coagulating ion.
A negative ion causes the precipitation of positively charged sol and vice versa
The coagulation of the lyophobic sols can be carried out in the following ways:
(i) By electrophoresis
(ii) By mixing two oppositely charged sols
(iii) By boiling
(iv) By persistent dialysis
(v) By addition of electrolytes
Coagulating value
The minimum concentration of an electrolyte in millimoles per litre required to cause precipitation of a sol in two hours is called coagulating value.
The smaller the quantity needed, the higher will be the coagulating power of an ion.
Protective colloids
A protective colloid is a lyophilic colloid that when present in small quantities keeps lyophobic colloids from precipitating under the coagulating action of electrolytes.
When a lyophilic sol is added to the lyophobic sol, the lyophilic particles form a layer around lyophobic particles and thus protect the latter from electrolytes.
Lyophilic colloids used for this purpose are called protective colloids.
Gold Number
The Gold Number is the minimum weight (in milligrams) of a protective colloid required to prevent the coagulation (colour change from Red to Violet) of 10 ml of a standard hydro gold sol when 1 ml of a 10% sodium chloride solution is added to it.
Emulsion
These are liquid-liquid colloidal systems, i.e., the dispersion of finely divided droplets in another liquid.
Stability of Emulsion
Emulsions of oil in water are unstable and sometimes they separate into two layers on standing.
For stabilisation of an emulsion, a third component called emulsifying agent is usually added.
The emulsifying agent forms an interfacial film between suspended particles and the medium.
The principal emulsifying agents for O/W emulsions are proteins, gums, natural and synthetic soaps and for W/O, heavy metal salts of fatty acids, long chain alcohols, lampblack
Colloids in our daily life
Blue colour of the sky
Fog, Mist and Rain
Food articles: Milk, Butter, Halwa, Ice Creams, Fruit Juices
Blood: Alum and Ferric Chloride solution used to coagulation of blood
Soils
Applications of colloids
1. Electrical precipitation of smoke
2. Purification of drinking water
3. Midicines:
a) Argyrol is a silver sol used as an eye lotion.
b) Colloidal antimony is used in curing kalaazar.
c) Colloidal gold is used for intramuscular injection
d) Milk of magnesia, an emulsion, is used for stomach disorders.
4. Tanning
5. Photographic plates and films: Photographic plates or films are prepared by coating an emulsion of the light sensitive silver bromide in gelatin over glass plates or celluloid films.
6. Rubber industry: Latex is a colloidal solution of rubber particles which are negatively charged. Rubber is obtained by coagulation of latex.
7. Industrial products: Paints, inks, synthetic plastics, rubber, graphite lubricants, cement, etc., are all colloidal solutions.