Tertiary Amine Uses || What is a Primary Secondary and Tertiary Amine?
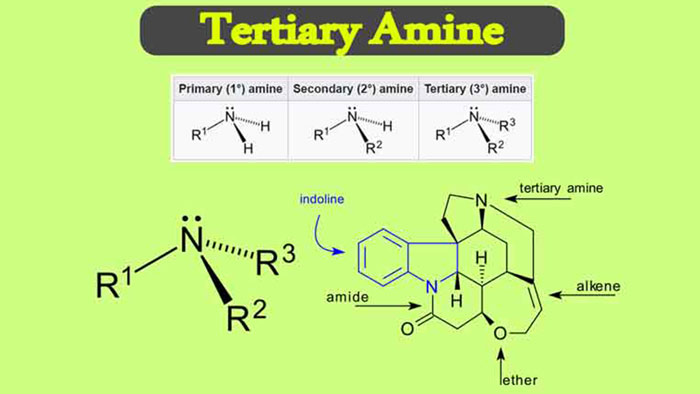
A tertiary amine refers to an amine having a trivalent group attached to three hydrocarbon groups in the molecule. Tertiary amines have a wide range of uses.
They can be used as components of formulated products and intermediate products of various specialized chemical derivatives. They are important raw materials for the production of quaternary ammonium salts.
Some Chemical compound we are using in this Post:-
- Potassium carbonate – K2CO3
- Methyl diethanolamine – CH3N(C2H4OH)2
- Triethanolamine – C6H15NO3
- Diethanolamine – C4H11NO2
- Monoethanolamine – C2H7NO
Carbon dioxide capture is one of the important ways to achieve carbon reduction. CO2 capture technology mainly includes the physical absorption method, the membrane separation method, the chemical absorption method, etc. Among them, the chemical solvent absorption method is the oldest and relatively mature and widely used decarbonization method.
The chemical absorption method is to take advantage of the acidic characteristics of CO2. It uses an alkaline solution for acid-base chemical reaction absorption and then realizes the regeneration of the solvent by means of a reverse reaction. Strong bases such as K2CO3, etc., although they can also be used as solvents and can be regenerated by heating, this solvent has severe corrosion on the system.
In the industrial chemical absorption method, an aqueous solution of organic alcohol amines is mainly used as an absorbent. A system consisting of an absorption tower and a regeneration tower is used to capture CO2.
Several alcohol amines commonly used in the industry are the primary amine MEA (monoethanolamine), the secondary amine DEA (diethanolamine), and the tertiary amine MDEA ( N -methyl diethanolamine) and TEA (triethanolamine).
Various amines have their own advantages and disadvantages in capturing CO2. Primary amines and secondary amines have fast absorption rates, but they tend to form relatively stable carbamates and have a low degree of regeneration. Tertiary amines have good regeneration performance, but their absorption rates are slow.
Which compound is a tertiary amine?
Mixed amine absorbent solution can make use of the advantages of single-component organic amines, make up for the shortcomings, and the composite absorbent with high efficiency and low consumption is the development trend of absorbent.
MEA is the earliest and most widely used absorbent for industrial production. Optimizing MEA absorbent is one of the current concerns. As far as absorbent performance is concerned, “efficient and low consumption” mainly refers to high absorption and low energy consumption (that is, high regeneration performance).
In view of the high regeneration performance of tertiary amines, which can make up for the shortcomings of MEA in this regard, mixed amine (MEA / tertiary amine) absorbents composed of MEA and tertiary amines have attracted widespread attention.
These studies have mainly focused on the mass transfer process of CO2 absorption (Kinetics). For the study of capture performance, the main research of tertiary amines is MDEA and TEA, and the research of other tertiary amines is less.
Experimental materials and methods
1 reagent
Chemical reagents used in experiments. Prepared with pure amine and distilled water: ① a single organic amine aqueous solution with a concentration of 2 mol/L, including MEA, DEAE, DMAE, and MDEA aqueous solutions; ② MEA/DEAE, MEA/DMAE, and MEA/MDEA mixed amines with a total concentration of 2 mol/L The molar ratio of MEA to tertiary amine in aqueous solution and mixed amine solution is 4: 1.
2 Experimental devices and methods
(1) Experimental device
The experimental apparatus for the absorption and regeneration of CO2 by the absorption liquid was measured. The thermostatic oil bath is composed of DF-101XP collector-type speed-measuring magnetic stirrer (Jintan Zhengji Instrument Co., Ltd.) and oil. 175-T2 digital thermometer (Testo Instrument Co., Ltd.) and D-600CD mass flow meter (Dongguan Dexin Electronic Technology Co., Ltd.) are controlled by computer. Temperature and flow data are collected every 2 s.
(2) Experimental method
Put the absorption bottle with 100 mL of absorption solution into a constant temperature oil bath, and set the stirring speed to 180 r/min. When the temperature of the absorption solution reaches 40°C, pure CO2 gas is passed into the absorption bottle. The inlet gas flow is set and controlled by a gas mass flow meter.
The experiment is 400mL / min. The CO2 flow at the outlet is recorded by the flowmeter. When it is close to the inlet flow, the experiment is stopped. At this time, it is the saturation absorption point for CO2 absorption. The absorption rate is integrated with the absorption time to obtain the absorption amount.
CO2 saturated rich solution was used for the regeneration experiment at 110 ℃. When the outlet flow rate was lower than 5 mL/min, the experiment was stopped.
Results and discussion
1 Organic monoamine absorption/regeneration
(1) Comparison of organic monoamine absorption
The relationship between CO2 absorption rate, adsorption amount, absorption temperature and absorption time of 2mol / L MEA, DEAE, DMAE, and MDEA aqueous solution.
The absorption rate and absorption of MEA are much higher than those of tertiary amines in about 8 minutes at the beginning of absorption. The order of MEA> DEAE> DMAE> MDEA is MEA, and the order of absorption rate and absorption of MEA and the tertiary amine is MEA <MDEA < DMAE <DEAE.
The change in temperature is a reflection of the degree of progress of the reaction. A large change in temperature indicates a large degree of reaction. The temperature increase in the reaction process of the MEA absorption solution is much larger than that of the tertiary amine, and the degree of reaction of MEA and CO2 is so large that the absorption rate is much larger than that of the tertiary amine.
Moreover, MEA has only one temperature peak (heat generation), which indicates that its absorption of CO2 is a chemical reaction that generates a more stable carbamate, and therefore the absorption rate is fast. H2O acts as a base to catalyze the reaction.
The absorption of CO2 by tertiary amines is composed of multiple absorption processes, and the degree of “reaction” in each absorption process is only slightly reduced, so the absorption rate is basically unchanged.
The pH of 2 mol / L MDEA, DMAE and DEAE absorbent was measured below 13.0. Studies have shown that for a tertiary amine solution with a pH value lower than 13.0. The absorption of CO2 mainly uses a pair of lone pairs of electrons of the N atom on the amine molecule to form a hydrogen bond between the free amine and water.
Enhancing the reaction between H2O and CO2 Activity, amine as a base catalyst to promote the hydration of CO2, the formation of unstable HCO3, so low heat, low degree of reaction, slow rate.
Because H2O is always sufficient in the absorption solution, the reaction continues until the tertiary amine is depleted, showing that the absorption rate of the tertiary amine has not changed much, that is, it exceeds the MEA in the later stage.
The maximum theoretical load of MEA for CO2 is 0.5 mol. CO2 / molMEA. The experimentally measured load of MEA is larger than the theoretical load.
This is because H2O not only catalyzes MEA, but also absorbs CO2 by itself, the maximum load of tertiary amine on CO2 is 1 mol CO2/mol tertiary amine, but the measured value less than this value, one of the reasons is that the absorption reaction rate is too slow and the reaction is not completely caused.
Although the absorption load of the tertiary amine is higher than that of MEA, the initial absorption rate is too low to be suitable as an industrial absorbent alone.
(2) Comparison of organic monoamine regeneration
The regeneration rate gradually increased first, then reached the highest value and then gradually decreased until the reaction was completed. It can be seen from the regeneration rate that tertiary amines are significantly higher than MEA. This is because regeneration is a reverse reaction of absorption. The salts formed by the absorption of CO2 by tertiary amines are unstable and easy to decompose.
Tertiary amines are completely regenerated in the shortest time, while MEA regeneration takes a long time and has the lowest regeneration level. The final regeneration amount is DEAE> DMAE> MDEA> MEA; the regeneration amount of tertiary amine is in the same order as the absorption amount, because when the same type of amine is absorbed and regenerated, the more the absorption amount, the larger the regeneration amount insufficient time.
The regeneration rate reflects the degree of regeneration. The order is different from the regeneration amount: MDEA> DEAE> DMAE> MEA. MDEA has become a research hotspot in recent years because of its high regeneration rate and regeneration rate.
2 MEA / tertiary amine mixed amine absorption and regeneration performance
(1) MEA/tertiary amine absorption performance
MEA/tertiary amine mixed amine absorption rate, the amount and temperature change during absorption. MEA / tertiary amine mixed solution has the absorption characteristics of MEA and a tertiary amine.
Since the chemical reaction rate between MEA and CO2 is higher than that of tertiary amines, the absorption rate of mixed amines in the initial stage of absorption is mainly determined by MEA, while the latter stage is mainly determined by the slower reaction rate of tertiary amines, as is the amount of absorption.
Therefore, the initial absorption rate MEA / tertiary amine <MEA, the latter is reversed. Since the degree of reaction of MEA with CO2 is much higher than that of tertiary amines, the temperature change of mixed amines is similar to that of MEA.
At the beginning of absorption, the absorption of MEA / tertiary amine at the same concentration is less than MEA, but it is higher than MEA in the later period.
The absorption of MEA / tertiary amine is greater than MEA. MEA / MDEA is the highest, which is MEA. 1.13 times. The experiment also found that monoamine DEAE and DMAE have obvious foaming phenomenon when they absorb CO2, their mixed amines with MEA also have low foaming properties, while the mixed amines of MEA and MDEA do not foam.
(2) MEA / tertiary amine regeneration performance
It can be seen from the regeneration of the mixed MEA / tertiary amine that the MEA / tertiary amine desorption rate is significantly higher than that of the single-component MEA, during the same desorption time, the desorption load MEA / MDEA> MEA / DMAE> MEA / DEAE> MEA, MEA / MDEA has better desorption effect.
The regeneration rate of the MEA/tertiary amine mixed system is much higher than that of the single-component MEA, which indicates that the energy consumption for the regeneration of the mixed amine is greatly reduced compared to the MEA.
3 Interaction between MEA and tertiary amine
Mixed amine absorbent liquids not only have the absorption characteristics of their constituent amines but also interact. Tertiary amines act as bases to catalyze the absorption of MEA, so there is an interaction between them. The interaction coefficient is calculated using an enhancement factor, which is complicated to calculate.
There is a strong interaction between MDEA and tertiary amines, that is, MEA and tertiary amines promote absorption, and the interaction between MEA and MDEA is the strongest. The interaction is also related to absorption time, which gradually increases and then decreases as absorption progresses.
During the regeneration process, the interaction of the mixed amine regeneration process is very different from that in the absorption process. The interaction decreases rapidly with the initial regeneration time and then increases. The synergy between MDEA and MEA is the strongest in both absorption and regeneration.
From the perspective of industrial application, to select a suitable absorption liquid, it is necessary to select a solvent that can absorb as much CO2 as possible in the initial stage of absorption and regeneration, and its regeneration rate and regeneration amount are sufficiently large.
MEA and tertiary amine meet the requirements of the former and the latter, respectively, and are not suitable for industrial applications when used alone. If it is mixed, the absorption and regeneration are both increased, but the absorption rate and initial absorption are low, which is not conducive to industrialization.
The regeneration synergy between MEA and the tertiary amine is strong, and the advantages of MEA absorption can be used, and the regeneration amount and regeneration rate can be improved. From the perspective of screened tertiary amines, MDEA can better optimize MEA.
Tertiary Amine Uses
(1) The absorption of CO2 by a single-component organic amine shows that MEA has a fast absorption rate, but regeneration is difficult, while tertiary amines have a low absorption rate and a long absorption saturation time, they have a high absorption capacity and are very easy to regenerate.
(2) The absorption amount and regeneration effect of the three MEA / tertiary amine mixed amines with MEA as the main absorption body are better than that of MEA, but the absorption rate is reduced.
(3) There are interactions between tertiary amines and MEA in the process of absorption and regeneration. The interactions are related to the types of tertiary amines and the absorption time, the synergy between MDEA and MEA is the strongest. MEA / MDEA has good absorption and regeneration performance and does not foam during the absorption process. It is a good decarburization absorbent.