Benzaldehyde Formula, Preparation, Properties, uses, and Tests
Benzaldehyde Preparation
Toluene: Benzaldehyde is obtained from oxidation of toluene by chromyl chloride CrO2Cl2. This reaction is called Etard’s Reaction.
C6H5CH3 + 2CrO2Cl2 → C6H5CH(OCrOHCl2)2 → C6H5CHO
Benzaldehyde is also obtained by oxidation of acidic solution of toluene’s manganese dioxide(MnO₂). In the presence of vanadium pentoxide(V₂O₅) at 350°C, oxidation of toluene by air oxygen also yields benzaldehyde.
Benzyl Chloride: benzyl chloride(C7H7Cl) gets benzaldehyde on heating with lead nitrate solution in the atmosphere of carbon dioxide gas.
2C6H5CH2Cl + Pb(NO3)2 → 2C6H5CHO + PbCl2 + 2HNO2
Preparation Method
To make benzaldehyde in the laboratory, take 10 grams of benzene chloride, 8 gram lead nitrate and about 50 ml of water in a round flask. Attaches a reflux condenser to the flask. CO2 gas flows into the flask. So that the atmosphere of CO2 remains in the flask.
Heats the flask for about 6 hours in this condition. The mixture is then cooled and extracted by ether. Benzaldehyde enters the ether layer. Separating the ether layer and adding a saturated solution of sodium bisulfite(NaHSO3) to it.
Benzoic acid to benzaldehyde
Preparation of Benzaldehyde.
<iframe width="834" height="469" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/xLe_bDnO18E" title="NCERT conversions part #3 || conversions in organic chemistry || aldehyde and ketones" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share" referrerpolicy="strict-origin-when-cross-origin" allowfullscreen></iframe>
Crystals of benzaldehyde sodium bisulfite are obtained. They are filtered and dried. Benzaldehyde is released upon heating these crystals with sulfuric acid. It is extracted by ether. Distill the ether solution and separate the ether. After benign distillation of the remaining fluid, pure benzaldehyde is obtained at 179°C.
Benzal Chloride: Benzaldehyde is obtained by reaction of benzal chloride(C7H6Cl2) with aqueous NaOH or KOH.
C6H5CHCl2 → C6H5CH(OH)2 → C6H5CHO
Benzene Alcohol: benzaldehyde can be obtained by oxidation of benzene alcohol by acidic potassium dichromate.
C6H5CH2OH + O → C6H5CHO + H2O
Benzaldehyde is also obtained when the vapors of benzene alcohol are precipitated at 300°C heated copper.
- Oxidation Number : How to find Oxidation State
- Bleaching Powder : Preparation, uses of Bleaching Powder
- Iodine : Properties, Preparation and uses
- Bromine – Preparation, Physical and Chemical Properties a Uses
- Chlorine Property : Physical and Chemical Properties | Uses
- Solar Energy : Light Waves, Reactions and Uses
- Chlorine Gas – Laboratory and Industrial Preparation
Benzoyl Chloride: benzaldehyde is obtained from rosenmund reduction of Benzoyl chloride.
C6H5COCl + H2 → C6H5CHO + HCl
Benzene: benzaldehyde is also obtained from benzene by gattermann koch aldehyde synthesis.
C6H6 + CO → C6H5CHO + HCl
Physical Properties
- Benzaldehyde is a colorless liquid. Its boiling point is 179°C.
- It smells like bitter almonds.
- It is less soluble in water and more soluble in alcohol and ether.
Reduction: The reduction of benzaldehyde by H2 and Ni, Na-Hg and water, Na-Hg and alcohol, LiAlH4 or NaBH4 gives benzene alcohol.
C6H5CHO + 2H → C6H5CH2OH
Toluene is formed when zinc mercury is reduced by amalgam and concentrated HCl. This reaction is called clemmensen reduction reaction.
C6H5CHO + 4H → C6H5CH3 + H2O
Addition of Hydrogen cyanide: Reaction with Hydrogen cyanide gives Benzaldehyde Cyanohydrin additive product.

Addition of sodium bisulfite: It reacts with sodium bisulfite(NaHSO3) to give a additive product[benzaldehyde sodium bisulfite(C7H7NaO4S)].
C6H5CHO + 4H → C6H5CH3 + H2O
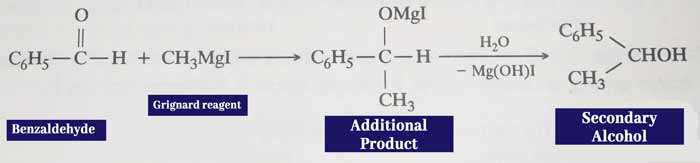
Reaction with grignard reagents: It reacts with grignard reagents to form additive which forms secondary alcohol upon water decomposition.
Example:
Reaction with hydraxyl amine: It reacts with hydraxyl amine to form oxime.
C6H5CHO + NH2OH → C6H5CH = NOH + H2O
Reaction with Hydrazine: It reacts with Hydrazine(N2H4) to form hydrazone. The reaction of benzaldehyde with phenylhydrazine and 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine test is similar.
C6H5CHO + NH2NH2 → C6H5CH = N – NH2 + H2O
Reaction with phosphorus penta chloride: The reaction of benzaldehyde from phosphorus penta chloride(PCl5) forms benzal chloride(C6H5CHCl2).
C6H5CHO + PCl5 → C6H5CHCl2 + POCl3
Oxidation: benzaldehyde is oxidized by acidic potassium dicromate, acidic potassium permagnate, nitric acid or tollens reagent. The oxidation of benzaldehyde gives benzoic acid.
C6H5CHO + O → C6H5COOH
C6H5CHO + Ag2O → C6H5COOH + 2Ag
It is not oxidized by the fahling solution.
Reaction with ammonia: It reacts with ammonia to form hydrobenzamide.
3C6H5CHO + 2NH3 → (C6H5CH = N)2CHC6H5 + 3H2O
Reaction with primary amines: benzaldehyde reacts with primary alifatic and aromatic amines to form imines with common names, also called schiffes bases.
Example:
C6H5CHO + C6H5NH2 → C6H5 – CH = N – C6H5 + H2O
Reaction with alcohols: In the presence of dry hydrogen chloride gas, it reacts with alcohols to form acetal.

Mixed aldol condensation: α–hydrogen atom is not present in benzaldehyde. Hence it does not exhibit aldol condensation.
This condensation forms aldehyde or ketone by reacting in the presence of dilute alkali with another α–hydrogen containing aldehyde or ketone. This reaction is called mixed aldol condensation. This reaction is also called claisen reaction or Claisen – Schmidt condensation.
- Importance of Biomolecules in Life || What are the 4 main biomolecules?
- Valency of Elements || How to Find Valency || What is the Valency of the atom?
- Resonance effect or mesomeric effect || What is resonance effect with example?
- Glucose Structure: Physical and chemical properties, Glucose Chemical Reaction
- Introduction of Inductive-Effect || How does Inductive Effect Work?
- IUPAC Name : How to find the IUPAC name of compounds.
- What is Urea || How to make Urea Fertilizer, || Urea uses
- Sodium Chloride Properties || Why Sodium Chloride is Soluble in Water
Cannizaro Reactions: a α–hydrogen is not present in benzaldehyde. Hence, it exhibits cannizaro reactions. By heating it with concentrated NaOH or KOH, benzene alcohol and sodium benzoate are obtained.
2 C6H5CHO + NaOH → C6H5CH2OH + C6H5COONa
Benzaldehyde Cannizzaro Reaction
Cannizzaro’s Reaction|| Reaction Mechanism || Internal and Cross Cannizzaro’s Reaction || ???? hydrogen
<iframe width="834" height="469" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/0CnwNQDa1IE" title="Cannizzaro’s Reaction|| Reaction Mechanism | Internal & Cross Cannizzaro’s Reaction | alpha hydrogen" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share" referrerpolicy="strict-origin-when-cross-origin" allowfullscreen></iframe>
Perkin reaction: Cinnamic acid is obtained by heating benzaldehyde with acetic anhydride and sodium acetate. This reaction is called perkin reaction.
C6H5CHO + (CH3CO)2O → C6H5CH = CHCOOH + CH3COOH
Benzoin condensation: Benzoaldehyde is obtained by reacting with an alcohol solution of NaCN or KCN. This reaction is called Benzoin condensation.
2 C6H5CHO → C6H5 – CH(OH) – CO – C6H5
Reaction with halogens: In the absence of catalyst, it reacts with chlorine to form benzoyl chloride.
C6H5CHO + Cl2 → C6H5COCl + HCl
It reacts with halogens in the presence of a halogen carrier to form a meta substitution product.

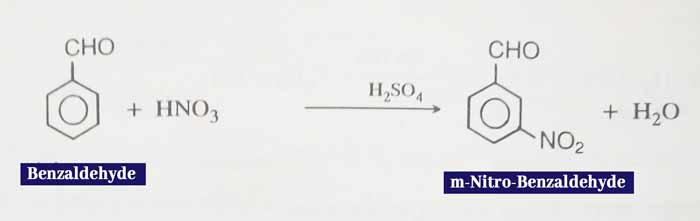
Nitration: This forms meta nitro benzaldehyde when heated with concentrated HNO3 and concentrated H2SO4.
Sulphonation: This meta benzaldehyde makes sulphonic acid when heated with gentle sulfuric acid.
 Benzaldehyde Uses
Benzaldehyde Uses
Benz aldehyde is used in the manufacture of aromatic substances, in the manufacture of dyes, and in the synthesis of other carbonic compounds.
Benzaldehyde Tests
- The smell of benzaldehyde is bitter almond-like.
- It gives the following general tests of the aldehyde group.
- schiffs test: pink color is obtained by adding schiffs reagent.
- tollens’ Tests: On heating it with ammonium silver nitrate solution ie tollens’ reagent, a silver mirror is obtained.
- It also gives positive results in 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine test and NaHSO3 test. But it does not give the test of fehling solution because It does not contain α-hydrogen.