Introduction of Inductive-Effect || How does Inductive Effect Work?
- 1: Introduction of the inductive effect
- 2: Types of inductive effect (+I and -I effect)
- 3: + I affecting groups
- 4: – I affecting groups
- 5: Application of inductive effect
The electrons of the covalent bond formed between two different atoms migrate to a more negative electrical atom. This type of displacement of electrons in molecules is called the inductive effect. This is a permanent effect.
The electrons of the covalent bond formed between similar atoms lie exactly in the middle of both atoms and the separation of charge in this type of molecule does not mean polarization.
· What is glycerol made of? Is glycerol a sugar?
· What is Chloroform Structure and Formula?
· IUPAC Name: How to find the IUPAC name of compounds.
· What is the use of methanol? Preparation and Properties
· How to make ethyl ether? Properties and Uses
· What does nitrous acid mean? Preparation and Properties
· What is sodium thiosulfate? Preparation and Properties
· What are the types of amines? Preparation and Properties
· How do you find the Valency of an element?
· Atomic Theory: What is the modern atomic theory?
· What is vitamin and its function? Vitamins in Chemistry
For example: In H2, CH3-CH3 and Cl2 molecules do not have a displacement of H-H, C-C, and Cl-Cl bond electrons. And the induction effect is not present in these molecules. In contrast, the electrons of the covalent bond formed between different atoms migrate to the more negative electric atom, and such molecules have polarisation and inductive effect present.

In CH3Cl, two electrons of the C – Cl bond are partially displaced towards the Cl atom. This causes a partial positive charge on the C atom and partial negative charge on the Cl atom.
Major symptoms of inductive effects
Inductive effects results in the only partial displacement of the electrons and electrons do not completely transfer from the octave of one atom to the octave of another atom. Partial displacement results in partial charge generation. Display partial positive charge from + σ and partial negative charge with – σ.
This effect is transmitted from one end to another in a series of carbon atoms. As the atoms that produce this effect keep away from it, the effect keeps on decreasing.
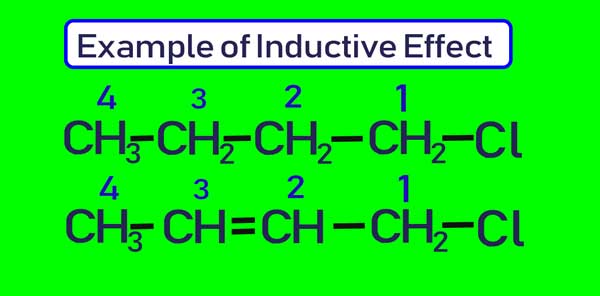
The polarity of the double and tri bond is less than that of the single bond. If two and three bonds are present in a series of carbon atoms, then this effect is transmitted to a greater extent in the chain.
The amount of partial positive charge present on C4 in the first compound above will be less than the amount of partial positive charge present on C4 in the second compound.
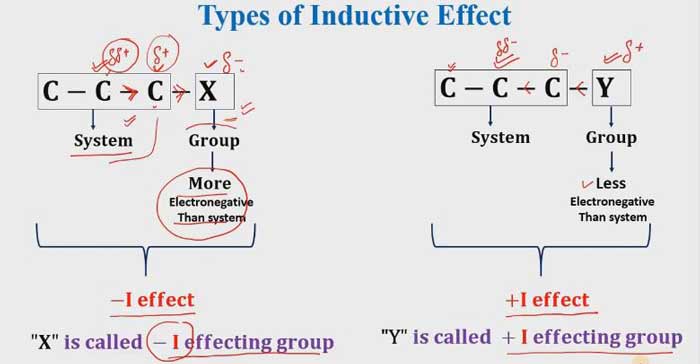
Let us denote the inductive effect from I. Groups in which the effect of this effect is higher in attractive to electrons than hydrogen. They are called the -I group. Groups that have lower attract to electrons than hydrogen. They are called + I groups.
Uses of Inductive Effect
The concept of inductive effect helps in clarifying the mechanism of many reactions and many other facts. With its help, the acid strength of acids and the power of the base can be compared.
What is I-effect?
Shifting of electrons in covalent bond from low electronegative atom to high electronegative atom.
Always sigma (σ) electrons are displaced (only occur in single bond)

It is a permanent effect
It is distance-dependent (decrease when the distance is an increase)
It is two types which depend on types of the group attached
- Iron Ores || Chemical Reaction and Preparation || Iron Deficiency
- Why Carbon Cycle is Important || How it Works
- Chlorine Gas Test || How Does Chlorine Reacts with Water
- Sodium Chloride Properties || Why Sodium Chloride is Soluble in Water
- Calcium Supplements || What Calcium is best for Bones
- Magnesium Benefits || Why Magnesium is so Good for You and Properties
Types of I-Effect
If Electron withdrawing groups that means it is a -I effecting group. and if the electron is donating groups that mean it is a + I effecting group.
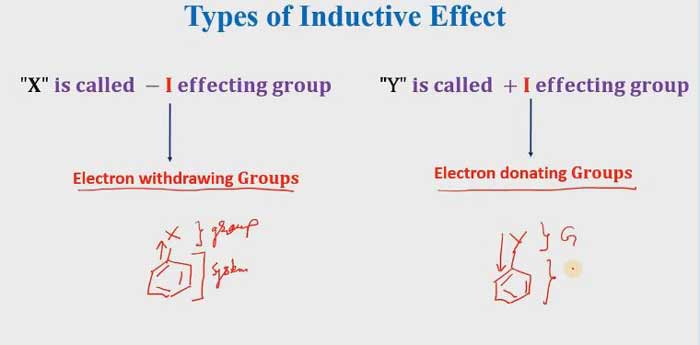
Application of Inductive Effect
- Stability of carbocation
- Stability of carbanion
- Stability of free radicals
- The acidity of carboxylic acid
- Basicity of amines
What is glycerol made of? Is glycerol a sugar? What is Chloroform Structure and Formula? IUPAC Name: How to find the IUPAC name of compounds. What is the use of methanol? Preparation and Properties
How to make ethyl ether? Properties and Uses What is ethyl ether used for? Preparation and Properties What are the uses of ammonia gas? Preparation What is the formula for stannous chloride? What are the physical properties of phosphine? What does nitrous acid mean? Preparation and Properties What is sodium thiosulfate? Preparation and Properties What are the types of amines? Preparation and Properties
How do you find the Valency of an element? Atomic Theory: What is the modern atomic theory? What is vitamin and its function? Vitamins in Chemistry How are alkanes named? What is alkane formula?
