What is Benzenesulfonic Acid used for? Preparation, Properties, and uses
Benzenesulfonic acid Preparation
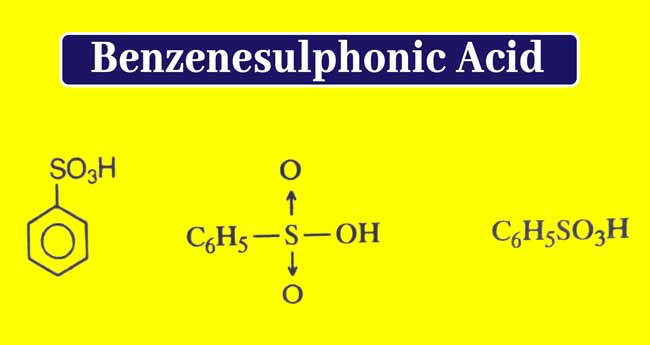
Benzenesulfonic acid is obtained from sulphonation of benzene. For this, benzene is heated with concentrated Sulfuric acid.
C6H6 + H2SO4(concentrated) → C6H5SO3H + H2O
Laboratory Method
To make Benzenesulfonic acid in the laboratory, take a mixture of one part banzene and two parts concentrated sulfuric acid in a round bottom flask. Attaches a reflux condenser to the flask. Heat the flask at 80 -100°C for about two hours by placing it on a water heater.
After this, the mixture is cooled and put in water. It contains barium carbonate. Unused sulfuric acid precipitates as barium sulfate. Filter it and separate it. Berium salt of Benzenesulfonic acid is filtered due to dissolution in water.
- What is Benzenesulfonic Acid used for? Preparation, Properties, and uses
- What is aniline used for? Preparation, Properties, and Tests
- How do you make Nitrobenzene? | Properties, Tests, and uses
- What is the formula of Chlorobenzene? Preparation, Properties and uses
- NEET 2021 / JEE 2021 Crash Course for Chemistry Subject
- What do you mean by Benzene? Preparation and Properties
- Why are aromatic compounds called aromatic? | Definition, Properties
- What is toluene used for? Preparation and Properties
On cooling after filtration, the cristal of Benzenesulfonic acid’s berium salt is obtained, separating these crystals and adding appropriate amounts of sulphuric acid. Berium sulfate precipitates and Benzenesulfonic acid is released.
The precipitates of berium sulfate are filtered and separated. Water containing crystals of Benzenesulfonic acid are obtained after cooling the filtrate. Anhydrous Benzenesulphonic(C6H5SO3H.3/2H2O) Acid is obtained after being isolated and heated.
Physical Properties
It is a colorless crystal solid. Its melting point is 65°C. Its water-containing crystals have a melting point of 47°C. It is more soluble in water.

Chemical Properties
Its chemical reactions can be divided into three parts.
- Reactions in which the -OH group of the -SO3H group participates.
- Reactions in which the –SO3H group is displaced.
- Replacement reactions of nuclei
Reactions in which the -OH group of the -SO3H group participates.
Acidic symptoms: It is an acid. Its aqueous solution is strongly acidic. The acid strength of its aqueous solution is as high as sulphuric acid. It reacts with bases to form salts.
example:
C6H5SO3H + NaOH → C6H5SO3Na + H2O
Reaction with Phosphorus pentachloride: In the reaction of Benzenesulfonic acid and phosphorus pentachloride, the -OH group of -SO3H group is displaced by the chlorine atom.
C6H5SO3H + PCl5 → C6H5SO2Cl + POCl3 + HCl
Reaction with alcohols: Like other acids it reacts with alcohols to form ester.
C6H5SO3H + C2H5OH → C6H5 – SO2 –O – C2H5 + H2O
Reactions in which the –SO3H group is displaced.
Displacement by hydrogen atom: On decomposition of benzene sulphonic acid with superheated steam or heating with dilute HCl or dilute H2SO4, its water decomposition occurs and benzene is obtained.
C6H5SO3H + H2O → C6H6 + H2SO4
Displacement by Hydroxyl Group: Phenol is obtained by melting its sodium or potassium salts with solid NaOH or KOH.
C6H5SO3Na + NaOH → C6H5OH + Na2SO3
Displacement by amines group: Aniline is obtained by melting its sodium or potassium salts with NaNH2 or KNH2.
C6H5SO3Na + NaNH2 → C6H5NH2 + Na2SO3
Displacement by cyano group: Cyano benzene is obtained by melting its sodium or potassium salts with NaCN.
C6H5SO3Na + NaCN → C6H5CN + Na2SO3
Displacement by carboxyle group: Its sodium or potassium salts are smelted with sodium phomate to obtain benzoic acid.
C6H5SO3Na + HCOONa → C6H5COOH + Na2SO3
Displacement by -SN group: thaophenol is obtained by melting its sodium or potassium salts with KSH.
C6H5SO3K + KSH → C6H5SH + K2SO3
Replacement reactions of nuclei
The sulphonic acid group is a meta director group. Hence meta products are obtained from its halogenation, nitration and sulphonation. Like all other meta director groups, it is also a deactivating group. This implies that its substitution reactions occur at a lower intensity than benzene. Following are its major nuclear substitution reactions.
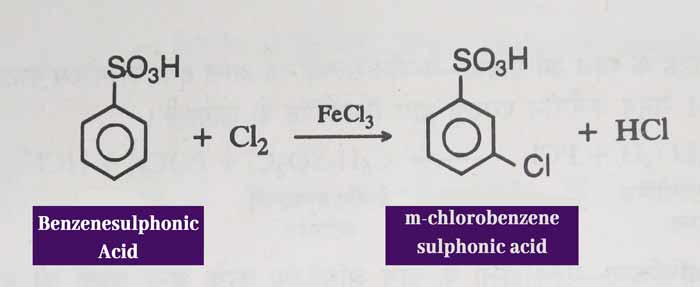
Halogenation: When replicated with chlorine in the presence of halogen carrier, it forms meta chlorobenzene sulphonic acid.
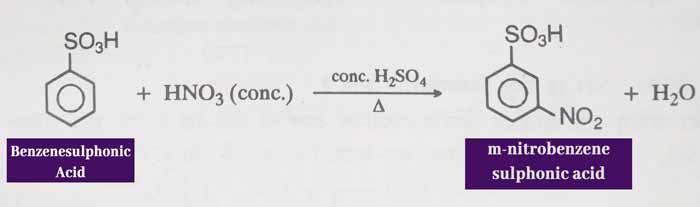
Nitration: When heated with a mixture of concentrated NHO3 and concentrated H2SO4, it forms m nitrobenzene sulphonic acid.
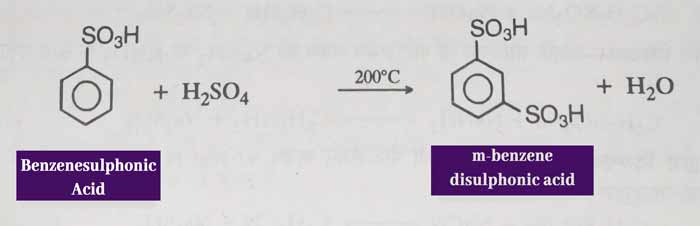
sulphonation: when heated at 200°C with gentle sulphuric acid, it forms meta benzene di sulphonic acid.
Benzenesulfonic acid Uses
- In the manufacture of dyes
- Sulpha drugs are prominent in the manufacture of drugs.
- In manufacture of saccharine
- In the manufacture of detergents