How to compose Cement? Cement Uses.
Cement Composition: It is heavy and very fine powder in gray color. When mixed with water and sand, it forms a compact paste. Which slowly hardens like a Portland stone. For this reason, it is also called Portland cement.
Portland cement was discovered in 1824 by Joseph Seldin, a resident of Leeds in England. It is a very useful material and it is used in making buildings, bridges, etc.
What is cement made of?
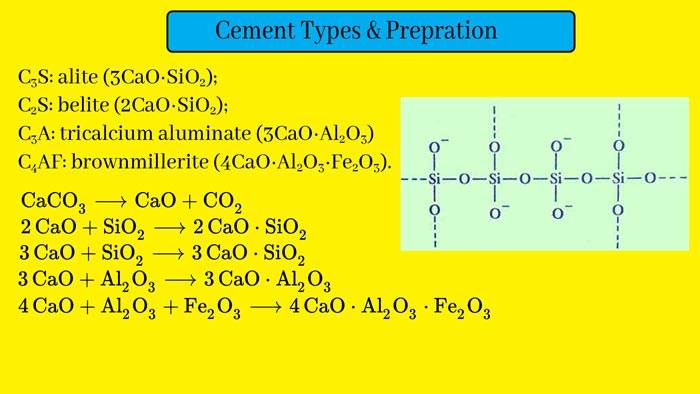
Cement is the main mixture of calcium silicones and aluminates. Its composition depends on the raw materials and method of making it. Its organization is almost as follows.
- Calcium Oxide: – 50-60%
- Silica – 20-25%
- Alumina – 5-10%
- Magnesium oxide – 2-3%
- Ferric oxide – 1-2%
- Sulfur trioxide – 0-1%
- Gypsum – 2-5%
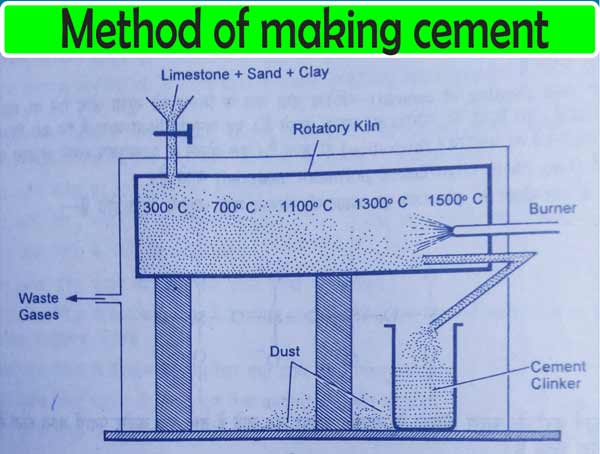
To make cement, each stone is grinding separately by taking suitable quantities of sand and smooth clay.

These are then mixed and heated to about 1500°C in a revolving furnace. On doing this, calcium silicates and aluminates are formed. And gases like carbon dioxide, water vapor, etc., come out of the furnace. The green and gray granular material obtained in this way are called cement clinker.
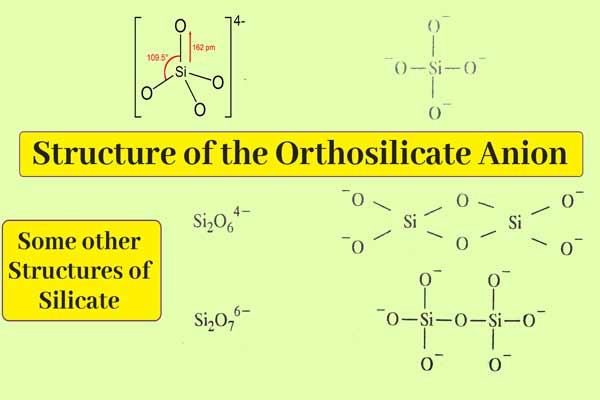
The structure of silicates depends on the following structural unit.
On this basis, the following are the lists of Si2O64-, Si2O76- and Si3O96-.
The cement clinker is cooled and grinded the mixture by mixing 2 to 5% of gypsum. Thus Portland cement is obtained.
By adding gypsum to the cement clinker, it controls the freezing time of the cement and water mixture.
The setting of cement
After leaving the mixture of cement and water open, it slowly forms a hard substance. This action is called the setting of cement. This estimate is made. That in this action, the hydration of calcium silicates and laminates occurs. Water addition results in the formation of polymers with a long chain and hybrid joints.
Such structure polymers are obtained as a result of the water addition of silicates.
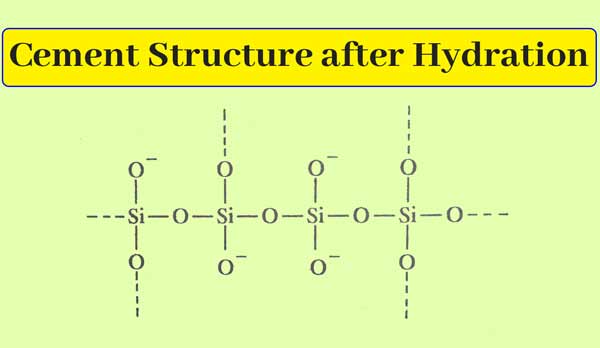
Due to the formation of polymer material, cement components are interconnected. And a hard substance is obtained. Which is called cement freezing.
Calcium silicates and aluminates are fast freezing substances. On adding
water in the presence of gypsum, the hydrated substances combine with
gypsum to form other substances which do not freeze quickly.
Cement Properties :-
Chemical Composition:
Primarily composed of calcium, silicon, aluminum, and iron.
Physical State: Powder
form
Color: Grayish-white
Odor: Odorless
Particle Size: Finely
ground, typically with a particle size distribution ranging from a few
micrometers to several tens of micrometers.
Setting Time: The time
it takes for the cement to harden after mixing with water; typically initial
set occurs within 30 minutes to a few hours, while final set occurs within a
few hours to several hours depending on the specific formulation and
conditions.
Strength Development:
Continues to gain strength over time through a process called hydration, where
water reacts chemically with the cement compounds to form hydration products
like calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) gel and calcium hydroxide.
Compressive Strength:
Measures the ability of the cement to withstand axial loading; typically
increases with time, reaching its peak after several days to weeks depending on
curing conditions.
Tensile Strength:
Measures the ability of the cement to resist pulling forces; generally lower
than compressive strength.
Flexural Strength:
Measures the ability of the cement to resist bending forces; influenced by
factors such as water-cement ratio, aggregate properties, and curing
conditions.
Density: Typically
ranges from 3.1 to 3.6 g/cm³ depending on the specific composition and density
of the materials used.
Shrinkage: During the
setting and hardening process, cement undergoes shrinkage due to the loss of
water; excessive shrinkage can lead to cracking and durability issues.
Porosity: Cement paste
contains pores of various sizes, which can affect properties such as
permeability and durability.
Durability: Influenced
by factors such as water-cement ratio, curing conditions, environmental
exposure, and the presence of additives or admixtures.
Chemical Resistance:
Ability to resist degradation when exposed to aggressive chemical environments,
such as acidic or alkaline solutions.
Workability: Ease of
handling and placing the cement paste or concrete mixture; influenced by
factors such as water content, consistency, and the use of additives or
admixtures.
These properties
collectively determine the performance and suitability of cement for various
construction applications, including concrete production, mortar, grout, and
other cement-based materials.