Exploring Electric Charges and Fields: Fundamentals of Electrostatics for Class 12
Charge: Electric charge(Electric Charges and Fields) is an intrinsic property of elementary particles of matter which gives rise to electric force between various objects.
Quantization: Charge is always in the form of an integral multiple of electronic charge and never its fraction.
q = ±ne
Where n is an integer and e = 1.6 × 10–19 C.
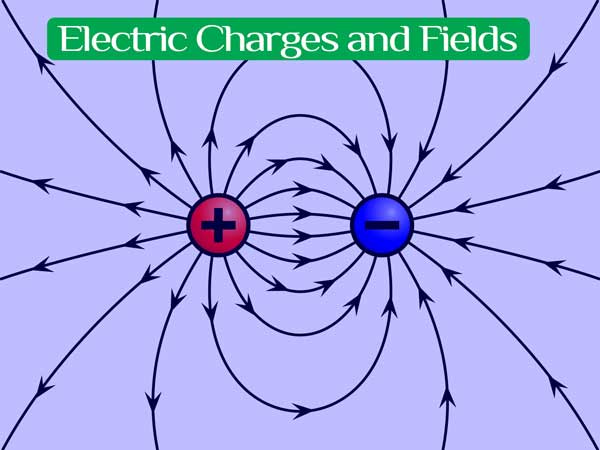
Electric charges are fundamental to understanding electric fields, which are integral to various phenomena in physics and electrical engineering. Here's an overview of key concepts related to electric charges and fields:
Electric Charge
- Definition: Electric charge is a basic property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electric field. The unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C).
- Types of Charge: There are two types of electric charges - positive and negative. Like charges repel each other, while unlike charges attract.
- Quantization of Charge: The charge on an electron is coulombs, while that on a proton is coulombs. This is the smallest unit of charge, and all charges are quantized as integer multiples of this elementary charge.
- Conservation of Charge: In any closed system, the total charge is conserved, meaning that charge cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred.
Electric Field
- Definition: An electric field is a region around a charged object where a force is exerted on other charges. It's a vector field, with both magnitude and direction.
- Electric Field Lines: These lines represent the direction of the electric field. They point away from positive charges and towards negative charges, never crossing one another.
- Strength of Electric Field: The electric field (E) is defined as the force (F) experienced by a small test charge (q) placed in the field, such that . It is measured in newtons per coulomb (N/C).
- Coulomb's Law: This law describes the force between two point charges. The magnitude of the force is given by , where , and are the charges, and is the distance between them.
Applications of Electric Fields
- Electric Field in Conductors: Inside a conductor in electrostatic equilibrium, the electric field is zero. This property is used in shielding sensitive electronics.
- Capacitors: These are devices designed to store electric charge and energy in an electric field between two conductive plates.
- Electric Field in Dielectrics: Dielectrics are insulating materials that can become polarized in an electric field, affecting the field's behavior and strength.
Further Considerations
- Electric Potential and Voltage: Electric potential, or voltage, is the work done to move a charge in an electric field. It is related to the electric field by the gradient .
- Gauss's Law: This law relates the electric field to the charge enclosed by a surface, providing a tool for calculating electric fields in symmetric situations.
- Electrostatic Induction: This occurs when a conductor is placed near a charged object, causing a redistribution of charges within the conductor without direct contact.
These concepts form the basis of a vast range of topics in electricity and electromagnetism. If you have specific questions or need more details on a particular topic, feel free to ask.
