Understanding Electromagnetic Waves: Types, Properties, and Applications Explained
Displacement Current: The current which comes into play in the region, wherever the electric field and hence the electric flux is changing with time.
Electromagnetic waves are a fundamental concept in physics, describing
the waves of the electromagnetic field, which propagate through space and
interact with matter. These waves are all around us, encompassing a broad range
of frequencies and wavelengths. This article delves into the types, properties,
and applications of electromagnetic waves, helping you understand their
significance in everyday life.
Ampere’s circuital law for conduction current during the charging of a capacitor was found inconsistent. Therefore, Maxwell modified Ampere’s circuital law.
Types of Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves are commonly categorized into seven types based on
their frequency and wavelength:
Radio Waves: These have the longest wavelengths and the lowest
frequencies. They're used for communication, broadcasting, and radar systems.
Microwaves: Shorter than radio waves, microwaves are used in microwave
ovens, satellite communications, and some forms of radar.
Infrared Waves: With wavelengths longer than visible light, infrared
waves are associated with heat. They're used in thermal imaging, remote
controls, and night-vision devices.
Visible Light: This is the narrow band of the spectrum that human eyes
can detect, encompassing all the colors of the rainbow, from red to violet.
Ultraviolet (UV) Light: UV waves have shorter wavelengths than visible
light. They're responsible for sunburns and are used in sterilization and black
lights.
X-rays: These have even shorter wavelengths and are widely used in
medical imaging and security scanners.
Gamma Rays: With the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies, gamma rays are extremely energetic and are used in cancer treatment and astrophysical studies.
Maxwell’s equations: The basic principle of electromagnetism can be formulated in terms of four fundamental equations known as Maxwell’s equations.
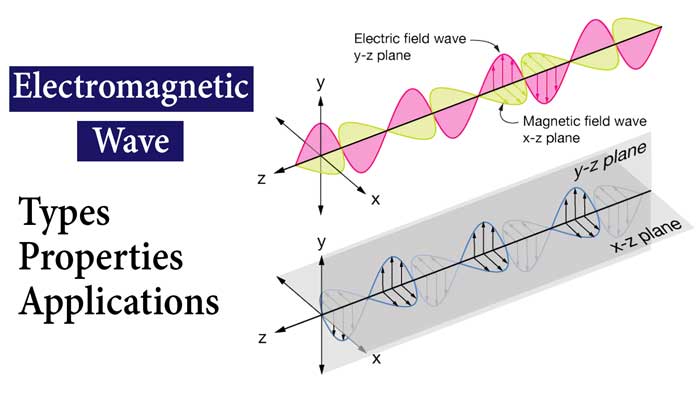
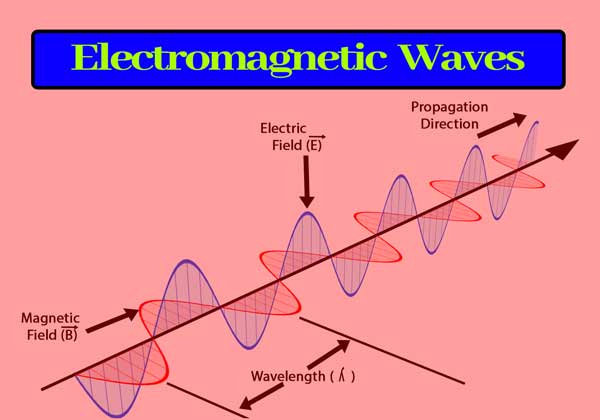
Electromagnetic waves: E.M. waves are those waves in which there is a sinusoidal variation of the electric and magnetic fields at right angles to each other as well as at right angles to the direction of wave propagation.
In an electromagnetic wave, the electric and magnetic fields vary with space and time and have the same frequency and are in the same phase.
Properties
Electromagnetic waves share some common properties:
Speed of Light: All electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light
in a vacuum, approximately 299,792,458 meters per second.
Transverse Nature: Electromagnetic waves are transverse, meaning the
electric and magnetic fields oscillate perpendicular to the direction of wave
propagation.
No Medium Required: Unlike mechanical waves, electromagnetic waves can
travel through a vacuum without a medium.
Energy and Frequency: The energy of an electromagnetic wave is
proportional to its frequency; higher frequency waves carry more energy.
– These waves do not carry any charge.
– These waves are not deflected by electric and magnetic fields.
– They travel with the speed of light c (= 3 × 108 ms–1) in a vacuum.
– The frequency of electromagnetic waves does not change when it goes from one medium to another but its wavelength changes.
– These waves are transverse in nature, hence they can be polarised.
Production
– Maxwell showed that an electric charge oscillating harmonically with frequency u produces electromagnetic waves of the same frequency.
– An electric dipole is a basic source of electromagnetic waves.
The Energy Density
– Electromagnetic waves carry energy as they travel through space and this energy is equally shared by an electric field and magnetic field of electromagnetic waves.
Electromagnetic spectrum: The orderly distribution of electromagnetic radiations according to their wavelength or frequency is known as the electromagnetic spectrum.
Applications of Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves have a vast array of applications in science,
technology, and everyday life:
Communication: Radio waves and microwaves are used for television, radio
broadcasting, cell phones, and Wi-Fi.
Medical Imaging: X-rays and gamma rays are crucial in medical
diagnostics and cancer treatment.
Astronomy: Electromagnetic waves are used to study distant celestial
bodies in radio astronomy, optical astronomy, and X-ray astronomy.
Consumer Electronics: Infrared waves are used in remote controls, while
visible light is used in displays and lighting.
Security and Detection: Various electromagnetic waves are used in
security scanners and radar systems.
Understanding electromagnetic waves is crucial to appreciating the technology
and science that power our modern world. These waves play a vital role in
communications, medicine, and various other fields, with ongoing research
expanding their potential applications.