Ethyl Alcohol: Are ethyl alcohol and ethanol the same?
Ethyl Alcohol : It is the second member of the alcohol category. It is an important member of this category. It is also known as alcohol only. Its name is methyl carbinol in the carbinol method.
In nature, it is found in the aromatic oils and fruits as an ester. It is used as a spirit in many processes in industries and laboratories.
The main ingredient of spirit is ethyl alcohol. The rectified spirit contains about 95% ethyl alcohol and 5% water. Methyl alcohol or any other toxic substance is added to the rectified spirit to make denatured spirit.
Ethyl alcohol is often made from starch-containing grains, so in trade it is also called grain alcohol.
Preparation of Ethyl Alcohol
From Alkyl Halide: Mono hydric alcohols can be obtained by water decomposition of alkhyl hylides by aqueous alkali or liquid oxide silver.
RX + KOH(Liquid) → R-OH + KX
RX + AgOH → R-OH + AgX
C2H5Br + KOH(liquid) → C2H5OH + KBr
By the action of nitrous acid on primary amino: Alcohol is obtained by the action of nitrous acid on primary amines.
R – NH2 + HNO2 → R – OH + N2 + H2O
C2H5NH2 + HNO2 → C2H5OH + N2 + H2O
Nitrous acid is a temporary acid. It is made by the action of sodium nitrite and hydrocloric acid. In order to react with a compound of nitrous acid, this additive is reacted with NaNO2 and HCl.
Industrial Preparation of Ethyl Alcohol
The following are the major methods of industrial manufacture of ethyl alcohol.
Ethylene(C2H4)
The ethylene obtained from the bleaching of petroleum is absorbed in concentrated sulfuric acid at 15 – 30 atmospheric pressure and 75°-80°C temperature. Ethyl hydrogen sulfate is obtained as a result. By boiling it with water, this water decomposes and ethanol is formed.
C2H4 + H2SO4 → C2H5HSO4
C2H5HSO4 + HOH → C2H5OH + H2SO4
Acetylene(C2H2)
Acetylene gas is obtained by the reaction of calcium carbide and water. Acetaldehyde is formed by flow of this gas in sulfuric acid solution in the presence of mercuric sulfate at 60°C heat, and the vapors of acetaldehyde combine with hydrogen at Nikhil powder at 100°-140°C temperature. By doing this, it is reduced and alcohol is obtained.
CaC2 + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + C2H2
C2H2 + H2O → CH3CHO
CH3CHO + H2 → CH3CH2OH
Fermentation
In ancient times ethyl alcohol was made only by this method. Even in modern times, the industrial manufacture of ethyl alcohol is mainly done by this method.
Commercial quantities of ethyl alcohol are produced from fermentation of sugars such as sugarcane juice, glucose molasses, fruit juices etc. or fermentation of starchy substances like barley, rice, corn etc.
The following reactions occur in the fermentation of sugars.
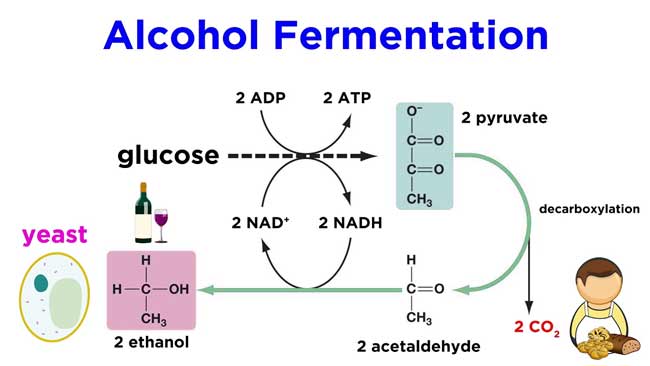
C12H22O11 + H2O → C6H12O6 + C6H12O6
C6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
The following reactions occur in the fermentation of starchy substances.
2(C6H10O5)n + nH2O → nC12H22O11
C12H22O11 + H2O → 2H6H12O6
H6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
Physical Properties of Ethyl Alcohol
It is a colorless and sweet smelling liquid. Its taste is pungent. Its boiling point is 78°C. It burns with a light blue flame in the air. It is miscible in water and organic solvents.
Chemical Properties of Ethyl Alcohol
Action from alkali metals: Sodium or potassium metal forms alkoxide by introducing hydrogen atom from -OH group of alcohols.
2ROH + 2Na → 2RONa + H2
2C2H5OH + 2Na → 2C2H5ONa + H2
Carboxylic acid action: Alcohol reacts with carboxylic acid to make ester. This reaction is called esterification. In this reaction, cation of hydrogen (H+) acts as a catalyst and this reaction is reversible. To prevent backward reaction, concentrated anhydrous agents such as H2SO4 or dry HCl are used.
Reaction with Acetyl Chloride or Acetic Anhydride: As a result of the action of alcohols with acetyl chloride, the hydrogen atom of the -OH group of alcohols is displaced by the acetyl group(- COCH3). This reaction is called Acetylation.
CH3COCl + C2H5OH → CH3COOC2H5 + HCl
Alcohols have a similar action with Acetic Anhydride in the presence of sodium acetate.
(CH3CO)2O + C2H5OH → CH3COOC2H5 + CH3COOH
- Valency of Elements || How to Find Valency || What is the Valency of the atom?
- Resonance effect or mesomeric effect || What is resonance effect with example?
- Importance of Biomolecules in Life || What are the 4 main biomolecules?
- Introduction of Inductive-Effect || How does Inductive Effect Work?
- Sodium Chloride Properties || Why Sodium Chloride is Soluble in Water
- Glucose Structure: Physical and chemical properties, Glucose Chemical Reaction
- DDT full Form || What was DDT used for? || Is DDT harmful to humans?
- Reproduction in Organisms
Action from ammonia: Alcohol, when heated at high pressure in the presence of zinc chloride, copper chromite or alumina, reacts with ammonia to form primary amine.
C2H5OH + NH3 → C2H5NH2 + H2O
If alcohol is taken in excess, then secondary and tertairy amine are also obtained.
C2H5OH + C2H5NH2 → (C2H5)2NH + H2O
C2H5OH + (C2H5)2NH → (C2H5)3N + H2O
Halogen acids: The alcoholic group is displaced by the halogen atom as a result of the action of alcohols with halogen acids. This reaction with concentrated HCl occurs in the presence of anhydrous zinc chloride.
R – OH + HCl → R – Cl + H2O
C2H5OH + HCl → C2H5Cl + H2O
This reaction with hydro bromic acid is carried out in the presence of concentrated H2SO4.
R – OH + HBr → R – Br + H2O
C2H5OH + HBr → C2H5Br + H2O
This reaction takes place with hydroIodic acid and the alcohol is refluxed with hydroIodic acid to conduct the reaction in advance.
C2H5OH + HI → C2H5I + H2O
They finally form elkene when heated with concentrated hydroIodic acid and red phosphorus.
C2H5I + HI → C2H6 + I2
Phosphorus halides: The alcoholic group is displaced by the helogen atom as a result of the action of the alcohols with phosphorus halides.
C2H5OH + PCl5 → C2H5Cl + POCl3 + HCl
3C2H5OH + PCl3 → 3C2H5Cl + H3PO3
Alcohols have the same action with thionyl chloride(SOCl2). These compounds are formed in the flask itself to react with the phosphorus tri bromide and phosphorus tri iodide of the alcohols. For this, bromine or iodine is added to the mixture of phosphorus and alcohol.
Reaction with sulphuric Acid: Alcohol reacts with concentrated sulfuric acid to produce different products at different temperatures.
Ethyl alcohol and concentrated sulfuric acid react at ordinary temperature and form ethyl hydrogen sulfate. The reaction takes place easily when the temperature increases, that is, the reaction speed increases.
C2H5OH + H2SO4 → C2H5HSO4 + H2O
Distillation of ethyl hydrogen sulfate at low pressure makes it ethyl sulfate.
2C2H5HSO4 → (C2H5)2SO4 + H2SO4
When ethyl hydrogen sulfate is distilled with water, it decomposes to form ethyl alcohol.
C2H5HSO4 + H2O → C2H5OH + H2SO4
A mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid in excess of ethyl alcohol and heating the mixture at 140°C gives diethyl ether. Diethyl ether is also obtained by heating the homogeneous mixture of ethyl alcohol and ethyl hydrogen sulfate at 140°C.
C2H5OH + H2SO4 → C2H5HSO4 + H2O
C2H5OH + C2H5HSO4 → C2H5-O-C2H5 + H2SO4
By heating ethyl alcohol to 160-170°C with concentrated H2SO4 it forms ethylene.
C2H5OH + H2SO4 → C2H5HSO4 + H2O
C2H5HSO4 → C2H4 + H2O
Reactions in which the alkyle group participates.
Dehydration: The dehydration of alcohols can also be done by passing their vapor over heated alumina. By passing ethyl alcohol vapors onto heated alumina, diethyl ether at 250 temperature and ethylene at 360° temperature are obtained.
2C2H5OH → C2H5 – O – C2H5 + H2O
C2H5OH → C2H4 + H2O
Chlorine action: Alcohols are first oxidized as a result of their reaction with chlorine. And aldehyde or ketones are made. This is followed by chlorination of aldehyde or alkyl radical of ketones.
C2H5OH + Cl2 → CH3CHO + 2HCl
CH3CHO + 3Cl2 → CCl3CHO + 3HCl
- Ethyl Alcohol: Are ethyl alcohol and ethanol the same?
- Methanol(CH3OH): Properties, Preparation, uses and Tests
- IUPAC Name : How to find the IUPAC name of compounds.
- Molarity Formula : What is Molarity and Normality with Solved Examples?
- Glass Material | Composition, Types of Glass, How to make colored glass?
- Ionisation Potential : What are the factors that decide the ionisation potential?
- Fertilizers Chemistry : Types of Fertilizers used in agriculture
- Electric Potential Energy: Definition, Formula and Example | Electrode and Electrode Potential
1) Ethanol is used as a solvent for many organic materials.
2) 100% pure ethyl alcohol is called absolute alcohol. 95.5% aqueous solution of ethyl alcohol is called rectified spirit. Rectified spirit is used in the manufacture of tincture ether chloroform dyes aromatic substances and many other substances. Absolute alcohol and rectified spirit are also used as surrogates in the laboratory. The fluid obtained by mixing methanol coatchoucine, peridin or any other toxic substance in rectified spirit is called denatured spirit.
3) Since rectified spirit can be used for drinking as a narcotic, denatured spirit is used as much as possible in place of rectified spirit in laboratory and industries to prevent its misuse.
4) Ethanol or rectified spirit is also used to make power alcohol. Power alcohol contains about 20 – 25% ethyl alcohol, 70 – 75% petrol, ether, tetralin etc. It can be used as a fuel in place of patrol in the engine.
5) It is also used in preservation of biological specimens.
6) Ethyl alcohol is also used for drinking as a narcotic. The drugs in which ethyl alcohol is present are of two types – (i) spirit (ii) wine.
7) If the alcoholic beverage is distilled, it is called spirit. If the alcoholic beverage is undispilled, it is called alcohol. Alcoholic beverages mainly contain 3 to 40% ethyl alcohol and the remaining water. Proof spirit contains 49.3% ethyl alcohol by weight. x° proof spirit has x% proof spirit.
