Hard Water and Soft Water : Permutit and Anion Exchange Resins
Hard Water and Soft Water
On rubbing soap with water, it is seen that sometimes it soapsuds Seasily, sometimes with difficulty. Due to this property, water is divided into two classes –
Soft water: The water which gives more and faster lather with soap is called soft water. Bicarbonate, chloride or sulphate salts of calcium and magnesium are not soluble in soft water. So soft water produces enough lather with soap.
Hard water: Water obtained from natural sources such as rivers, ponds, lakes, wells, etc., sometimes does not produce lather with soap. This is due to the hardness of water.
Therefore, the water which produces little or no lather with soap but forms a clump of insoluble, is called hard water. Many salts like calcium and magnesium of chloride, sulphate, bicarbonate etc. are soluble in it. Due to whose presence the water becomes hard.
These salts present in the water form insoluble calcium and magnesium salts, due to which hard water does not produce foam.
Example: sodium stearate is the salt (soap) of a higher fatty acid (stearic acid). It reacts with calcium and magnesium salts present in hard water to form insoluble salts. Due to which the soap does not make foam.
2C17H35COONa + CaCl2 → (C17H35COO)2Ca + 2NaCl
2C17H35COONa + MgCl2 → (C17H35COO)2Mg + 2NaCl
These salts present in the water form insoluble calcium and magnesium salts, due to which hard water does not produce foam.
Example: sodium stearate is the salt (soap) of a higher fatty acid (stearic acid). It reacts with calcium and magnesium salts present in hard water to form insoluble salts. Due to which the soap does not make foam.
Difference Between Soft water and Hard water
- Soft water lathers easily with soap
- Soap costs less than washing clothes with soft water.
- It lacks calcium and magnesium chloride, sulfate and bycarbonate salt.
- This water is not suitable for drinking, because calcium salts are not dissolved in it for the growth of the body.
- The boiler does not deteriorate quickly due to its use.
- Hard water produces less amount and late lather with soap
- Soap is more expensive in washing clothes than hard water.
- It contains calcium and magnesium chloride, sulfate and bycarbonate salt soluble.
- This water is useful for drinking in small quantities.
- Due to its use, the boiler gets spoiled quickly.
Disadvantages of hard water
Hard water produces less lather with soap, so soap costs more.
If the water is too hard, then its taste becomes bad, so it is not used for drinking. Its use leads to kidney stone disease and dysentery.
The use of hard water causes a crust to settle on the surface of the boilers, which in turn increases the cost of fuel.
By reacting with salt water, acid is formed, which quickly destroys the surface of the boiler.
Types of Hardness of Water :
The hardness of water is of the following two types –
Temporary hardness: This hardness is due to the presence of bicarbonate salts [Ca(HCO3)2 and Mg(HCO3)2] of calcium and magnesium soluble in water. When bicarbonates are dissolved in water, the water is called Temporary hard water. This hardness can be easily removed by boiling water.
Permanent Hardness: This hardness is due to the presence of soluble calcium and magnesium in sulphate and chloride and water in their presence is called permanent hard water. This hardness is not removed only by boiling.
How to remove hardness from water ?
1) remove temporary hardness
Temporary hardness of water can be removed by the following methods –
By boiling :- By boiling, calcium and magnesium bycarbonate soluble in water decompose to give insoluble carbonate. Which are filtered and separated.
Ca(HCO3)2 → CaCO3 + H2O + CO2
Mg(HCO3)2 → MgCO3 + H2O + CO2
By clarks method :- By boiling slaked lime or lime water in temporary hard water, the dissolved bycarbonate salt in it turns into insoluble carbonate salts, which are filtered and separated.
Ca(HCO3)2 + Ca(OH)2 → 2CaCO3 + 2H2O
Mg(HCO3)2 + Ca(OH)2 → CaCO3 + MgCO3 + 2H2O
Only temporary hardness can be removed by both the above methods.
Both permanent and temporary hardness of water can be removed by the following methods –
By Sodium Carbonate :- If sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) is mixed with hard water and heated, then the soluble magnesium and calcium salts are converted into insoluble carbonates. These salts are separated by filtration.
Ca(HCO3)2 + NaCO3 → CaCO3 + 2NaHCO3
Mg(HCO3)2 + NaCO3 → MgCO3 + 2NaHCO3
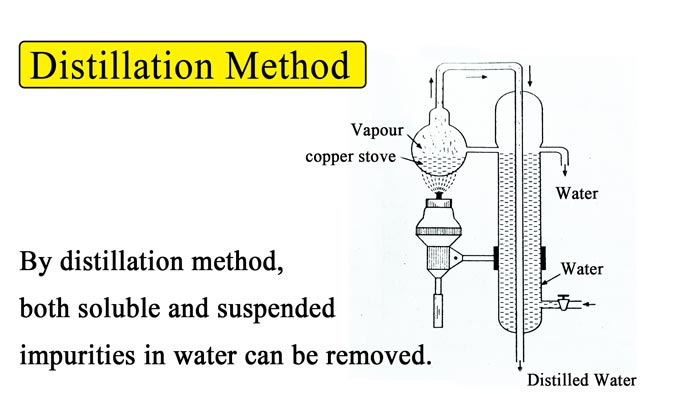
By Distillation :- By distillation method, both soluble and suspended impurities in water can be removed.
For this continuous action is still used. In this, a copper stove is filled with water and heated. The generated steam is passed through the tap. While passing through this tap, the steam heats the water and cools itself to become a liquid.
This water is collected in the receptacle vessel. The water thus obtained does not contain any salt. This pure water is called distilled water. In this way, both types of hardness of water can be removed by distillation method.
Removing permanent hardness:
The permanent hardness of water is removed by the following methods.
By Sodium Carbonate :- By adding sodium carbonate to permanent hard water, the soluble chloride and sulfate of calcium and magnesium are converted into insoluble carbonate.
MgCl2 + Na2CO3 → MgCO3 + 2NaCl
CaSO4 + Na2CO3 → CaCO3 + Na2SO4
CaCl2 + Na2CO3 → CaCO3 + 2NaCl
MgSO4 + Na2CO3 → MgCO3 + Na2SO4
Permutit process :- This is a method of softening hard water in commercial quantities. In this method sodium zeolyte is used.
It is actually a substance called sodium aluminum silicate. Its chemical formula is Na2Al2Si2O8.
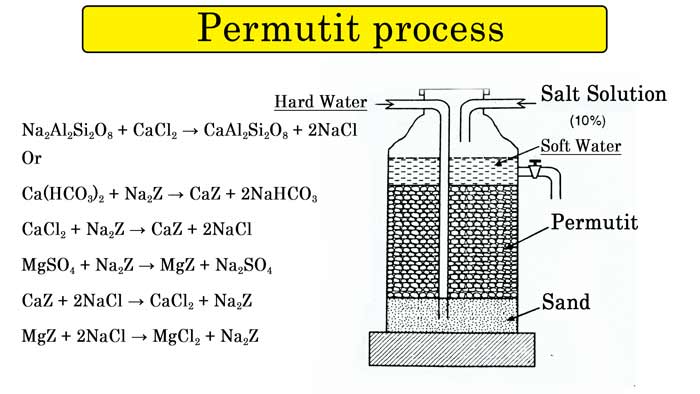
For simplicity, sodium ziolyte is represented by Na2Z formula by writing Z in place of aluminum silicate or ziolyte ion (Al2Si2O8). Both types of hardness can be removed from the permutit process. This property of sodium salts present in sodium zeolyte is that they get displaced by other ions.
If the permutit is kept in a special vessel and hard water is passed through it, then the salts of calcium and magnesium present in the water react with it. In place of sodium atoms, calcium or magnesium atoms come and calcium or magnesium permutit is formed.
Na2Al2Si2O8 + CaCl2 → CaAl2Si2O8 + 2NaCl
Or
Ca(HCO3)2 + Na2Z → CaZ + 2NaHCO3
CaCl2 + Na2Z → CaZ + 2NaCl
MgSO4 + Na2Z → MgZ + Na2SO4
CaZ + 2NaCl → CaCl2 + Na2Z
MgZ + 2NaCl → MgCl2 + Na2Z
Calgons process :- In this process instead of permutit sodium hexametaforfate, whose industrial name is calgon, is used. By passing hard water in calgon, instead of sodium hexametafosfate, hexametaforphate of calcium and magnesium is formed and gets converted into hard water.
Na2[Na4(PO4)6] + 2MgCl2 → 4NaCl + Na2[Mg2(PO4)6]
Na2[Mg2(PO4)6] → 2Na+ + [Mg2(PO4)6]—
By Anion exchange resins :- Nowadays this modern method is being used a lot. The following two types of resins are used in water softening by this method –
Anion exchange resins
Cation exchange resins
In this, a tank is filled with a resin R– about half, water flows through it. The resin absorbs the cations and the water coming out of the tank does not contain calcium and magnesium cations, so the water becomes soft.
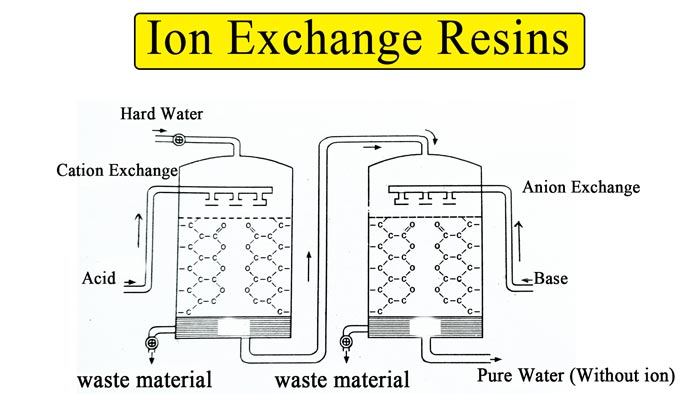
After this, this soft water is passed to another such regin R+ which absorbs the anion.
Thus, the water obtained does not contain mineral salts at all and is like distilled water.
Mechanism :- resin R– contains large carbonic molecules and contains acidic functional groups (-COOH, carboxyl group). The cations Ca++, Mg++ present in hard water are absorbed by these acidic functional groups and the acid introduces H+ ions into the water.
2RCOOH + Mg++ → (RCOO)2Mg + 2H+
Resin R– is recovered by passing concentrated sulfuric acid into it.
(RCOO)2Mg + H2SO4 → 2RCOOH + Mg++ + SO4—
resin R+ consists of ammonia hydroxide granules displaced between large carbonic molecules, to which the functional hydroxyl group (OH–) is attached. The negative electric ions of salts present in hard water are combined with ammonia ions (NH4) of resin R+.
RNH3OH + Cl– + H+ → RNH3Cl + H2O
2RNH3OH + SO4— + 2H+ → (RNH3)2SO4 + 2H2O
It can be recovered by passing concentrated caustic soda (NaOH) solution in resin R+.
RNH3Cl + NaOH → RNH3OH + Na+ + Cl–
Thus the water coming out of resin R– and R+ does not contain any ions and it is like distilled water.
Measurement of hardness of water :
For measurement of hardness of water, each salt present in water, which produces hardness, is calculated by calculating the mass of equivalent calcium carbonate.
This hardness is measured in ppm, so the hardness of water in ppm –
= weight of CaCO3 (gram)/ weight of hard water(gram) x 106
Example: The gram molecular weight of each of Ca(HCO3)2, CaCl2, CaSO4, MgSO4 and Mg(HCO3)2 is equivalent to (=100 grams).
The amount (in grams) of CaCO3 present in 1000000 grams of water is the measure of its hardness.
