Hydrogen : Properties, Preparation, Purification and uses
Hydrogen :- History
Hydrogen was discovered by the German physician and natural scientist Paracelsus in the first half of the 16th century. In 1766, Henry Cavendish of England Scientist obtained this gas by the reaction of sulfuric acid on iron and zinc.
After studying its properties in detail gave it the name of flammable gas. In 1783, Lavosier obtained hydrogen gas from water. He made water by chemical combination of hydrogen and oxygen gas and named this gas hydrogen (Greek – Hydro = water, Gennao = generates).
Occurrence and Availability :
Hydrogen is found only in very small amounts in free form on Earth. It comes out with other gases during the eruption of volcano. This gas is also obtained from oil-wells during oil extraction. In combined state it is also found in water, acids, bases etc.
Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe. About half the mass of the Sun and most stars is made up of this gas. It makes up 1/9 of the mass of water. Hydrogen gas is present in all vegetarian, living thing, minerals and natural gas.
Methods of Preparation :
Laboratory Method :-
Hydrogen gas in the laboratory is prepared by the reaction of dilute sulfuric acid on zinc (granular).
Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
Material Required :-
Wolf bottle, thistle funnel, glass drain tube, perforated seat, trough, gas jar, granular pieces of zinc, dilute sulfuric acid and water.
Method :-
Putting pieces of granulated zinc in a Wolf bottle having two mouths, with the help of a cork, a thistle tube is placed in one mouth of the bottle and a drain tube in the other.

The other end of the drain pipe is placed under the porous seat of a trough filled with water. Now with the help of thistle funnel, slowly pour dilute sulfuric acid into the wolf bottle. Chemical reaction starts as soon as sulfuric acid is applied to the pieces of zinc.
As a result of this reaction, the hydrogen wolf which comes out from the bottle in the beginning, the air inside the bottle is also mixed in it, so this gas is allowed to leave for some time. Then the gas jar filled with water is turned upside down and placed on the Water-tub and the hydrogen gas is collected by the downward displacement of the water in the gas jar.
Precautions :-
- The bottom end of the thistle funnel should be immersed in dilute sulfuric acid, otherwise hydrogen gas will escape from the thistle funnel.
- The equipment must be airtight otherwise the gas will leak out.
- Initially, some amount of gas is released from the water, then only after that the gas should be collected in the gas jar, because water vapor is found in the hydrogen gas that comes out in the beginning.
- Do not bring any burning object near the equipment, as there is a risk of explosion.
Other method :-
Hydrogen gas can also be prepared with the help of water, acids and bases.
From water : –
By the reaction of water on different metals at ordinary temperature, metals like sodium, potessium and calcium etc.
2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2
2K + 2H2O → 2KOH + H2
Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2
By the reaction of water vapor on metals:
Metals like magnesium, zinc, iron, etc., after decomposition of hot water vapor give hydrogen gas.
Mg + H2O → MgO + H2
Zn + H2O → ZnO + H2
Precautions :-
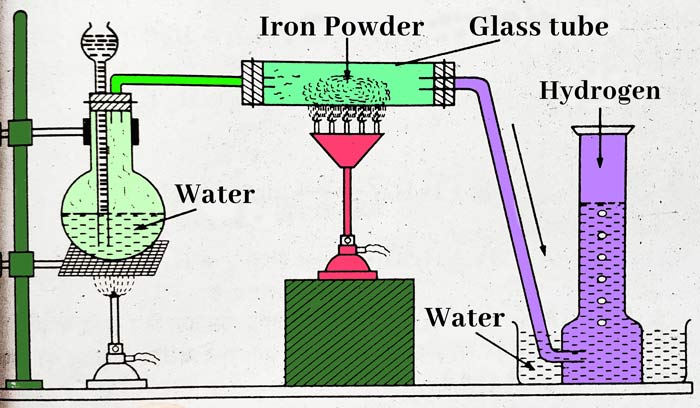
First of all, take water in a round bottom flask and heat it. Iron powder is heated in a hard glass tube and the vapor formed in the flask is passed over the hot iron powder through the glass tube. In this way hydrogen gas is obtained –
3Fe + 4H2O ⇌ Fe3O4 + 4H2
By electrolysis of water :-
First of all, by adding a few drops of acid and alkali to water, make it a conductor of electricity. By the electrolysis of water, hydrogen is collected at the cathode and oxygen is collected at the anode.

H2O ⇌ H+ OH–
H+ + e– → H
H + H → H2
OH– – e– → OH
4OH → 2H2O + O2
By the reaction of metal hydrates :-
Calcium hydrates (Hydrolith) decomposes water at ordinary temperature to generate hydrogen –
CaH2 + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + 2H2
From Acids :-
Zinc magnesium, iron and tin etc. react with dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sulfuric acid at ordinary temperature to produce hydrogen gas –
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2
Mg + H2SO4 → MgSO4 + H2
Fe + H2SO4 → FeSO4 + H2
From Alkalies :-
Metals like zinc, lead, aluminum and tin etc. produce hydrogen gas by decomposition of boiling concentrated aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide and potessium hydroxide –
Zn + 2NaOH → Na2ZnO2 + H2
2Al + 2NaOH + 2H2O → 2NaAlO2 + 3H2
Pb + 2NaOH → Na2PbO
Sn + 2NaOH + H2O → Na2SnO3 + 2H2
Purification of Hydrogen :-
In hydrogen gas prepared with suitable methods, phosphine (PH3), arsine (AsH3), hydrogen sulfide (H2S), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfure dioxide (SO), carbon dioxide (CO2) etc. are found as impure. To remove these impurities, hydrogen gas is passed through the following substances –
Silver nitrate solution – This solution separates sedentary (AsH3), phosphine (PH3) hydrogen sulphide (H2S).
Lead nitrate solution – This solution absorbs the remaining hydrogen sulphide (H2O).
Caustic potash solution – SO2, CO2 and NO2 are separated by this solution.
Phosphorus Pentaoxide – it absorbs the moisture of the gas.
Dissolution of Hydrogen :
By Electrolysis of Water: Where electricity is cheap, it is used there. Hydrogen gas in excess of acid or base mixed water is collected by the method of electrolysis at the cathode.
By lanes Process :- In this process hydrogen is obtained by passing steam over hot iron.
3Fe + 4H2O ⇌ Fe3O4 + 4H2
After all the iron is reduced, the flow of steam is stopped and water gas (CO + H2) is passed, as a result of which iron is again obtained from ioran oxide.
Fe3O4 + 4CO → 3Fe + 4CO2
Fe3O4 + 4H2 → 3Fe + 4H2O
From water gas: – Water gas is obtained when water vapor is passed over blood-heated carbon. Nowadays hydrogen is obtained in large quantities through water gas –
C + H2O → CO + H2
Liquification of water gas: – Bioling temperature of carbon monoxide is – 2525 C, so on cooling water gas (CO + H2), carbon monoxide (CO) liquefies and remains in hydrogen gasic state –
Basch process: – When a mixture of water gas and water vapor is passed over a hot catalyst (Fe2O3 and Cr2O3), carbon dioxide and hydrogen gas are obtained. This process is called Basch process.
At high pressure, CO2 is dissolved in water and separated, due to which pure hydrogen gas is obtained –
CO + H2 + H2O –(Fe2O3+Cr2O3)→ CO2 + 2H2
Hydrogen Test :-
- The mixture of hydrogen and air burns with a loud sound.
- When a piece of burning wood is taken in a hydrogen jar, it gets extinguished, because this gas is not helpful in burning.
- It burns in oxygen or air with a blue flame.
Hydrogen Properties :-
Physical properties :-
- It is soluble in water in very small amounts.
- It is absorbed by metals like platinum and palladium.
- It is a good conductor of heat.
- It is a lighter gas than all other gases and the mass of 1 ml hydrogen gas at S.T.P. is 0.00009 grams.
- Hydrogen gas can be liquefied at low temperature (-253°C) and high pressure.
- Hydrogen gas burns by itself, but does not help in the burning of other things.
- Its relative density is 0.0695.
- Hydrogen gas is colourless, odourless, tasteless and transparent.
Chemical properties :-
Reaction with litmus :- Hydrogen gas has no effect on litmus. Hence this gas is neither acidic nor alkaline.
Reaction with metals :- Hydrogen gas reacts with metals like sodium, calcium etc. to form their hydrides.
2Na + H2 → 2NaH
Ca + H2 → CaH2
Reaction with sulfure – By passing this gas into hot boiling sulfure solution, hydrogen sulfide gas is formed –
H2 + S → H2S
Reaction with nitrogen – In the presence of iron (Fe) and Molibdenum (Mo), it combines with nitrogen at 450°C and 200 atmospheric pressure to produce ammonia gas –
N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3
Reaction with Chlorine :- In sunlight it reacts with chlorine to form hydrogen chloride gas –
H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
Reaction with oxygen :- Hydrogen gas burns in oxygen with a blue flame, as a result of which water is formed –
H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
Reducing properties :- When hydrogen gas is passed over hot oxides of lead, copper etc., these oxides get reduced to their metals –
PbO + H2 → Pb + H2O
CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
Hydrogenation :- When hydrogen gas is passed at 120°C to 180°C temperature in the presence of nickel powder, vegetable oil becomes vegetable oil (Ghee). This process is called Hydrogenation of oils.
vegetable oil + H2 → vegetable oil (Ghee)
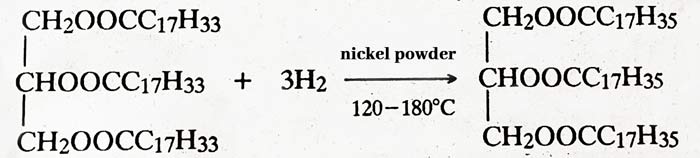
Additive reactions with unsaturated organic compounds
CH2 = CH2 → CH3 – CH3
CH≡CH + H2 → CH2 = CH2 → CH3 – CH3
Uses of Hydrogen :-
Hydrogen is used by Haber method to obtain ammonia.
It is used in making hydrochloric acid and vegetable ghee.
It is used for joining and cutting metals by generating oxyhydrogen flame (2800°C temperature).
It is also used as a reducing agent.
Earlier it was used in balloons, but now a mixture of helium and hydrogen is used in its place.
Used in the synthesis of mthenol.
CO + H2 + H2 → CH3OH
Hydrogen gas is used to make water gas (CO + H2).
With the help of hydrogen coal, it is used to make artificial petrol.
