Exploring Magnetism and Matter: Key Concepts, Formulas, and Real-World Applications
Magnetism is a fundamental force in nature, arising from the
motion of electric charges. It plays a crucial role in many aspects of science
and technology. The interaction between magnetic fields and matter is a rich
area of study with both theoretical and practical significance. This brief
discussion examines the key concepts, formulas, and applications of magnetism
and matter, providing a clear understanding of this intriguing topic.
Key Concepts in Magnetism and Matter
Magnetic Field: A region where a magnetic force is
experienced. Represented by the symbol B, it is a vector quantity with both
magnitude and direction.
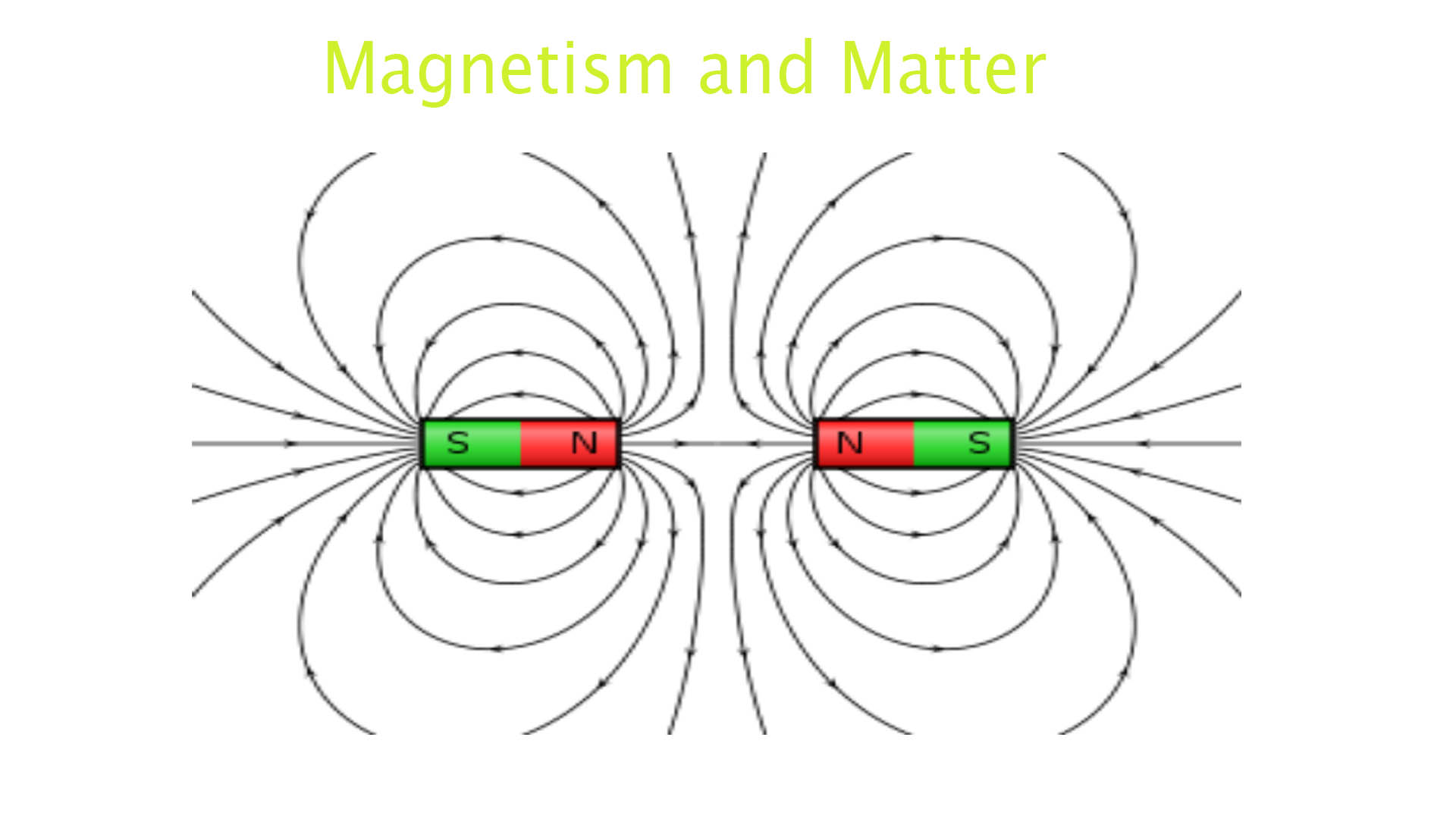
Magnetic Dipole: A simple magnet with a north and south
pole. Earth is an example of a large-scale magnetic dipole.
Magnetization: The process by which a material becomes
magnetic. It refers to the magnetic dipole moment per unit volume of a
material.
Ferromagnetism: A property of materials like iron, nickel,
and cobalt, where magnetic domains align, creating a strong overall magnetic
field.
Paramagnetism and Diamagnetism: Paramagnetic materials are
weakly attracted to a magnetic field, while diamagnetic materials are repelled.
Real-World Examples of Magnetism and Matter
Electric Motors: Motors rely on the interaction between
magnetic fields and electric currents to produce motion.
Magnetic Storage: Data storage devices, like hard drives,
use magnetism to record and retrieve information.
MRI Scanners: Magnetic resonance imaging uses strong
magnetic fields to create detailed images of the human body for medical
diagnostics.
Compass: A simple but powerful tool that uses Earth's
magnetic field to determine direction.
Applications in Everyday Life
Magnetism and its interaction with matter have a profound
impact on everyday life. From the electricity that powers our homes to the
technology that stores our data, magnetism plays a critical role. Understanding
these concepts is not only academically significant but also provides a deeper
appreciation of the technology that shapes our world.
Natural magnet: A natural magnet is an ore of iron (Fe2O4) which
– Attracts small pieces of iron, cobalt, and nickel towards it
– When suspended freely, it comes to rest along the north-south direction.
Artificial magnet: Magnet which is prepared artificially is known as artificial magnets. e.g. a horseshoe magnet, a bar magnet, magnetic needle, etc.
Properties of magnets
Attractive property: When a magnet is dipped into iron filings, it is found that the concentration of iron filings, i.e., attracting power of the magnet is maximum at two points near the ends and minimum at the center. The places in a magnet where its attracting power is maximum are known as poles while the place of minimum attracting power is known as the neutral region.
Directive property: When a magnet is suspended, its length becomes parallel to the N-S direction. The pole at the end pointing north is known as the North Pole while the other pointing south is known as the South Pole.
Magnetic poles always exist in pairs i.e., an isolated magnetic pole does not exist.
Like poles repel each other and unlike poles attract each other.
Magnetic Field: The space around a magnet within which its influence can be experienced is known as its magnetic field. The line joining the two poles of a magnet is known as the magnetic axis.
Magnetic dipole: A magnetic dipole consists of two unlike poles of equal strength and separated by a small distance, e.g. a bar magnet, a compass needle, etc. are magnetic dipoles.