General Principles and processes of isolation of elements or Metallurgy
<iframe width="833" height="469" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/Nh570WKqzhQ" title="JEE-Main Previous Years Paper Solution || Metallurgy | JEE Preparation | 16 Years (2019-2004)" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share" allowfullscreen></iframe>
Concentration of the Ore
The ores are extracted from the mines and there are pieces of stone, pebbles, pebbles, sand, and stones of pollutants. These residues are called gangue or matrix. The process of separating gangues present in ores obtained from mines is called concentrating of ore.
To concentrate the ore, firstly by separating large pieces of ore by hand. After this, they are broken into small pieces by handcuffs. These small pieces are put in the crushers. The crushers are like a millstone. Which consists of two plates.
One plate runs and the other plate stays level. The crushers crumble small pieces. The small pieces obtained in this way puts pieces in stamp mill. Where there are frequent hammer injuries on them. This process grinds ore into a very fine form.
Several methods can be used after grinding large pieces of ore to concentrate the ore. Depending on the nature of the ore and the gangue, one or more of these methods is sometimes used. Some of the following are the major methods.
Gravity Separation Method
This method concentrates heavy ores such as SnO2 and Fe3O4.
The finely powdered ore powder is stirred in a pond filled with water. When doing so, the impurities dissolved in water dissolve.
Impurities of working density remain upwards in water. And high density ore particles are made below.
Water impurities are dissolved in the water by dissolving in the water and working density. And the ore particles are separated. Concentrated ore is thus obtained.
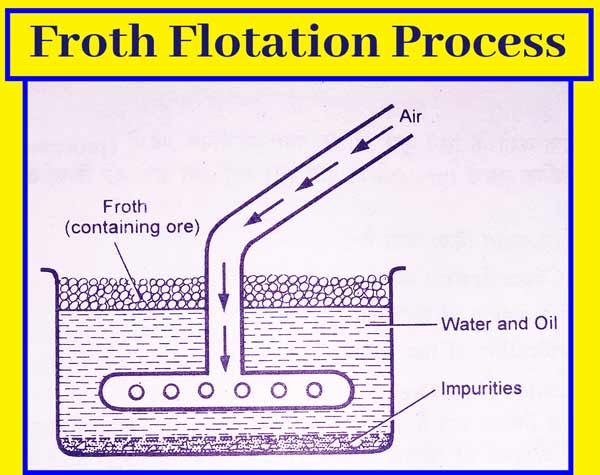
Froth Flotation Method
This method mainly concentrates sulfide ores. When sulfide ores are added to the oil and water mixture. Sulfide ores are then drenched by oil faster than impurities present in them and impurities present in sulfide ores are drenched by water faster than sulfide ores. This method is very common in Metallurgy.
In this way, when the air flows in suspension of sulfide ore made in oil and water, the particles of sulfide ore become foamy and come to the upper surface and the impurities settle down. This method is also called froth buoyancy method.
In this method, sulfide ore is grinded very finely and put in a pond filled with water. It contains small amounts of pine oil, turpentine oil, eucalyptus oil, or sodium xanthate oil to flow a strong stream of air and the oil-soaked sulphide ores get deposited as foam.
And other impurities present in the ore, such as soil, are deposited on the bottom of the pond. Concentrated ore is thus obtained.
Magnetic Separation Method
This method is used to separate a mixture of magnetic and non-magentic substances when the ore is magnetic or other substances are magnetic.
Some magnetic materials (Fe3O4 etc.) are present in tin stone. This method is used to separate the ore of tin stone. The belt is driven by the cylinders by placing the ore on two cylinders on a stretched strip.
One of these cylinders is magnetized. Magnetic and non-magnetic materials are collected at different places on running the belt.
In this method, the ore is grinded finely and put on the belt. The strip keeps moving with the help of cylinders.
Due to the effects of electric magnetic poles, the magnetized material separates itself near the magnet and away from the magnetic material automatically, thus concentrating ores are obtained.

Extraction of the Metal
The complete process of obtaining metal from concentrated ore is called extraction of metal. Depending on the nature of the ore and the method used for extraction of the metal, several terms are used in this process. Following are some of the key terms commonly used in metal extraction.
Calcination
In the process of Calcination, the concentrated ore is heated
enough that volatile metals are released from it. But the ore is not allowed to
melt. Carbonate oxidase and hydroxide ores are usually disposed of.
Example: The water present in Al2O3 is evaporated and released.
Al2O3.2H2O → Al2O3 + 2H2O
Example: The water present in Fe2O3 is evaporated and released.
Fe2O3.3H2O → Fe2O3 + 3H2O
Roasting
Roasting is the process of heating concentrated ore alone or mixed with other substances in the presence of a controlled amount of air without melting. This action is mainly used for sulfide ores. In this process, the ore is partially or completely oxidized and the impurities of sulfur and arsenic present in the ore are removed. This action is often performed in a reflex furnace.
Heats the concentrated ore of copper pyrite (CuFeS2) in a reflective furnace in the presence of low temperature and controlled air.
Copper pyrite ores are oxidized to form copper sulphide and ferrous sulphide, some parts of which are converted to oxidation.
2CuFeS2 + O2 → Cu2S + 2FeS + SO2
2Cu2S + 3O2 → 2Cu2O + 2SO2
2FeS + 3O2 → 2FeO + 2SO2
The impurities of sulfur and arsenic present in the ore are converted into volatile oxidants and pass out with air.
S + O2 → SO2
4As + 3O2 → 2As2O3
Smelting
Smelting is called smelting by mixing the ore with coke and proper flux and heating the mixture to a high temperature.
The smelting process is called smelting by mixing the ore mixture with coke and proper cheek and heating the reaction mixture to a high temperature.
This action is often performed in the Blast furnace.
In this process, coke often acts as a detergent and converts the ore into molten metal.
To obtain iron from Hematite (Fe2O3), coke and Limestone are concentrated in the concentrated ferrous and fermented ore and melt in the Blast furnace. In this action Fe2O3 is converted.
Fe2O3 + 3C → 2Fe + 3CO
Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
Flux
Those substances which react with impurities present in the ore at high temperature and easily dissolve them as detachable substances are called chelants. Easily dissolved substances are called slag.
Basic Fluxes:
If impurities of acidic nature are present in the ore, then alkaline fluxes are used. MaCO3 and CaCO3 are the major alkaline fluxes.
MgCO3 + SiO2 → MgSiO3 + CO2
CaCO3 + SiO2 → CaSiO3 + CO2
Acidic Fluxes:
Acidic fluxes are used if impurities of natural alkaline are present in the ore.
Silicon dioxide (SiO2) is an Acidic Fluxe.
SiO2 + FeO → FeSiO3
SiO2 + CaO → CaSiO3
Reduction
To get the metal from ore, it is reduced. Reduction is usually done by one of the following methods.
By Coke: This action is done during smelting. The reduction of oxides ore is mainly done by this method.
By aluminum: This process is called goldsmith thermite process. It is mainly used for extraction of Cr and Mn.
By legal decomposition of molten salts: this action is used for more functional metals such as alkaline metals, alkaline soil metals, aluminum, etc.
Purification of the Metal
The metal obtained from the extraction of the metal from the ore is often impure. It often contains impurities of carbon silicon phosphorus etc.
The method of refining of any metal depends on its nature and the nature of impurities present in it. Therefore, different types of methods are used for this. Electrolytic method is main in this. Very pure metal is obtained in this method.
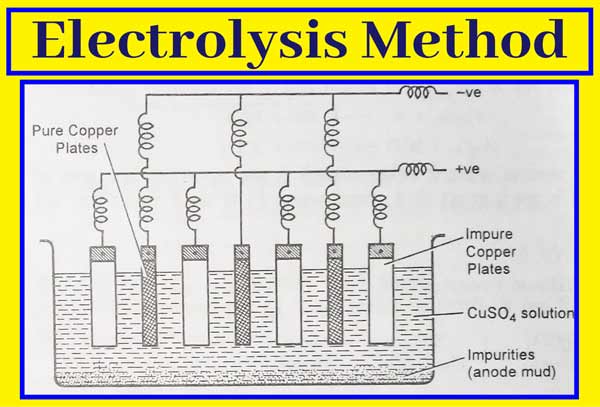
The electrolytic method of refining metals can be explained by the example of refining of copper metal by this method. For the refining of copper metal, electrolyte solution of copper metal salts in electrolytic cell acts as an electrolyte, thick plates of impure metal act as anode and thin plates of pure metal act as cathode.
When electrolysed in an acidic solution of copper sulphate, thick plates of impure copper metal at the anode begin to dissolve and impurities accumulate down the solution. These impurities are called anode mud. Cu forms its cations that move into the solution.
Metallurgy Processes
Mining:
Extraction of ores from the earth's crust.
Crushing
and Grinding: Ores are crushed into small pieces and ground into powder to
increase surface area.
Ore Concentration:
Separation of valuable minerals from the ore through processes like flotation,
gravity separation, or magnetic separation.
Smelting:
Heating the concentrated ore to a high temperature in a furnace with a reducing
agent to extract the metal.
Refining:
Further purification of the metal through processes like electrolysis, zone
refining, or distillation to remove impurities.
Alloying:
Mixing the purified metal with other elements to enhance its properties.
Forming:
Shaping the metal into desired products through processes like casting,
forging, rolling, or extrusion.
Heat
Treatment: Applying controlled heating and cooling processes to modify the
metal's properties such as hardness, strength, and ductility.
Surface
Treatment: Applying coatings, plating, or other surface modifications to
enhance corrosion resistance, appearance, or other properties.
Recycling:
Reclaiming metals from scrap or waste materials to conserve resources and
reduce environmental impact.

