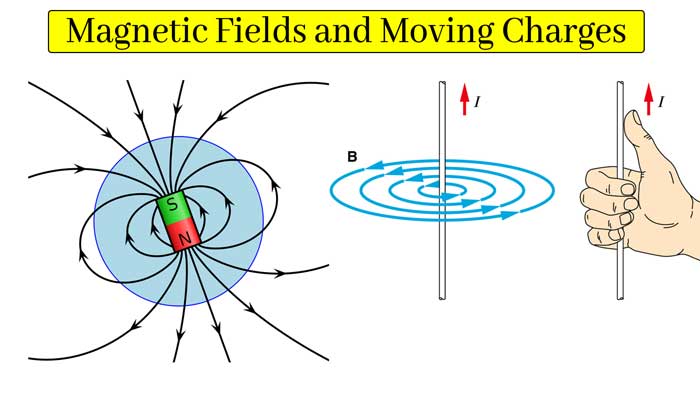
Magnetic Fields and Moving Charges : Magnetic Force and Circular Motion
Magnetic Fields and Moving Charges
- Magnetic Fields: A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials.
- Magnetic Field Generation: A magnetic field is created by moving charges, such as electrons in a current-carrying wire. This is encapsulated in Ampère's Law, part of Maxwell's equations.
- Direction of Magnetic Field: The direction of the magnetic field created by a current-carrying wire can be determined by the right-hand rule.
Lorentz Force
- Definition: The force experienced by a charged particle moving through a magnetic field is known as the Lorentz force. It is given by , where:
- is the charge of the particle,
- is the electric field,
- is the velocity of the particle,
- is the magnetic field.
- Direction of Force: The force is perpendicular to both the velocity of the particle and the magnetic field, following the right-hand rule.
Magnetic Force and Circular Motion
- Circular Motion of Charged Particles: If a charged particle moves perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field, it will experience a centripetal force causing it to move in a circular path. The radius of this circular motion is given by:
- , where is the mass of the particle, is its velocity, is its charge, and is the magnetic field strength.
Magnetic Fields in Different Configurations
- Straight Wires and Loops: A current in a straight wire creates a magnetic field in circular loops around the wire. For a loop, the field is more concentrated in the center, forming a magnetic dipole.
- Solenoids and Toroids: Coiling a wire into a solenoid amplifies the magnetic field. Solenoids and toroids are useful in creating uniform magnetic fields.
- Magnetic Materials: Ferromagnetic materials like iron can be magnetized, aligning their magnetic domains with an external magnetic field, resulting in a stronger magnetic effect.
Applications of Magnetism and Moving Charges
- Electric Motors and Generators: Motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy using magnetic fields and currents. Generators do the opposite, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): This medical imaging technique uses powerful magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body's internal structures.
- Particle Accelerators: These devices use magnetic fields to steer and focus charged particles at high speeds.
Discussion Points
- Electromagnetic Induction: A changing magnetic field can induce an electric current in a conductor, as described by Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction.
- Relativity and Magnetism: From the perspective of special relativity, electric and magnetic fields are interrelated, and moving charges can be understood through the frame of reference concept.
- Practical Uses of Magnetism: Beyond the aforementioned applications, magnetism plays a role in data storage, maglev trains, and various electronic devices.
If you have specific questions or concepts you'd like to explore further, I'm happy to dive deeper into any of these topics.