Oxalic Acid: What is the formula of oxalic acid? | Properties | Uses
Chemical Formula
-
Oxamide – C2H4N2O2
- diethyl oxalate – C6H10O4
- glycolic acid – C2H4O3
-
Calcium oxalate – CaC2O4
- Sodium formate – HCOONa
- Magnesium Carbonate – MaCO3
Oxalic Acid is the first member of the di-carboxylic acid group. Two carboxyl groups are present in one molecule. It is found in Rhubarb, sorrel and oxalic group plants as its potassium salt. In some plants and animals it is found as calcium oxalate.
In the laboratory, it is made by oxidizing sugar cane sugar. At the commercial level it is made by heating Sodium Formate. It is found in crystal and Amorphous forms.
One molecule of crystalline oxalic acid consists of 2 molecules of Kelsan water. The molecular formula for amorphous oxalic acid is H2C2O4 and the following is the composition formula.
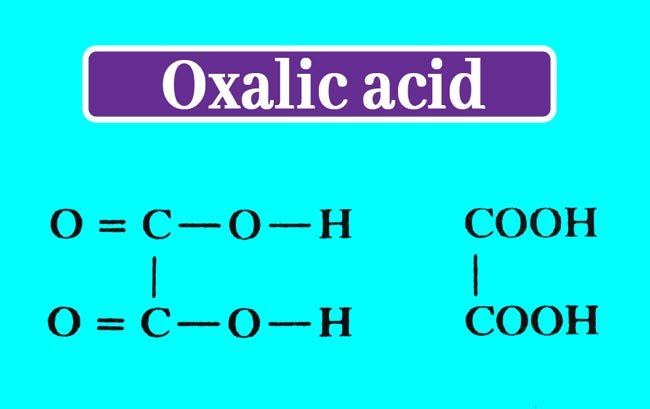
Physical Properties of Oxalic Acid
It is a colorless and odorless solid. The melting point of crystalline oxalic acid is 101.5°C and the melting point of anhydrous oxalic acid is 189.5°C. It is soluble in water and alcohol. And is indestructible in ether.
Chemical Properties of Oxalic Acid
Reaction with bases: oxalic acid is a dual incinerate acid. Hence it reacts with bases to form two types of salt. Example:

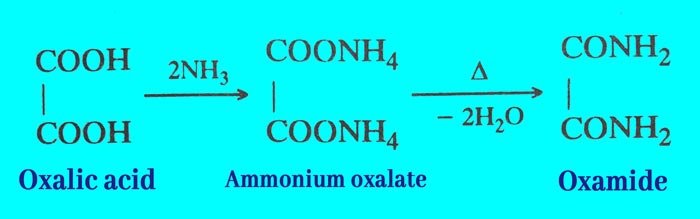
It reacts with ammonia to form ammonium oxalate, which upon heating gives oxamide.
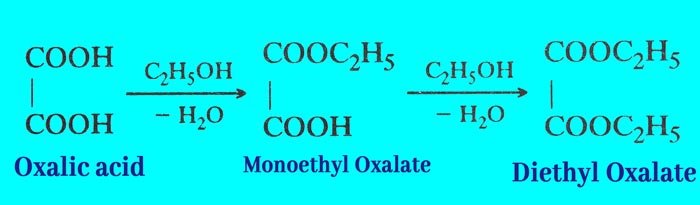
Reaction with Ethanol: On heating anhydrous oxalic acid with ethanol, it forms mono ethyl oxalate and diethyl oxalate, respectively.
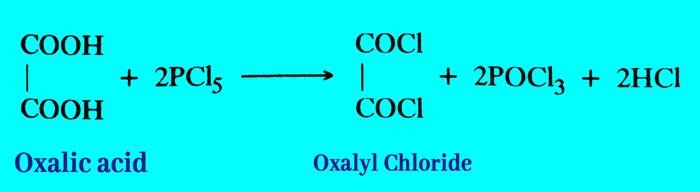
Reaction with phosphorus penta chloride: It reacts with phasphorus penta chloride to form oxalyl chloride.
Effect of heat: On heating crystalline oxalic acid to 100°C, its crystal water is separated. After heating to about 200°C, it forms formic acid.
H2C2O4.2H2O → H2C2O4 → HCOOH + CO2
At 200°C formic acid partially decomposes to water and carbon mono oxide.
HCOOH → H2O + CO
Therefore, heating of crystal oxalic acid at 200°C gives a mixture of formic acid, carbon mono oxide, carbon di oxide and water.
When heated to about 90°C with sulphuric acid, it decomposes and forms carbon di-oxide, carbon mono oxide and water.
H2C2O4 → CO2 + CO + H2O
Oxidation: It is quickly oxidized to carbon d oxide and water under the influence of oxidants such as acidic potassium permanganate, potassium dichromate and lead peroxide.
H2C2O4 + O → H2O + 2CO2
The following is the balanced equation of the reaction of oxalic acid to acidic KMnO4.
2KMnO4 + 3H2SO4 + 5H2C2O4 → K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 8H2O + 10CO2
Reduction: (i) It is reduced by zinc and sulphuric acid to form glycolic acid.
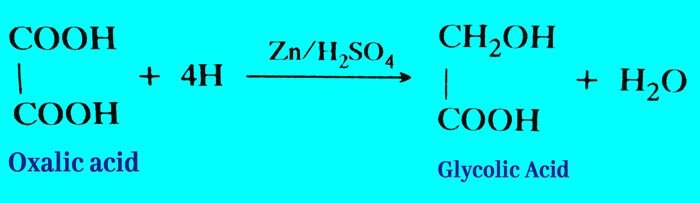
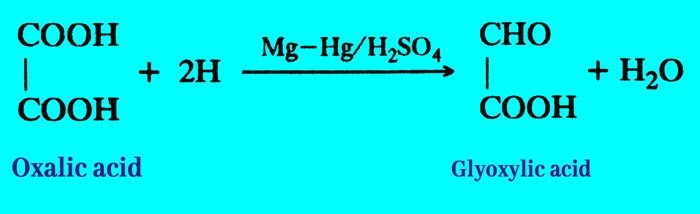
(ii) It is reduced by magnesium mercury (Mg-Hg) amalgam and H2SO4 to form Glyoxylic acid.
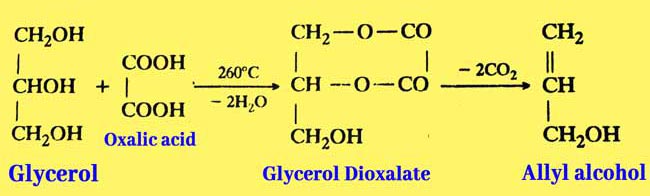
Reaction with Glycerol: when heated with glycerol at 100-110°C makes it formic acid and Allyl Alcohol at 260°C.
What is oxalic acid used for?
As reagents in the laboratory and in oxidation reduction measurements
Allyl alcohol, formic acid and other useful organic compounds
As mordant in printing and dyeing of clothes
To get rid of ink stains on clothes
Polish of metals, inks and dyes
Potassium ferrous oxalate is used as a developer in photography.
How do you test for oxalic acid?
Oxalic acid provides general tests of carboxylic acid.
Effervescences are obtained due to the formation of CO2 gas when
oxalic acid is added to the NaHCO3 solution. Specific tests are as
follows.
The addition of calcium chloride to a neutral solution
of oxalic acid gives a white precipitate of calcium oxalate, which is insoluble
in acetic acid but soluble in mineral acids.
The oxalic acid becomes colourless when the oxalic acid
solution is added to the hot and acidic potassium par magnate solution.
On heating it with concentrated sulphuric acid, carbon
monoxide gas is formed which burns with a blue flame.
The addition of silver nitrate to neutral solution of
oxalic acid gives a white precipitate, which is soluble in ammonium hydroxide
and does not give silver mirror when heated.
