How Sodium Thiosulfate Works: Chemistry Explained
- Sodium sulfate – Na2SO4
- Sodium pentasulfide – Na2S5
- Sodium tetrathionate – Na2S4O6
- Silver nitrate – AgNO3
- Silver Thiosulfate – Ag2S2O3
- Sodium sulfate – Na2SO4
- Sodium sulfide – Na2S
- Sodium silver thiosulfate – AgNa3O6S4
- Ferric thiosulfate – Fe2(S2O3)3

Sulfur is boiled with caustic soda solution.
[S + 2NaOH → Na2S + H2O + O] X 3
Na2S + 3O → Na2SO3
Na2SO3 + S → Na2S2O3
=——————————————-
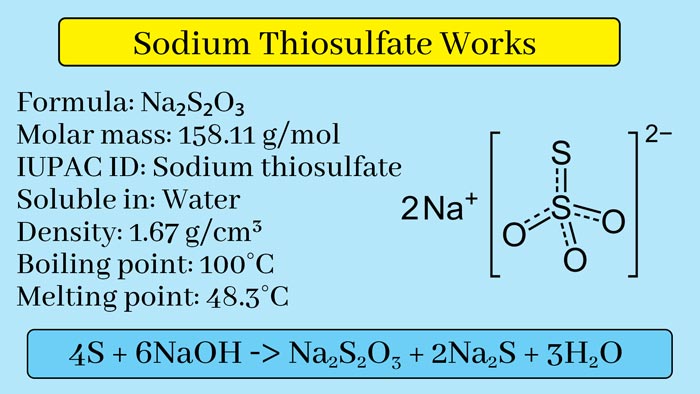
4S + 6NaOH → Na2S2O3 + 2Na2S + 3H2O
When an aqueous solution of sodium sulfide is boiled with sulfur, sodium thiosulfate is obtained. After filtering the solution and cooling it, monoclinic shaped crystals of Na2S2O3.5H2O are obtained.
Na2SO3 + S → Na2S2O3
Hypo is obtained when a mixture of sodium sulfate and sodium sulfide is reacted with iodine.
Na2S + I2 → 2NaI + S
Na2SO3 + S → Na2S2O3
==———————————–
Na2SO3 + Na2S + I2 → Na2S2O3 + 2NaI
In this reaction, iodine is used in moderation. Otherwise, it reacts with the product to make another product.
When sulfur dioxide gas flows in a solution of sodium carbonate and sodium sulfide
2Na2S + 2H2O + SO2 → 4NaOH + 3S
Na2CO3 + SO2 → Na2SO3 + CO2
Na2SO3 + S → Na2S2O3
When flow of SO2 in sodium carbonate solution in the presence of sulfur
Na2CO3 + SO2 → Na2SO3 + CO2
Na2SO3 + S → Na2S2O3
By the reaction of sodium hydrogen sulfide and sodium sulfate
2NaHS + 4NaHSO3 → 3Na2S2O3 + 3H2O
Sodium Thiosulphate Structure

It is a colorless crystalline solid. Its melting point is 48°C. It is soluble in water.
Thermal Decomposition: By heating to 215°C, its crystallization water is separated.
Na2S2O3.5H2O → Na2S2O3 + 5H2O
At 220°C or higher temperature, it is decomposed into sodium sulfate and sodium pentasulfide.
4Na2S2O3 → 3Na2SO4 + Na2S5
Reaction with dilute HCl: It reacts with dilute acids to produce SO2 gas and the sulfur precipitate is obtained.
Na2S2O3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + SO2 + S
Action with Chlorin: By acting with chlorine, it forms hydrochloric acid. For this reason, it is called AntiChlor.
Na2S2O3 + Cl2 + H2O → Na2SO4 + 2HCl + S
Action with iodine: It reacts with iodine to make NaI and sodium tetrathionate. Both these compounds are colorless, so the violet color of iodine disappears. This reaction is used in the quantitative analysis of iodine.
2Na2S2O3 + I2 → 2NaI + Na2S4O6
- The electron configuration of Elements
- How do you write a Chemical Formula?
- What is a molecule’s easy definition?
- NEET Exams 2020 cancelation, Admit card, Study for NEET 2020
- Chemicals in Medicine: Class 12
- Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices, and Simple Circuits
Reaction with silver nitrate: By reacting with silver nitrate it first forms a white precipitate of silver thiosulfate. Whose color eventually turns black due to reduction.
Na2S2O3 + 2AgNO3 → Ag2S2O3 + 2NaNO3
Ag2S2O3 + H2O → Ag2S + H2SO4
If sodium is taken in excess, the white precipitate of silver thiosulphate forms sodium agents by dissolving in excess of Sodium silver thiosulfate and black precipitate of Ag2S is not obtained.
Ag2S2O3 + 3Na2S2O3 → 2Na3[Ag(S2O3)2]
Action with silver bromide: Silver chloride, silver bromide, and silver iodide are insoluble in water but dissolve in an aqueous solution of sodium thiosulfate. The reason for this is that the reaction of silver halide and sodium Thiosulfate forms a hybrid salt called Sodium Argento Thiosulphate which is soluble in water.
AgBr + 2Na2S2O3 → Na3[Ag(S2O3)2] + NaBr
Action with ferric chloride: The reaction of ferric chloride and sodium thiosulfate gives pink color due to the formation of ferric thiosulfate.
2FeCl3 + 3Na2S2O3 → 6NaCl + Fe2(S2O3)3
After some time the pink color disappears due to the following reaction.
2Fe3+ + 2S2O32- → 2Fe2+ + S4O62-
Uses Of Sodium Thiosulfate(Hypo)
Sodium thiosulfate works through various chemical reactions and applications due to its unique properties. Some common ways it works include:
Photography: In photography, sodium thiosulfate is used as a photographic fixer. It works by dissolving undeveloped silver halide crystals from photographic film or paper, leaving behind a permanent image.
Medical Uses: Sodium thiosulfate is employed in medicine as an antidote to cyanide poisoning. It reacts with cyanide to form thiocyanate, which is less toxic and can be excreted from the body.
Water Treatment: It is utilized as a dechlorination agent in water treatment processes. Sodium thiosulfate reacts with chlorine to form sodium chloride (table salt) and sulfur dioxide, effectively removing chlorine from water.
Chemical Industry: Sodium thiosulfate is used in various chemical reactions as a reducing agent and sulfur donor. It finds applications in gold extraction, analytical chemistry, and as a component in certain chemical processes.
Analytical Chemistry: In chemical analysis, particularly in titration procedures, sodium thiosulfate is used as a standard solution to determine the concentration of other substances, such as iodine or to analyze for various metals.
In quantitative analysis, titrations with iodine determine their amounts in solutions of oxidizers such as CuSO4, KMnO4, K2Cr2O7 etc.
These are just a few examples of how sodium thiosulfate works in different contexts, showcasing its versatility and importance in various industries and applications.