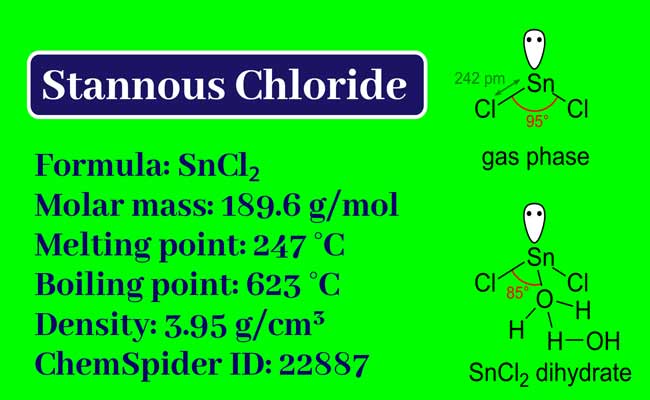
A Short Notes on Stannous Chloride and Basic Lead Acetate
Chemical Formula
- Copper pyrites – CuFeS2
- Silver Sulphide – Ag2S
- Lead Sulphide – PbS
- Hematite – Fe2O3
- Silicon Dioxide – SiO2
- Magnesium Carbonate – MaCO3
It is made in the forms of stannous chloride and Dihydrate Stannous Chloride.
Preparation of Stannous Chloride
Anhydrous stannous chloride is obtained when the dry hydrochloride acid gas flows in the hot tin.
Sn (s) + 2HCl (aq) → SnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Stannous chloride is obtained by heating the tin with mercuric chloride.
Sn + HgCl2 → Hg + SnCl2
Anhydrous stannous chloride cannot be obtained by heating the hydrous stannous chloride(SnCl2.2H2O), as tin oxidechloride is formed upon heating.
SnCl2.2H2O → HCl + Sn(OH)Cl + H2O
Crystals of stannous chloride are obtained by evaporating the solution obtained by heating the tin with concentrated hydrochloride acid.
Sn + 2HCl + 2H2O → SnCl2.2H2O + H2
Stannous chloride solution is also obtained by heating stannous oxide or stannous hydroxide with concentrated hydrochloric acid. Crystals are obtained by evaporation.
SnO + 2HCl + H2O → SnCl2.2H2O
Sn(OH)2 + 2HCl → SnCl2.2H2O
Physical Properties
It is a transparent material like glass. It dissolves in water, ether, and alcohol.
Chemical Properties
Reaction with water: It hydrolysed in excess of water to form tin oxychloride.
SnCl2 (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ Sn(OH)Cl (s) + HCl (aq)
Reaction with marcuric chloride: Hg2Cl2 is first formed by adding marcuric chloride solution to the stannous chloride solution, which is reduced by the addition of stannous chloride to Hg.
SnCl2 + 2HgCl2 → SnCl4 + Hg2Cl2
Hg2Cl2 + SnCl2 → SnCl4 + 2Hg
Reaction with ferric chloride: It reduces the ferric chloride to ferrous chloride.
2FeCl3 + SnCl2 → 2FeCl2 + SnCl3
Reaction with iodine: In the presence of HCl acid, it also reduces iodine.
I2 + 2HCl + SnCl2 → SnCl4 + 2HI
Reaction with NaOH: It reacts with NaOH to form stannous hydroxide precipitates which dissolve in excess of NaOH and dissolve sodium.
SnCl2 + 4NaOH → 2NaCl + 2H2O + Na2SnO2
Reaction with H2S gas: Black precipitate of stannous sulfide is obtained when hydrogen sulfide gas flows in the stannous chloride solution, which dissolves in the yellow ammonium sulfide solution.
Read More Articles
- Metallurgy Process | Definition with Examples
- How to compose Cement? Cement Uses.
- What is the use of plaster of Paris?
- What is the formula of sodium thiosulphate?
- Method of Preparation of Microcosmic Salt
- What is sodium carbonate used for? Sodium carbonate properties
- Sodium Hydroxide (Caustic Soda) NaOH
- How to make Hydrogen peroxide?
- What is heavy water used for?
- Isotopes of Hydrogen: Deuterium
- What is sodium carbonate used for? Sodium carbonate properties
SnCl2 + H2S → 2HCl + SnS
SnS + (NH4)2S2 → (NH4)2SnS3
Reduction: Tin metal is obtained by heating SnCl2 with Zn.
SnCl2 + Zn → ZnCl2 + Sn
Uses of Stannous Chloride
- The lab serves as a reagent.
- Used as reducing agent.
- The dyeing of cloth is used as a color bond in printing.
- It is used as calico printing.
Basic Lead Acetate
[Pb(OH)2.Pb(CH3COO)2]

In the presence of air, Basic lead acetate is obtained by the reaction of lead and acetic acid.
2Pb + 2CH3COOH + O2 → Pb(OH)2.Pb(CH3COO)2
In the presence of air, Basic lead acetate is obtained by the reaction of lead and acetic acid.
2PbO + 2CH3COOH → Pb(OH)2.Pb(CH3COO)2
2PbCO3 + 2CH3COOH → Pb(OH)2.Pb(CH3COO)2 + 2CO2
Basic Lead Acetate Properties
It is white colored powder. It is toxic. It is soluble in water, acids and alcohol.
Reaction with carbon dioxide: It reacts with the reaction of carbon dioxide.
3[Pb(OH)2.Pb(CH3COO)2] + 4CO2 + 2H2O
→ 2[2PbCO3.Pb(OH)2] + 6CH3COOH
Basic Lead Acetate Uses
It is white colored powder. It is toxic. It is soluble in water, acids and alcohol.
Reaction with carbon dioxide: It reacts with the reaction of carbon dioxide.
