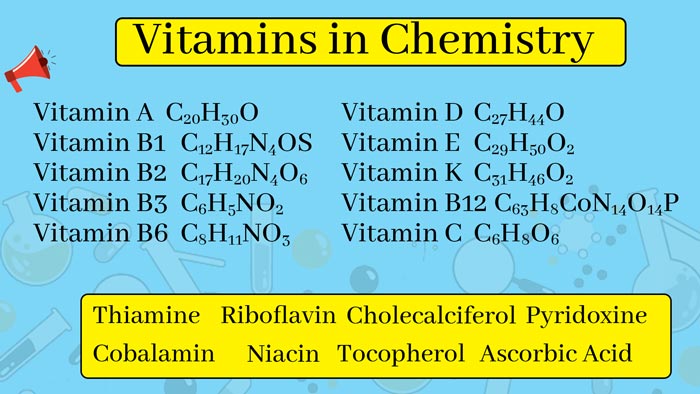
Vitamins in Chemistry || What are the most common vitamin deficiencies?
Vitamins are trace organic substances that humans and animals must obtain from food in order to maintain normal physiological functions. They play an important role in human growth, metabolism, and development. Vitamins are neither involved in the formation of cells nor provide energy for the body. Some common vitamin deficiency in the human body like Rough skin, itching, deep white lines on nails, dry hair,
Vitamins are a group of organic compounds necessary to maintain good health. This kind of substance can neither be a raw material constituting body tissue nor a source of energy in the body, but a kind of regulating substance, which plays an important role in material metabolism.
Vitamins Definition Nutrition
Vitamins are a group of organic compounds necessary to maintain good health. This kind of substance is neither a raw material for body tissues nor a source of energy in the body, but a type of regulating substance that plays an important role in material metabolism.
Because such substances cannot be synthesized or insufficiently synthesized in the body, although they are required in small quantities, they must always be supplied by food.

① vitamins are provitamin form found in foods.
② Vitamins are not components of body tissues and cells, nor do they produce energy. Its role is mainly to participate in the regulation of body metabolism.
③ most of the vitamins, the body can not synthesize or insufficient amount of synthetic, can not meet the needs of the body, they must often be obtained through food.
④The human body needs a small number of vitamins. The daily requirement is usually calculated in milligrams or micrograms, but once it is lacking, it will cause the corresponding vitamin deficiency and cause damage to human health.
Vitamin Function
Vitamins are different from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. They only make up a small percentage of natural foods, but they are necessary for the human body. Some vitamins, such as B6.K, can be synthesized by bacteria in the intestines of animals, and the amount of synthesis can meet the needs of animals.
- Ammonia Formula || why ammonia is toxic || Ammonia Poisoning
- Why Ozone Layer is Important || Ozone Layer Depletion
- What is the Concentration of solution || How Concentration Affects Reaction
- Why Carbon Cycle is Important || How it Works
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes NCERT Solutions || Haloalkane Structure
- Carbon Dioxide Cycle and Formula || How Carbon Dioxide is Produced
Animal cells can convert tryptophan into nicotinic acid (a B vitamin ), but the amount produced is not required, vitamin C can be synthesized by other animals except primates and guinea pigs. Plants and most microorganisms can synthesize vitamins on their own, without having to be supplied from the outside. Many vitamins are part of the co-group or co-enzyme.
Vitamins are certain small amounts of organic compounds necessary for human and animal nutrition and growth and have a very important role in the metabolism, growth, development, and health of the body.
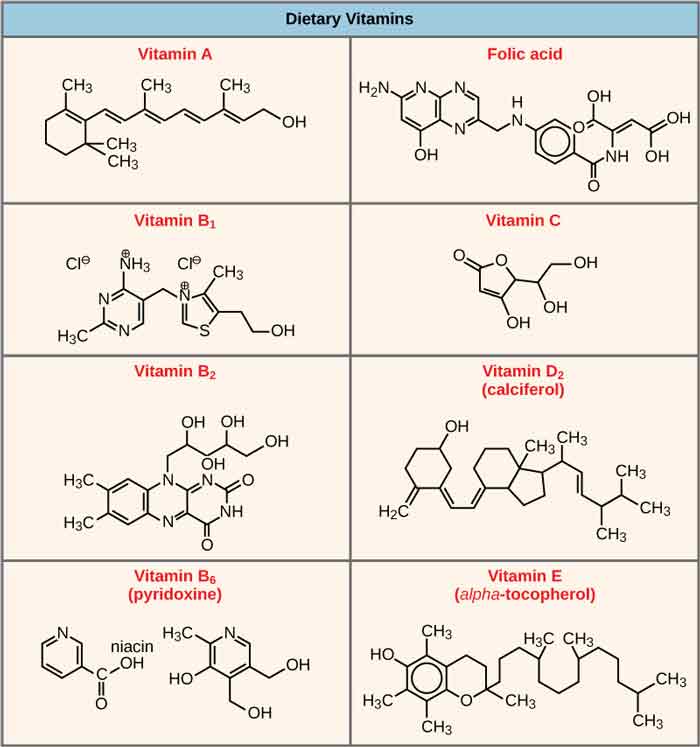
If a certain vitamin is lacking for a long time, it will cause physiological dysfunction and cause certain diseases. Generally obtained from food. We found dozens of stages, such as vitamin A, vitamin B, vitamin C and the like.
Vitamins are essential organic compounds in human metabolism. The human body is like very complex chemical plants, continue to carry out a variety of biochemical reactions.
The reaction is closely related to the catalytic action of the enzyme. Enzymes to produce the active, coenzyme must participate. Many vitamins are known to be coenzymes or constituent molecules of coenzymes.
Therefore, vitamins are important substances for maintaining and regulating the body’s normal metabolism. It can be considered that the best vitamins exist in human tissues in the form of ” bioactive substances “.
Lack of Reason
1. The food supply is seriously insufficient and the intake is insufficient. for example single food, improper storage, cooking damage, etc. Such as folic acid heat loss.
2. Decreased absorption and utilization. such as digestive system disease or too little fat intake which affects the absorption of fat-soluble Vit.
3. Vitamin demand is relatively high. such as pregnant and lactating women, children, special types of work, and people in special environments.
4. Improper use of antibiotics will lead to increased demand for vitamins.
Essential Vitamins
The definition of vitamins requires vitamins to meet the following four characteristics before they can be called essential vitamins.
Exogenous: The human body cannot synthesize itself and needs to be supplemented by food.
Traces: The amount required by the human body is small, but it can play a huge role.
Regulatory: Vitamins must be able to regulate human metabolism or energy transition.
Specificity: When a certain vitamin is lacking, a person will be characteristically ill.
According to these four characteristics, the human body needs a total of 13 vitamins, which are commonly referred to as 13 essential vitamins:
Vitamin A, Vitamin B, Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Vitamin E, Vitamin K, Vitamin H, Vitamin P, Vitamin PP, Vitamin M, Vitamin T, Vitamin U, Water-soluble Vitamins.
Vitamins Origin
The discovery of vitamins was one of the great discoveries of the 19th century. In 1897, Ekman discovered in Java that beriberi could be effected only by eating finely polished white rice, and unmilled brown rice could treat the disease.
It was found that a substance that can cure beriberi can be extracted with water or alcohol, which was then called “water-soluble B”. In 1906 it was proved that food contains “cofactors” other than protein, lipids, carbohydrates, inorganic salts, and water.
The amounts are small but necessary for animal growth. In 1911, Casimir Funk identified amines as substances that can fight beriberi in brown rice, and their properties were similar to those in foods, and most were coenzymes.
Some supply must be balanced with each other, such as vitamin B1, B2, and PP, otherwise, it can affect physiological effects. Vitamin B complexes include pantothenic acid, niacin, biotin, folic acid, vitamin B1 ( thiamine ), vitamin B2 ( riboflavin ), pyridoxine ( vitamin B6 ), and cyanocobalamin ( vitamin B12 ). Some people also include choline, inositol, p-aminobenzoic acid ( p-aminobenzoic acid ), carnitine, and lipoic acid in the B complex.
Classification of Vitamins
Vitamin A, anti-dry eye vitamin, also known as cosmetic vitamin, fat-soluble. Discovered by Elmer McCollum and M. Davis between 1912 and 1914. Not a single compound, but a series of retinol derivatives (retinol is also translated as vitamin A alcohol, rosin oil), nicknamed anti-dry eye vitamins are mostly found in cod liver oil, animal liver, green vegetables, and lack vitamin A Susceptible to night blindness.
Vitamin B1, thiamine, also known as an anti-beriberi factor, anti-neuritis factor, etc., are water-soluble vitamins. Discovered by Casimir Funk in 1912 (one said in 1911). It is usually present in the body as thiamine pyrophosphate. Mostly found in yeast, grains, liver, soybeans, and meat.
Vitamin B2, riboflavin, water-soluble. Discovered by DT Smith and EG Hendrick in 1926. Vitamin G is also found in yeast, liver, vegetables, and eggs. Lack of vitamin B2 is prone to inflammation of the mouth (oral ulcers).
Vitamin PP, water-soluble. Discovered by Conrad Elvehjem in 1937. Including nicotinic acid (nicotinic acid) and nicotinamide ( nicotinamide ), both are pyridine derivatives. Mostly found in nicotinic acid, nicotine acid yeast, cereals, liver, rice bran.
Vitamin B4 is no longer considered a true vitamin at this stage. Choline was discovered by Maurice Gobley in 1850. One of the vitamin B family was first isolated from pig liver in1849.
Since then, choline has been considered a component of phospholipids. In 1940, Sura and Gyorgy Goldblatt showed that it has vitamin properties according to their respective work. Eggs, animal brains, beer yeast, malt, and soy lecithin are higher.
Vitamin B5, pantothenic acid, water-soluble. Discovered by Roger Williams in 1933. Also called pentatonic acid. Mostly found in yeast, grains, liver, and vegetables.
Vitamin B6, pyridoxine, water-soluble. Discovered by Paul Gyorgy in 1934. Includes pyridoxine, pyridoxal, and pyridoxamine . Mostly found in yeast, cereals, liver, eggs, dairy products.
Biotin, also known as Vitamin H or Coenzyme R, is water-soluble. Mostly found in yeast, liver, and grain.
Vitamin B9 folic acid, water-soluble. Also called folic acid, pteroic acid mono glutamic acid, vitamin M or leaf essence. Mostly found in vegetable leaves and liver.
Vitamin B12, cyanocobalamin, water-soluble. Discovered by Karl Folkers and Alexander Todd in 1948. Also known as cyanocobalamin or coenzyme B12. Mostly found in the liver, fish, meat and eggs.
Inositol, water-soluble, cyclohexyl alcohol, vitamin Bh. Mostly found in the heart and meat.
Vitamin C, ascorbic acid, water-soluble. Discovered by James Lind in 1747. Also known as ascorbic acid. Mostly found in fresh vegetables and fruits.
Vitamin D, calcified alcohol, fat-soluble. Discovered by Edward Mellanby in 1922. Also known as calciferol and rickets-resistant vitamins, there are mainly vitamin D2, ergocalciferol and vitamin D3, cholecalciferol. This is the only vitamin that the body can synthesize in small amounts. Mostly found in cod liver oil, egg yolk, dairy products, yeast.
Vitamin E, tocopherol is fat-soluble. Discovered by Herbert Evans and Katherine Bishop in 1922. There are four kinds of α, β, γ and δ. Mostly found in eggs, liver, fish, and vegetable oils.
Vitamin K, naphthoquinones, fat-soluble. Discovered by Henrik Dam in 1929. It is a collective name for a series of naphthoquinone derivatives. There are mainly natural plant-derived vitamin K1, animal-derived vitamin K2, and synthetic vitamin K3 and vitamin K4. Also known as clotting vitamins. Mostly found in spinach, alfalfa, cabbage, and liver.
Water-Soluble Vitamins
In the ideal situation, people need to get vitamins in your diet. The following conditions cause a deficiency of vitamins required by the human body. All water-soluble vitamins are involved in catalytic functions. B vitamins are a component of many coenzymes that carry the transfer of hydrogen, electrons, or groups.
They are involved in the metabolism of sugars, fats, proteins, and nucleotides catalyzed by enzymes, and vitamin C is involved in many hydroxylation reactions. Water-soluble vitamins are widely found in animal and plant cells.
Fat-soluble vitamins do not function as well as B vitamins. Vitamin K is involved in the carboxylation of glutamic acid in some proteins, vitamin D promotes the absorption of calcium, and vitamin A is a component of rhodopsin.
1. Food shortage, improper transportation, storage, and processing of food cause vitamins in food to be lost, resulting in insufficient vitamin intake.
2. When people’s digestive and absorption functions are reduced, such as insufficient chewing, reduced gastrointestinal function, too little fat in the diet, too much fiber, etc. will cause the vitamin digestion and absorption rate to decrease.
3. People in different physiological periods, such as women during pregnancy and lactation, children during growth and development, and the population of diseases and surgery have a relatively high demand for vitamins.
4. People living and working under special circumstances have relatively higher vitamin requirements due to mental stress or environmental pollution.
It is often due to a deficiency of a vitamin that attracts people’s attention. Then it is found that the symptoms disappear after supplementing a certain food, and then the effective ingredients are extracted from this kind of food, and then the substance is obtained by chemical synthesis and added. Further research.
Vitamins Effect on the Body
Vitamin A is closely related to normal keratinization of the skin. In the absence of it, the skin has dry skin, thickened cornea, and small pores plugged by small horn plugs, which affects sebum secretion in severe cases. Therefore, people with dry, rough, dull, desquamated, and small-horned suppositories are good at taking vitamin A.
Vitamin B6 has a close relationship with amino acid metabolism. It can promote the absorption of amino acids and protein synthesis. It is necessary for cell growth and has an effect on fat metabolism. It is closely related to sebum secretion.
Therefore, it is often used for scalp seborrhea and dandruff.
Vitamin C is known as the skin’s closest partner. It promotes the metabolism of tyrosine and tryptophan in amino acids, prolongs the life of the body, and is an essential component of the skin cell interstitial. Therefore, the integrity of skin tissue, the maintenance of normal permeability of blood vessels and the balance of pigment metabolism are inseparable from it.
Vitamin E is recognized to have anti-aging effects, can promote skin blood circulation and granulation tissue growth, and make hair skin smooth, and smooth wrinkles.
Vitamin K1 is an oil-soluble vitamin that improves dark circles caused by fatigue. Clinical findings found vitamin A and vitamin K. After using it, it can obviously improve the dark circles.
“Pseudo” Vitamins
During the discovery of vitamins, some compounds were mistaken for vitamins, but did not meet the definition of vitamins, and some compounds were deliberately incorrectly named vitamins because of commercial interests:
Some compounds in the vitamin B family were once considered vitamins, such as vitamin B4 (adenine).
Vitamin F-Originally used to indicate the fatty acids that are necessary for the body but cannot be synthesized by itself, because the English name of fatty acids (Fatty Acid) starts with F. But because it is actually the main component of fat, and fat is also a source of energy in the body and forms cells, so vitamin F is not a vitamin.
Vitamin K-Ketamine is labeled as vitamin K in the composition of some recreational drugs (drugs) as a sedative, but it is not the real vitamin K, it is commonly known as “Kitamen”.
Vitamin Q-Some experts believe that ubiquinone (coenzyme Q10) should be regarded as a vitamin, in fact, it can be synthesized by the human body in small amounts.
Vitamin S-Some people suggest naming salicylic acid (o-hydroxybenzoic acid) as vitamin S (S is the first letter of Salicylic Acid).
Vitamin T-It is used in some natural medical materials to refer to the substance extracted from sesame. It does not have a single and fixed component, so it cannot be a vitamin. And its function and effect are not clearly judged. In some cases, vitamin T is slang for Testosterone.
Vitamin U-Some pharmaceutical companies use vitamin U to refer to Methylmethionine Sulfonium Chloride, an anti-ulcer agent, mainly used to treat gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer. It is not human Essential nutrients.
Vitamin V-This is the colloquial term for Sildenafil Citrate (trade name: Viagra / Viagra / Viagra), which is used to treat ED.
In real life, vitamins are often referred to as medicines or other products that supplement the human body with vitamins and trace elements or other nutrients. For example, many manufacturers of multidimensional element tablets label their products directly as vitamins.
Vitamin Deficiency
Vitamin A: night blindness, corneal dryness, dry skin, desquamation
Vitamin B1: Neuritis, beriberi, loss of appetite, indigestion, growth retardation
Vitamin B2: oral ulcer, dermatitis, angular cheilitis, glossitis, cleft lip disease, keratitis, etc.
Vitamin B12: megaloblastic anemia
Vitamin C: scurvy, decreased resistance
Vitamin D: rickets in children, osteoporosis in adults
Vitamin E: infertility, abortion, muscular atrophy, etc.
Vitamins Precautions
If vitamins are taken on an empty stomach, they will be excreted from the feces before the body has time to absorb them. Fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamin A can be absorbed by the gastrointestinal mucosa by dissolving in fat. They should be eaten after meals to be absorbed by the body more completely.
Vitamin distribution
Vitamin A: Animal liver, eggs, dairy products, carrots, pumpkins, bananas, oranges and some leafy greens.
Vitamin B1: Sunflower seeds, peanuts, soybeans, pork, cereals, wild edible fungus yellow slippery mushrooms.
Vitamin B2: in meat, cereals, vegetables and nuts.
Vitamin B12: Pig, beef, mutton, fish, poultry, shellfish, eggs.
Vitamin C: lemon, orange, apple, jujube, strawberry, pepper, potato, spinach.
Vitamin D: Cod liver oil, eggs, margarine, milk, tuna.
Vitamin E: Cereal embryos, vegetable oils, green leaves.
Vitamin K: in green leafy vegetables.
Vitamin Supplements are Harmful to the Body
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is an essential nutrient for the body, and many people often take vitamin E supplements. However, a recent scientific research result shows that the abuse of vitamin E is not only not good for the body, but also reduces life and conflicts with cholesterol-lowering drugs.
Researchers from Tel Aviv University in Israel have published a study in a new issue of the journal “Arteriosclerotic Thrombosis and Vascular Biology” in the United States. They tracked about 300,000 people from the United States, Europe and Israel. The comparison was made for people who did not take vitamin E. It was found that the former had a “quality-adjusted life year” that was nearly 4 months shorter than the latter.
The so-called “quality-adjusted life year” is the concept of converting the number of years of survival with different quality of life into the number of years of full health, which is used to evaluate the degree of change in the quality of life and quantity brought by the treatment and health care.
However, researchers point out that this does not mean that every person taking vitamin E supplements will live 4 months less.
Previous studies have also found that vitamin E supplements not only do not prevent certain diseases but may also conflict with cholesterol-lowering drugs. Researchers say that if you get enough vitamin E from your food, taking supplements is not necessary.
Vitamin A
Adults ingesting more than 50,000 IU per day for several months can cause poisoning. Toddlers can cause poisoning if they consume more than 18,500 IU in a day.
Main manifestations: Due to enhanced osteoclast activity, bone decalcification, increased bone fragility, suppressed growth, thickened long bones, and pain in bones and joints, dry skin, itching, scales, rash, peeling, hair loss, finger (toe ) Nail is brittle, easily agitated, tired, headache, nausea, vomiting, muscle weakness, restlessness.
Decreased appetite, abdominal pain, diarrhea, hepatosplenomegaly, jaundice decreased hemoglobin and potassium in the blood, prolonged clotting time, and prone to bleeding.
Studies have shown that vitamin A can prevent and inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells, and is particularly significant in preventing gastrointestinal cancer and prostate cancer. It restores normal tissue function and helps chemotherapy patients reduce the rate of cancer recurrence.
Vitamin B6
Due to premenstrual tension, taking pyridoxine in large doses (2 ~ 6g daily, even for 2 ~ 40 months) will cause progressive sensory ataxia and severely impaired positioning of the lower limbs and vibration. And pain is rarely affected. Exercise and central nervous system are not damaged, recovery is slow after stopping pyridoxine, and some patients can only recover partially.
Anti-cancer vitamins. The components of human tissues cannot provide energy. Excessive intake is not beneficial to the human body, and some of them will produce toxic side effects and even death.
B vitamins
Including vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B6, vitamin B12 and so on. They can inhibit the growth of cancer cells and help synthesize some important enzymes in the body to regulate metabolism in the body. Grains, beans, yeast, dried fruits, animal offal, and other foods are more abundant.
Vitamin C
It is also called ascorbic acid, which can reduce the accumulation of carcinogen nitrosamines in the body and greatly reduce the incidence of esophageal and gastric cancer. Vegetables and fruits are rich in vitamin C.
Vitamin E
Eating more foods containing vitamin E can improve the body’s immune system and inhibit the formation of carcinogens. Vitamin E is mainly present in vegetable oils, especially soybean oil, foods such as eggs, cereals, carrots, and fresh lettuce are also abundant.
vitamin deficiency diseases chart
If you notice the following conditions or symptoms in yourself or your family, please pay attention to the early manifestations of vitamin deficiency.
Vitamin Deficiency:
There is some common vitamin deficiency in the human body like Rough skin, itching, deep white lines on nails, dry hair, memory loss, irritability and insomnia, dry conjunctiva, and urinary tract stones. Should eat more beef liver, eggs, red and yellow vegetables, fruits and cod liver oil.
Vitamin B1 deficiency:
For voice allergy, allergic reactions have to sound, leg pain and intermittent, beriberi suffering from neurodermatitis. Eat more beans, cereals, hard fruits, fruits, milk, and leafy greens.
Vitamin B2 deficiency:
Inflammation of the mouth, various skin diseases such as dermatitis, scrotum, etc., burning sensation in the hands and limbs, and excessive sensitivity to light. We should eat liver, milk, eggs, beans, green vegetables.
Vitamin B3 deficiency:
Thick tongue coating, puffy lips, tongue pain, lip pain, scalp, and dry oral mucosa. Eat more yeast.
Vitamin B12:
It is easy to lose balance in action, the body will have intermittent pains in irregular positions, fingers and tingling sensation should eat more animal liver and yeast.
Vitamin C deficiency:
There are no objective reasons such as overwork, drastic changes in the environment, or other organic diseases, but they often feel fatigued, often susceptible to colds, coughs, decreased resistance, bleeding gums often, wounds difficult to heal, and deep marks on the tongue. We should eat more oranges, oranges, grapefruit, red dates and so on.
Supplementary notes for the elderly
Elderly cells are susceptible to damage and their resistance is relatively low. The main role of vitamin A is to maintain the growth of various epithelial cells. Therefore, proper supplementation of vitamin A is necessary.
In addition to taking part in the diet (such as carrots, milk, eggs, animal livers, dark vegetables, milk), you can also take vitamin A capsules once a day, 1 capsule each time. The content is 25,000 IU and is taken intermittently.
Deficiency can cause children to a runny nose
Infants and toddlers have two lines of snot every day, and sometimes yellow pus and runny nose, which is a kind of morbidity in infants and young children, and may suffer from symptoms such as sinusitis. Infants and young children often have a runny nose, and parents can choose to supplement their children with vitamin A and vitamin B to relieve their symptoms.
Vitamin C is easily destroyed
Vitamin C is an extremely delicate water-soluble vitamin. Its properties are very unstable, and it can easily be destroyed by oxidation if you don’t pay attention. Vitamin C cannot be self-synthesized in the human body and must be supplied by food, so care must be taken in daily cooking.
Vitamin C is afraid of water, heat, light, oxygen, and smoke, so immersion in water, heating, cooking, or placing it in the store and letting the sunshine will greatly destroy vitamin C, and each cigarette will consume 25 Milligrams of vitamin C, and eating 100mg of fried food will also consume 25mg of Vc.
Vitamins Good and Bad
Vitamin A
Avoid alcohol when taking vitamin A. The main function of vitamin A is to convert retinol to retinal, while ethanol can inhibit the production of retinal during the metabolic process, which seriously affects the visual cycle and male spermatogenesis.
Vitamin AD
Avoid porridge when taking vitamin AD. Porridge, also known as rice soup, contains fat oxidase, which can dissolve and destroy fat-soluble vitamins, leading to the loss of vitamin A and vitamin D.
Vitamin B1
Clams and fish contain a thiamine substance that can destroy vitamin B1, so fish and clams should be avoided when taking vitamin B1.
Vitamin B2
High-fiber foods can increase intestinal motility and speed up the passage of intestinal contents, thereby reducing the absorption rate of vitamin B2; high-fat diets will increase the demand for vitamin B2, thereby aggravating vitamin B2 deficiency. Therefore, high-fat foods and high-fiber foods should be avoided when taking vitamin B2.
Vitamin B6
After the boron element in food meets the digestive liquid in the human body, if it is combined with vitamin B6, it will form a complex, which will affect the absorption and utilization of vitamin B6. Therefore, should eat vitamin B6 containing boron food. Generally, boron-rich foods include cucumbers, carrots, and eggplants.
Determination of Vitamin C Content-Titration
Principle
In the neutral and slightly acidic environment, VC can reduce the dye 2,6 -dichlorophenol indophenol to a colorless reduced 2,6 -dichlorophenol indophenol. At the same time, VC is oxidized to dehydroascorbic acid.
The oxidized 2,6 -dichlorophenol indophenol is red in acidic solution, so the titration endpoint is when the acid solution containing VC is titrated with 2,6-dichlorophenol indophenol. The amount of VC can be calculated from the amount of 2,6 -dichlorophenol indophenol consumed.
Reagent
1% oxalic acid, 2% oxalic acid, 0.001 mol / L 2,6-dichlorophenol indophenol
step
1. Weigh 4.0g fresh sample-add 5ml 2% oxalic acid to grind-filter into a 50ml volumetric flask-extract the residue with 2% oxalic acid-make up to volume with 1% oxalic acid.
2. Pipette 10ml of filtrate into a triangle flask and titrate with 2,6 -dichlorophenol indophenol, and record the volume of the titrant used.
3. Control: Add 35ml 2% oxalic acid to another volumetric flask to make up the volume with 1% oxalic acid. Take 10ml for titration and record the volume.
Results processing
VC content (ug / 100gFW) = 100 * (V1-V2) KV/W V3
In the formula, W: sample weight V1: ml of titration solution for titration sample V2: ml of titration solution for titration control V3: ml of filtrate V: total volume of extract solution K: mg of VC of 1ml titration solution oxidation
Determination of Trace Vitamin B2 by Aqueous Two-Phase Extraction with Acetone and Ethanol
Extraction is a very important means of chemical separation. Extraction is generally conventional in the two immiscible phases – an organic phase and an aqueous phase inter Such different phase extraction efficiency are usually low.
In fact, some are miscible with water in an organic-inorganic solvent Aqueous two-phase systems may also form under the action of salt, but there are relatively few studies in this area, which need to be further expanded and deepened.
Compared with the polymer two- aqueous system, the water-soluble organic solvent-salt two-aqueous system has the advantages of simple operation, fast phase separation, low cost, low toxicity, clear phase separation, small interference to the measurement, and unfavorable viscosity of the extraction phase. Difficult to handle polymers and other characteristics.
Vitamin B2 (vB2, also known as riboflavin) is clinically used to prevent and treat vitamin island deficiency such as keratitis, cleft lip, glossitis, scrotal inflammation, and corneal vascularization. The measurement methods include spectrophotometry, catalytic kinetics, and phosphorescence.
The method, voltammetry, chemiluminescence, fluorescence, and chromatography.
In this paper, the conditions for water-soluble organic solvents ethanol and acetone to form a bi- aqueous phase under the action of inorganic salts and the properties of extracting VB2 are compared. Acetone/ethanol- (NH4) 2SO4-H2O two-aqueous phase extraction and fluorescence determination of VB2 New method.
For the determination of VB2 tablets Jingjing and injection.