14 Most Important Reactions in Chemistry
Kolbe Reaction
The preparation of hydrocarbons at the anode by electrolysis of aqueous solutions of sodium or potessium salts of acids is called Kolbe synthesis and this reaction is called Kolbes reaction. Both types of hydrocarbons (saturated and unsaturated) can be obtained by this reaction.
Example
2CH3COONa → CH3.CH3 + 2CO2 (Anode) | 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2 (Cathode)

Wurtzs Reaction
This reaction is used in the synthesis of saturated hydrocarbons. is done in this reaction. In this reaction alkyl halide is treated with sodium metal in the presence of dry ether to form corresponding paraffin.
RX + 2Na + XR → R – R + 2NaX
a) Methyl Iodide gives Ethane
CH3 I + 2Na + I CH3 → CH3.CH3 + 2NaI
b) Ethyl Iodide gives n-butane
C2H5 I + 2Na + I C2H5 → C4H10 + 2NaI
Franklands Reaction
The formation of paraffin by the combination of two molecules alkyl halide in the presence of zinc metal is called Franklands reaction.
Example:-
R I + Zn + I R → R – R + ZnI2
CH3 I + Zn + I CH3 → CH3.CH3 + ZnI2
Wurtz Fitting Reaction
The reaction of combining alkyl halide with aryl halide in dry ether in the presence of sodium to obtain aromatic hydrocarbon is called Wurtz fitting reaction.
Iodo reacts with benzene methyl iodide to form toluene.
C6H5 I + 2Na + I CH3 → C6H5.CH3 + 2NaI
Same here,
C6H5 I + 2Na + I C2H5 → C6H5.C2H5 + 2NaI
Friedel Crafts Reaction
When benzene or other aromatic hydrocarbon and an alkyl or acyl halide are treated in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 (catalyst), the hydrogen atom of the benzene nucleus is replaced by an alkyl or acyl radical. This reaction is called Friedel Crafts reaction.
C6H6 + CH3Cl → C6H5.CH3 + HCl
C6H6 + CH3COCl → C6H5COCH3 + HCl
Cannizzaros Reaction
When aldehyde is treated with aqueous or alcoholic castic alkali solution, one molecule of aldehyde is reduced to alcohol and the other molecule gets oxidised to acid. This reaction gives only those aldehydes which do not have alpha hydrogen atom. This reaction is called Cannizzaros Reaction.
Example :-
2HCHO + NaOH → CH3OH + HCOONa
2C6H5CHO + NaOH → C6H5CH2OH + C6H5COONa
Carbylamine Reaction
When anylene and alcoholic KOH are heated with a few drops of chloroform, a strong odorous phenyl isocyanide is obtained. Alyphatic primary amine also gives this reaction. Read more
C6H5NH2 + CHCl3 + 3KOH → C6H5NC + 3KCl + 3H2O
CH3NH2 + CHCl3 + 3KOH → CH3NC + 3KCl + 3H2O
Aldol Condensation
Carbonil compounds having alpha hydrogen atom condense in the presence of NaOH, K2CO3 etc. Aceteldehyde condenses to form alcohol and this reaction is called aldol condensation.
Example :-
CH3CHO + HCH2CHO (2 Molecules) → CH3CH(OH)CH2CHO
CH3CH2CHO + H.CH2CHO → CH3CH2CH(OH)CH2CHO
This condensation can occur in molecules of two similar or different aldehydes, in two similar or different ketones, and between an aldehyde and a ketone.
CH3CH2CHO + H.CH2CHO → CH3CH2CH(OH)CH2CHO
Claisen Condensation
Condensation between two esters or between an ester and a ketone in the presence of sodium metal or C2H5ONa is called claisen condensation.
CH3CO OC2H5 + H CH2COOC2H5 → CH3COCH2COOC2H5 + C2H5OH
Perkins Reaction
The reaction of an aromatic aldehyde with an anhydrous salt of aliphatic acid and anhydride of the same acid to obtain alpha, beta unsaturated aromatic acid is called Perkin reaction.
Example: By heating banzeldehyde with a mixture of acetic alhydride and sodium acetate at 180°C, cinnamic acid is formed.
C6H5CHO + (CH3CO)2O → C6H5CH=CHCOOH + CH3COOH
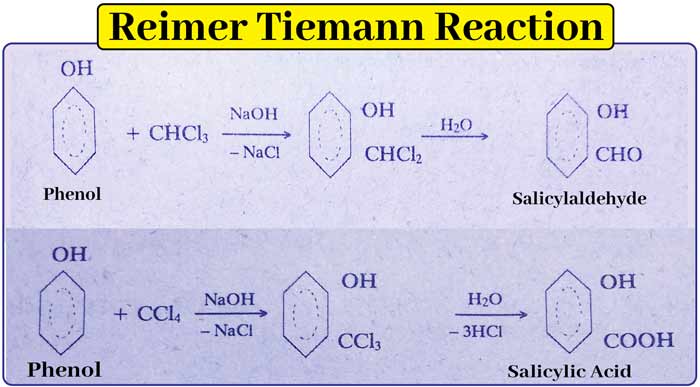
Reimer Tiemann Reaction
This is the main method of preparation of hydroxy aldehydes and acids.
The -CHO and -COOH groups enter the ortho and para positions of the -OH group. In this reaction, heating an alkaline solution of phenol with chloroform or CCl4 at 60°C gives salicylaldehyde and silicic acid, respectively.
Etards Reaction
The partial oxidation of toluene by cromil chloride – CrO2Cl2 is called Etards reaction.
Benzaldehyde is obtained from toluene by this reaction. First an additive complex compound is obtained as a precipitate which on hydrolysis gives Benzaldehyde.
C6H5CH3 → C6H5.CH3.2CrO2Cl2 → C6H5CHO
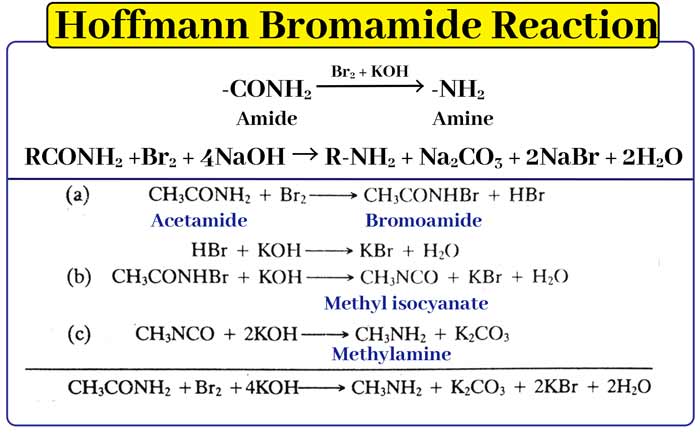
Hoffmans bromamide reaction
With the help of this reaction -CONH2 group is converted into -NH2 group. When an amide is heated with bromine and caustic potash solution, an amine is formed.
-CONH2(amide) –Br2 + KOH→ -NH2(amine)
In this reaction acet amide, prophile amide and benz amide can be converted to methyl amine, ethyl amine and anelyn respectively. This reaction takes place in the following steps.
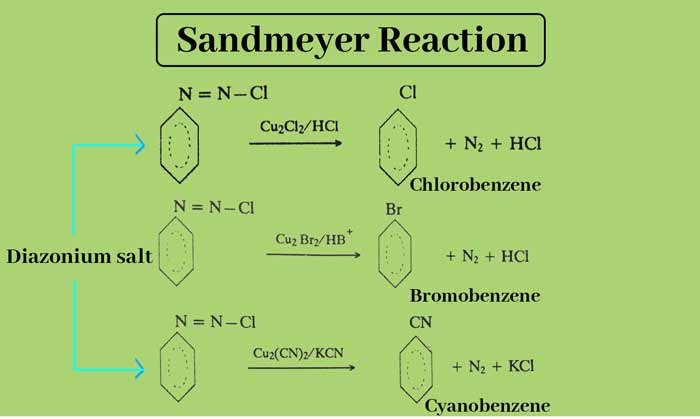
Sandmeyers Reaction
When diazonium salt solution is heated with Cu2Cl2/HCl, Cu2Br2/HBr or Cu2(CN)2/KCN, the diazo group gets replaced by Cl, Br and CN respectively. This reaction is called Sandmeyers Reaction.
Rosenmunds Reaction
Reduction of an acid chloride by hydrogen in the presence of Pd / BaSO4 (catalyst) is called Rosenmunds Reaction.
RCOCl + H2 → RCHO + HCl
CH3COCl + H2 → CH3CHO + HCl
C6H5COCl + H2 → C6H5CHO + HCl
