Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones : Chemistry Page
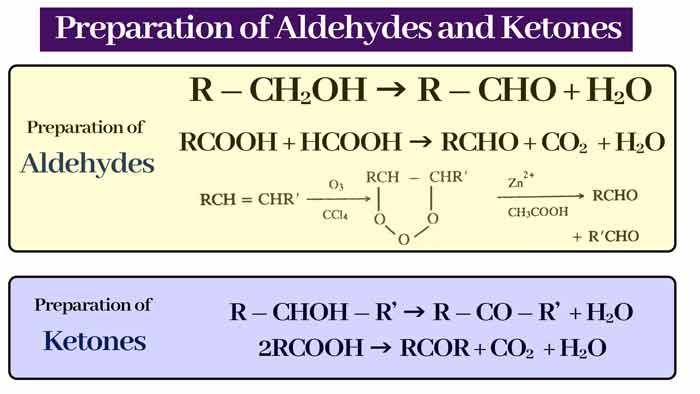
Preparation of Aldehydes
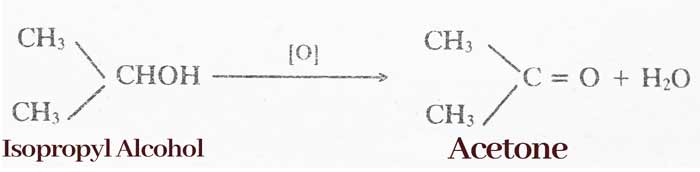
By oxidation of alcohol: Oxidation of primary alcohol to aldehyde and secondary alcohol to form ketone.
Aldehyde :-
R – CH2OH → R – CHO + H2O
H.CH2OH (methyl alcohol) → HCHO + H2O
CH3.CH2OH (ethyl alcohol) → CH3.CHO + H2O
Ketone :-
R – CHOH – R’ → R – CO – R’ + H2O
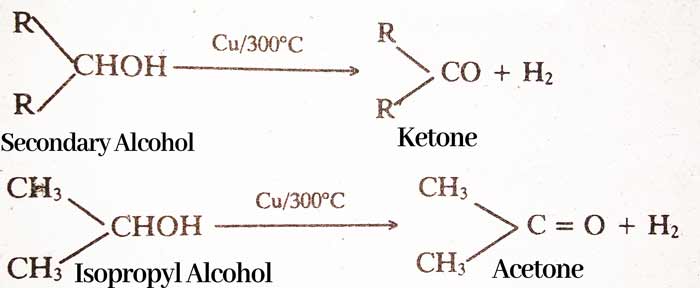
By Dehydrogenation of Alcohol: On passing the vapor of primary alcohol on copper heated at 300°C, aldehyde and secondary alcohol vapor is formed to form ketone. And H2 gas is liberated.
RCH2OH → RCHO + H2
CH3OH → HCHO + H2
Reduction of Chlorides Acid: Reduction of chloride acids by Rozenmund reaction in the presence of a paledium catalyst containing barium sulfate to form aldehyde. Ketones cannot be obtained by this method.
RCOCl (Chloride Acid) + H2 → R – CHO + HCl
CH3COCl (Acetyl chloride) + H2 → CH3CHO + HCl
From fatty acids: On passing the vapors of fatty acids over MnO heated at 300°C, aldehyde and ketone are formed.
RCOOH + HCOOH → RCHO + CO2 + H2O
2HCOOH (formic acid) → HCHO + CO2 + H2O
CH3COOH + HCOOH (formic acid) → CH3CHO + CO2 + H2O
2RCOOH → RCOR + CO2 + H2O
CH3COOH (acetic acid) + HOOCCH3 → CH3COCH3 + CO2 + H2O
By calcium salts of fatty acids: On heating calcium formate alone (dry distillation) formaldehyde and on heating with calcium salt of any other fatty acid, aceteldyhide is formed.
(HCOO)2Ca → HCHO + CaCO3
(HCOO)2Ca(calcium formate) + (CH3COO)2Ca → 2CH3CHO + 2CaCO3
Ketone is formed by heating the calcium salt of any fatty acid other than calcium formate by heating the salts of alone or two fatty acids.
(CH3COO)2Ca (calcium acetate) → CH3COCH3 + CaCO3
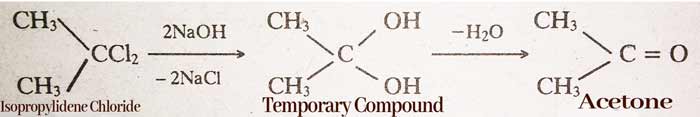
By hydrolysis of Alkylidene Halides:-
CH3CHCl2 (ethylidene)→ CH3CH(OH)2 → CH3CHO(Acetaldehyde)
By Alkynes: Acetaldehyde is formed when acetylene is passed through 20% H2SO4 in the presence of 1% HgSO4 at 60°C. The ketone is formed when the higher member of the acetylene series is taken.
CH≡CH (acetylene) + H2O → CH3CHO
CH3 – C ≡ CH (Propene) + H2O → CH3COCH3
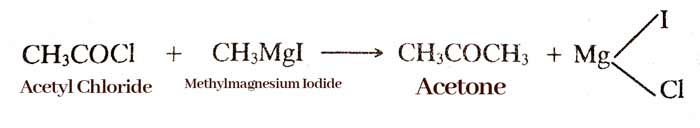
By Grignard reagent:- On hydrolysis of Grignard reagent with ethyl formate, aldehyde is formed.

Grignard reagent reacts with chloride acids to form ketone.
example
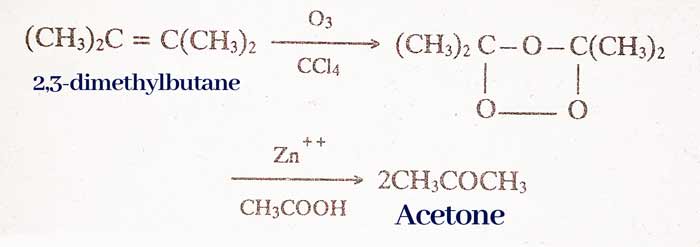
By ozonisation of alkynes:
RCH = Ozonisation of CHR type alkynes gives aldehydes.

Ketone R2C = CR2‘ type of alkynes gives ketone by ozonisation.