Bromine – Preparation, Physical and Chemical Properties a Uses
Bromine History
Bromine was discovered by Antoine-Jérôme Balard in 1826. It is a very volatile and syrupy liquid of reddish brown color. It has a strong and unpleasant odor. Hence it was named Bromine (Greek: Bromos).
Bromine Presence
Being more reactive, it is not found in free state in nature. Bromine salt (Example: NaBr, KBr, MgBr2 etc.) is found in sea water in the combined state. Magnesium bromide (MgBr2) is also found in small amounts in the magnesium mineral carnallite – KCl MgCl2 6H2O.
Bromine Preparation
Common Methods for making Bromine
On heating any bromide salt with manganese dioxide and sulfuric acid, bromine gas is obtained.
2KBr + MnO2 + 3H2SO4 → 2KHSO4 + MnSO4 + 2H2O + Br2
- Importance of Biomolecules in Life || What are the 4 main biomolecules?
- Valency of Elements || How to Find Valency || What is the Valency of the atom?
- Resonance effect or mesomeric effect || What is resonance effect with example?
- Glucose Structure: Physical and chemical properties, Glucose Chemical Reaction
- Introduction of Inductive-Effect || How does Inductive Effect Work?
Bromine is obtained when chlorine gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a bromide salt.
2NaBr + Cl2 → 2NaCl + Br2
2KBr + Cl2 → 2KCl + Br2
Bromine is also obtained by adding hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid to a solution of potassium bromide and potassium bromate (KBrO3).
5KBr + KBrO3 + 6HCl → 3Br2 + 6KCl + 3H2O
5KBr + KBrO3 + 3H2SO4 → 3Br2 + 3K2SO4 + 3H2O
Laboratory method of making bromine
In this method a mixture of manganese dioxide, potassium bromide and sulfuric acid is heated in a retart. In this process bromine gas is formed which is sent to a flask kept in cold water where it collects as a liquid.
Industrial methods of making Bromine
Bromine is industrially produced from carnallite or sea water.
Carnallite
Carnallite – KCl.MgCl2.6H2O also contains some amount of magnesium bromide. Potassium chloride crystals are formed on concentrating carnallite by dissolving it in water.
Which are filtered and separated. The filter solution obtained is called mother liquor. The mother liquor is sent from the top to a tower in which the pieces of bricks are filled and a mixture of chlorine gas and steam is passed from the bottom.
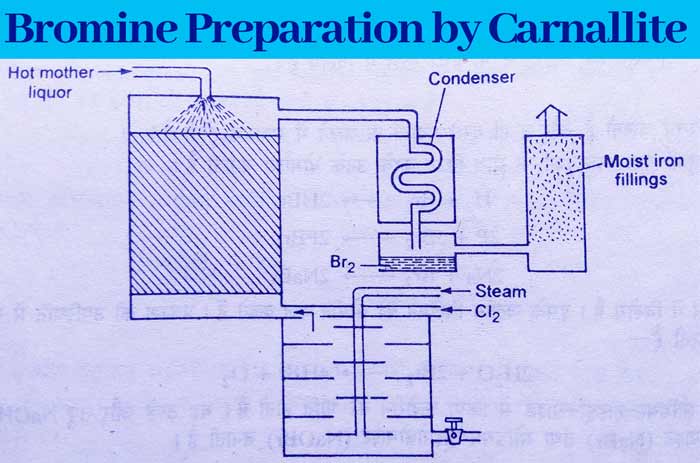
The gaseous mixture obtained from this tower is sent to a condenser where the bromine liquefies. Thus bromine is obtained in liquid state.
MgBr2 + Cl2 → MgCl2 + Br2
Some bromine remains in the gaseous mixture obtained from the capacitor. This mixture is sent to another chamber, which is filled with iron powder.
The remaining bromine reacts with iron in this cell to form iron bromide (Fe3Br8). Bromine can be recovered from iron bromide by appropriate methods.
- Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones : Chemistry Page
- Arsenious Oxide : Preparation, Properties and Uses
- How to find Equivalent Weight in Chemistry ? Chemical Formula
- Oxidation Number : How to find Oxidation State
- Bleaching Powder : Preparation, uses of Bleaching Powder
Another method of obtaining bromine from mother liquor is by its electrolysis. In the presence of magnesium bromide, the electrolysis of magnesium chloride does not occur and bromine is obtained at the anode.
From sea water
Potassium bromide and magnesium bromide are also found in small quantities in sea water. By concentrating sea water and making it acidic, chlorine gas is passed into it. Chlorine removes bromine from these bromides which dissolves in water itself.
2KBr + Cl2 → 2KCl + Br2
MgBr2 + Cl2 → MgCl2 + Br2
On heating the solution thus obtained, bromine evaporates which is passed into a hot and saturated solution of sodium carbonate or caustic soda.
3Br2 + 3Na2CO3 → 5NaBr + NaBrO3 + 3CO2
3Br2 + 6NaOH → 5NaBr + NaBrO3 + 3H2O
On adding sulfuric acid to the solution of sodium bromide and sodium bromate, vapors of bromine are obtained, which are cooled and liquefied. The bromine thus obtained mainly contains impurities of chlorine and water vapor.
On adding sulfuric acid to the solution of sodium bromide and sodium bromate, vapors of bromine are obtained, which are cooled and liquefied. The bromine thus obtained mainly contains impurities of chlorine and water vapor.
Refinement of industrial Bromine
The samples of bromine obtained by the above methods contain impurities of water, chlorine and iodine. The impurity of chlorine is usually present in the form of bromine chloride and the impurity of iodine is often present in the form of Iodine bromide.
To remove these impurities, first distillation is done by mixing potassium bromide and zink oxide in impure bromine.
Potassium bromide removes the impurities of chlorine and zinc oxide removes the impurity of iodine. After this, the water content is also removed by distillation with concentrated sulfuric acid.
3Br2 + 3Na2CO3 → 5NaBr + NaBrO3 + 3CO2
3Br2 + 6NaOH → 5NaBr + NaBrO3 + 3H2O
Bromine Properties
Physical Properties
It is a reddish brown volatile and syrupy liquid. Its boiling point is 58°C.
Its average density is 3.12.
The smell of its vapors is very pungent and distasteful. Its vapor is very toxic and when it comes in contact with the skin, it causes wounds on it.
It is soluble in water in sufficient quantity. Its aqueous solution is called Bromine Water. It is also abundantly soluble in carbnic solvents.
Chemical Properties
It neither burns on its own nor does it help in the burning of other substances.
It reacts with metals and non-metals to form their bromides.
H2 + Br2 → 2HBr
2P + 5Br2 → 2PBr5
2Na + Br2 → 2NaBr
It is soluble in water. Its aqueous solution is called bromine water. In the presence of light, it reacts with water as follows.
2H2O + 2Br2 → 4HBr + O2
Its action with sodium hydroxide is similar to that of chlorine. It reacts with cold and dilute NaOH to form sodium bromide (NaBr) and sodium hypobromite (NaOBr).
2NaOH + Br2 → NaBr + NaOBr + H2O
It reacts with hot and concentrated NaOH to form sodium bromide (NaBr) and sodium bromate (NaBrO3).
6NaOH + 3Br2 → NaBrO3 + 5NaBr + 3H2O
It reacts with dry slaked lime [Ca(OH)2] to form calcium bromohypobromide (CaOBr2).
Ca(OH)2 + Br2 → CaOBr2 + H2O
Its action with ammonia is similar to that of chlorine. If ammonia content is high then the following reaction takes place.
2NH3 + 3Br2 → N2 + 6HBr
6NH3 + 6HBr → 6NH4Br
8NH3 + 3Br2 → 6NH4Br + N2
If the amount of bromine is high, then the explosive substance nitrogen tri bromide is formed.
Br2 + NH3 → NBr3 + 3HBr
Oxidizing Properties
It is a strong oxidising agent. Its oxidising power is less than that of chlorine. It oxidizes various substances.
example :
SO2 to H2SO4 :-
SO2 + Br2 + 2H2O → 2HBr + H2SO4
Sulfite to sulfate :-
Na2SO3 (Sodium Sulfite) + Br2 + H2O → Na2SO4 + 2HBr
KI to Iodine :-
2KI + Br2 → 2KBr + I2
H2S to Sulfur :-
H2S + Br2 → 2HBr + S
Bromination
It reacts with some carbonic compounds and replaces hydrogen atoms in them. This process is called Bromination.
example :
H2S + Br2 → 2HBr + S
Addition compounds reactions: It forms addition compounds with unsaturated carbonic compounds.
example :
C2H4 + Br2 → C2H4Br2
Bromine Uses
It is used in the preparation of various Organic and Inorganic compounds.
Silver bromide is used in photography. Sodium and potessium bromides are used in making medicines.
